Year :
2003
Title :
Mathematics (Core)
Exam :
JAMB Exam
Paper 1 | Objectives
11 - 20 of 45 Questions
| # | Question | Ans |
|---|---|---|
| 11. |
Given: A. {2, 10, 14, 22, 26} B. {0, 10, 14, 22, 26} C. {2,4, 14, 18, 26} D. {0, 2, 6, 22, 26} Detailed SolutionU = {2,4,6,8,10,12,14,16,18,20,22,24,26,28,30}P = {6,12,18,24,30} Q = {4,8,12,16,20,24,28} P∪Q = {4,6,8,12,16,18,20,24,28,30} (P∪Q)c = {2,10,14,22,26} |
|
| 12. |
X varies directly as the product of u and v and inversely as their sum. If x = 3 when u = 3 and v = 1, what is the value of x if u = 3 and v = 3? A. 3 B. 4 C. 6 D. 9 Detailed Solution\(x\propto \frac{uv}{u+v}\\x = \frac{kuv}{u+v}\\K = \frac{x(u+v)}{uv}\\\frac{3(3+1)}{3\times1}\\\frac{3\times4}{3}\\k = 4\\x=\frac{4uv}{u+v}\\x=\frac{4\times 3\times3}{3+3}\\x=\frac{36}{6}\\x=6\) |
|
| 13. |
Find the range of the value of x satisfying the inequalities 5 + x \(\leq\) 8 and 13 + x \(\geq\) 7 A. -3 \(\leq\) x \(\leq\) 3 B. 3 \(\leq\) x \(\leq\) 6 C. -6 \(\leq\) x \(\leq\) 3 D. -6 \(\leq\) x \(\leq\) -3 Detailed Solution5 + x \(\leq\) 8 and 13 + x \(\geq\) 75 + x \(\leq\) 8 X \(\leq\) 8 – 5 X \(\leq\) 3 And 13 + x \(\geq\) 7 X \(\geq\) 7 – 15 X \(\geq\) -7 Combining the two together -6 \(\leq\) x \(\leq\) 3 |
|
| 14. |
The graph of the function y = x\(^2\) + 4 and a straight line PQ are drawn to solve the equation x\(^2\) - 3x + 2 = 0. What is the equation of PQ? A. y = 3x - 2 B. y = 3x + 2 C. y = 3x - 4 D. y = 3x + 4 Detailed Solutionx\(^2\) + 4 = x\(^2\) - 3x + 23x + 2 = y |
|
| 15. |
The length a person can jump is inversely proportional to his weight. If a 20 kg person can jump 1.5 m, find the constant of proportionality A. 60 B. 30 C. 20 D. 15 Detailed SolutionL ∝ 1/WL = K/W K = WL = 1.5 * 20 30 |
|
| 16. |
Find the value of x and y respectively if 3x - 5y + 5 = 0 and 4x - 7y + 8 = 0 A. -5, -4 B. -5 C. 4, 5 D. 5, 4 Detailed Solution3x - 5y + 5 = 0 → eqn14x - 7y + 8 = 0 → eqn2 eqn1 * 4; 12x - 20y + 20 = 0 → eqn3 eqn2 * 3; 12x - 21y + 24 = 0 → eqn4 eqn3 - eqn4 = y - 4 = 0 ∴ y = 4 From eqn1, 3x - 5y + 5 = 0 3x - 5(4) + 5 = 0 3x - 20 + 5 = 0 3x - 15 = 0 3x = 15 x = 5 x and y = 5, 4 respectively |
|
| 17. |
Three consecutive terms of a geometric progression are given as n-2, n and n+3. Find the common ratio A. 1/4 B. 1/2 C. 2/3 D. 3/2 Detailed Solution\(r=\frac{n}{n-2}\hspace{1mm}and\hspace{1mm}r=\frac{n+3}{n}\\∴\frac{n}{n-2}=\frac{n+3}{n}\\n^2 = n^2 +3n - 2n-6\\0=n-6\\∴n=6\\But\hspace{1mm}r = \frac{n}{n-2}\\r=\frac{6}{6-2}\\\frac{6}{4}=\frac{3}{2}\) |
|
| 18. |
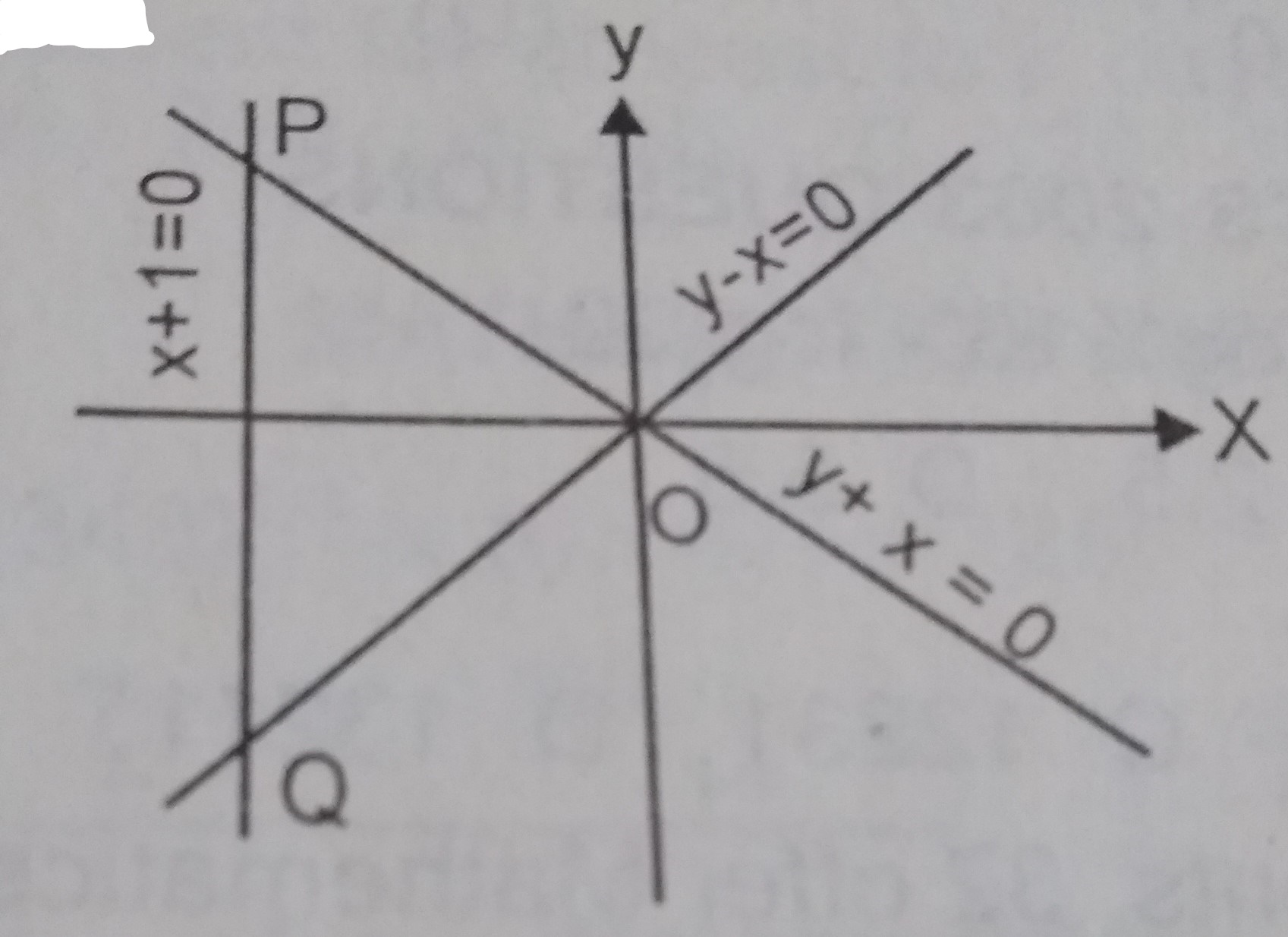 Triangle OPQ above is the solution of the inequalities A. x + 1 ≥ 0, y + x ≤ 0, y - x ≥ 0 B. y + x ≤ 0, y - x ≥ 0, x -1 ≥ 0 C. x - 1 ≤ 0, y - x ≥ o, y + x ≥ 0 D. x - 1 ≤ 0, y + x ≤ 0, y - x ≤ 0 Detailed SolutionLines bounding Δ OPQOQ; y - x = 0 y - x ≥ 0 PQ; x + 1 = 0 x + 1 ≥ = 0 PO; y + x = 0 y + x ≤ 0 ∴ x + 1 ≥ 0, y + x ≤ 0, y - x ≥ 0 |
|
| 19. |
Factorize completely 4abx - 2axy -12b2x + 6bxy A. 2x(a - 3b)(2b - y) B. 2x(3b - a)(2b - y) C. 2x(a - 3b)(y - 2b) D. 2x(2b - a)(3b - y) Detailed Solution4abx - 2axy - 12b2x + 6bxy = (4abx - 2axy) - (12b2x - 6bxy)= 2ax(2b - y) -6bx(2b - y) = (2ax - 6bx)(2b - y) = 2x(a - 3b)(2b - y) |
|
| 20. |
The sum of the first n terms of an arithmetic progresssion is 252. If the first term is -16 and the last term is 72, find the number of terms in the series A. 6 B. 7 C. 8 D. 9 Detailed Solution\(S_n = 252, a = -16\hspace{1mm}and\hspace{1mm}l = 72\\S_n = \frac{n}{2}(-16+72)\\252 = \frac{n}{2}(-16+72)\\n=\frac{504}{56}\\n=9\) |
| 11. |
Given: A. {2, 10, 14, 22, 26} B. {0, 10, 14, 22, 26} C. {2,4, 14, 18, 26} D. {0, 2, 6, 22, 26} Detailed SolutionU = {2,4,6,8,10,12,14,16,18,20,22,24,26,28,30}P = {6,12,18,24,30} Q = {4,8,12,16,20,24,28} P∪Q = {4,6,8,12,16,18,20,24,28,30} (P∪Q)c = {2,10,14,22,26} |
|
| 12. |
X varies directly as the product of u and v and inversely as their sum. If x = 3 when u = 3 and v = 1, what is the value of x if u = 3 and v = 3? A. 3 B. 4 C. 6 D. 9 Detailed Solution\(x\propto \frac{uv}{u+v}\\x = \frac{kuv}{u+v}\\K = \frac{x(u+v)}{uv}\\\frac{3(3+1)}{3\times1}\\\frac{3\times4}{3}\\k = 4\\x=\frac{4uv}{u+v}\\x=\frac{4\times 3\times3}{3+3}\\x=\frac{36}{6}\\x=6\) |
|
| 13. |
Find the range of the value of x satisfying the inequalities 5 + x \(\leq\) 8 and 13 + x \(\geq\) 7 A. -3 \(\leq\) x \(\leq\) 3 B. 3 \(\leq\) x \(\leq\) 6 C. -6 \(\leq\) x \(\leq\) 3 D. -6 \(\leq\) x \(\leq\) -3 Detailed Solution5 + x \(\leq\) 8 and 13 + x \(\geq\) 75 + x \(\leq\) 8 X \(\leq\) 8 – 5 X \(\leq\) 3 And 13 + x \(\geq\) 7 X \(\geq\) 7 – 15 X \(\geq\) -7 Combining the two together -6 \(\leq\) x \(\leq\) 3 |
|
| 14. |
The graph of the function y = x\(^2\) + 4 and a straight line PQ are drawn to solve the equation x\(^2\) - 3x + 2 = 0. What is the equation of PQ? A. y = 3x - 2 B. y = 3x + 2 C. y = 3x - 4 D. y = 3x + 4 Detailed Solutionx\(^2\) + 4 = x\(^2\) - 3x + 23x + 2 = y |
|
| 15. |
The length a person can jump is inversely proportional to his weight. If a 20 kg person can jump 1.5 m, find the constant of proportionality A. 60 B. 30 C. 20 D. 15 Detailed SolutionL ∝ 1/WL = K/W K = WL = 1.5 * 20 30 |
| 16. |
Find the value of x and y respectively if 3x - 5y + 5 = 0 and 4x - 7y + 8 = 0 A. -5, -4 B. -5 C. 4, 5 D. 5, 4 Detailed Solution3x - 5y + 5 = 0 → eqn14x - 7y + 8 = 0 → eqn2 eqn1 * 4; 12x - 20y + 20 = 0 → eqn3 eqn2 * 3; 12x - 21y + 24 = 0 → eqn4 eqn3 - eqn4 = y - 4 = 0 ∴ y = 4 From eqn1, 3x - 5y + 5 = 0 3x - 5(4) + 5 = 0 3x - 20 + 5 = 0 3x - 15 = 0 3x = 15 x = 5 x and y = 5, 4 respectively |
|
| 17. |
Three consecutive terms of a geometric progression are given as n-2, n and n+3. Find the common ratio A. 1/4 B. 1/2 C. 2/3 D. 3/2 Detailed Solution\(r=\frac{n}{n-2}\hspace{1mm}and\hspace{1mm}r=\frac{n+3}{n}\\∴\frac{n}{n-2}=\frac{n+3}{n}\\n^2 = n^2 +3n - 2n-6\\0=n-6\\∴n=6\\But\hspace{1mm}r = \frac{n}{n-2}\\r=\frac{6}{6-2}\\\frac{6}{4}=\frac{3}{2}\) |
|
| 18. |
 Triangle OPQ above is the solution of the inequalities A. x + 1 ≥ 0, y + x ≤ 0, y - x ≥ 0 B. y + x ≤ 0, y - x ≥ 0, x -1 ≥ 0 C. x - 1 ≤ 0, y - x ≥ o, y + x ≥ 0 D. x - 1 ≤ 0, y + x ≤ 0, y - x ≤ 0 Detailed SolutionLines bounding Δ OPQOQ; y - x = 0 y - x ≥ 0 PQ; x + 1 = 0 x + 1 ≥ = 0 PO; y + x = 0 y + x ≤ 0 ∴ x + 1 ≥ 0, y + x ≤ 0, y - x ≥ 0 |
|
| 19. |
Factorize completely 4abx - 2axy -12b2x + 6bxy A. 2x(a - 3b)(2b - y) B. 2x(3b - a)(2b - y) C. 2x(a - 3b)(y - 2b) D. 2x(2b - a)(3b - y) Detailed Solution4abx - 2axy - 12b2x + 6bxy = (4abx - 2axy) - (12b2x - 6bxy)= 2ax(2b - y) -6bx(2b - y) = (2ax - 6bx)(2b - y) = 2x(a - 3b)(2b - y) |
|
| 20. |
The sum of the first n terms of an arithmetic progresssion is 252. If the first term is -16 and the last term is 72, find the number of terms in the series A. 6 B. 7 C. 8 D. 9 Detailed Solution\(S_n = 252, a = -16\hspace{1mm}and\hspace{1mm}l = 72\\S_n = \frac{n}{2}(-16+72)\\252 = \frac{n}{2}(-16+72)\\n=\frac{504}{56}\\n=9\) |