
Mathematics (Core)
Paper 1 | Objectives | 50 Questions
WASSCE/WAEC MAY/JUNE
Year: 2004
Level: SHS
Time:
Type: Question Paper
Answers provided
FREE
No description provided
Feedbacks
This paper is yet to be rated

Paper 1 | Objectives | 50 Questions
WASSCE/WAEC MAY/JUNE
Year: 2004
Level: SHS
Time:
Type: Question Paper
Answers provided
No description provided
This paper is yet to be rated
Revision tips on test preparation for Grade A students to. Grade A students tips for any test.
Middle East and North Africa MENA Scholarship Program (MSP) initiative provides scholarships
Make sure you study hard but not into the late-night hours to give your body the enough rest you need.
| # | Question | Ans |
|---|---|---|
| 1. |
1. Evaluate A. 21120 B. 21121 C. 21112 D. 21011
Show Content
Detailed SolutionReconvert to base three |
|
| 2. |
If A. 1110 B. 10111 C. 11101 D. 111100
Show Content
Detailed SolutionConverting to base two |
|
| 3. |
Given that sin (5x - 28)o = cos (3x - 50)o,0 < x < 90o, find the value of x A. 14o B. 21o C. 32o D. 39o
Show Content
Detailed SolutionSin (5x – 28)o = cos (3x - 50)oSince by the trigonometry relation Sin(5x – 28)o = cos[90 – (5x – 28)]o Hence cos(3x – 50)o = cos[90 – (5x – 28)]o 3x – 50 = 90 - (5x-28) 3x – 50 = 90 – 5x + 28 3x + 5x = 90 + 28 + 50 8x = 168 |
|
| 4. | ||
| 5. |
A school girl spends A. B. C. D.
Show Content
Detailed SolutionLet the girls pocket money be rep. by x. The amount spent on books =The amount spent on dress ∴The fraction that remains = |
|
| 6. |
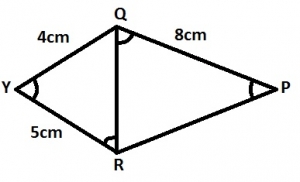 In the diagram, A. 2.0cm B. 2.5cm C. 6.4cm D. 10.0cm
Show Content
Detailed Solution= 6.4 cm |
|
| 7. |
 Find the value of x in the diagram A. 10o B. 28o C. 36o D. 44o
Show Content
Detailed SolutionThe sum of angles at point = 360o(x+10)o + (4x+50)o + 20o + 3xo + 2xo = 360o 10x + 80o = 360o 10x = 360o - 80o = 280o |
|
| 8. |
There are m boys and 12 girls in a class. What is the probability of selecting at random a girl from the class? A. B. C. D.
Show Content
Detailed SolutionProb. (a girl) |
|
| 9. |
Simplify A. 33 B. 8 C. 7
Show Content
Detailed Solution= 7.166 The nearest whole number is 7 |
|
| 10. |
The angle of elevation of the top of a tower from a point on the ground which is 36m away from the foot of the tower is 30o. Calculate the height of the tower. A. 62.35m B. 20.78m C. 18.00m D. 10.39m
Show Content
Detailed Solution
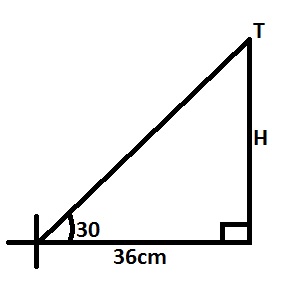 |
Preview displays only 10 out of the 50 Questions