Year :
2006
Title :
Mathematics (Core)
Exam :
WASSCE/WAEC MAY/JUNE
Paper 1 | Objectives
31 - 40 of 46 Questions
| # | Question | Ans |
|---|---|---|
| 31. |
The temperature in a chemical plant was -5oC at 2.00 am. The temperature fell by 6oC and then rose again by 7oC. What was the final temperature? A. -6oC B. -4oC C. 4oC D. 8oC Detailed SolutionTemperature = -5oCIt fell by 6oC = -5oC - 6oC = -11oC Then rose by 7oC = -11 + 7 = -4oC (final temperature) |
|
| 32. |
Simplify \(\frac{20}{5\sqrt{28} - 2 \sqrt{63}}\) A. \(\frac{5\sqrt{7}}{7}\) B. \(\frac{5\sqrt{5}}{7}\) C. \(\frac{7\sqrt{5}}{7}\) D. \(\frac{7\sqrt{7}}{5}\) Detailed Solution\(\frac{20}{5 \sqrt{4 \times 7} - 2\sqrt{9 \times 7}}\)\(\frac{20}{10 \sqrt{7} - 6\sqrt{7}}\) = \(\frac{20 \sqrt{7}}{4 \sqrt{7}}\) = \(\frac{5\sqrt{7}}{7}\) |
|
| 33. |
A ladder 16m long leans against an electric pole. If the ladder makes an angle of 65o with the ground, how far up the electric pole does its top reach A. 6.8m B. 14.5m C. 17.7m D. 34.3m Detailed SolutionSin 65o = \(\frac{x}{16}\)x = 16x sin 65 = 16 x 0.9063 x = 14.5m |
|
| 34. |
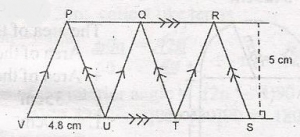 In the diagram, PQUV, PQTU, QRTU and QRST are parallelograms. |UV| = 4.8cm and the perpendicular distance between PR and VS is 5cm. Calculate the area of quadrilateral PRSV A. 96cm2 B. 72cm2 C. 60cm2 D. 24cm2 Detailed Solution|VU| = |UT| = |TS||VS| = (4.8) x 3 = 14.4cm |PQ| = |QR| = 4.8 |PR| = (4.8) x 2 = 9.6cm Since quad. PRSV is a trapezium of height 5cm Area of quad. PRSV = \(\frac{1}{2}(a + b)h\) = \(\frac{1}{2}(14.4 + 9.6) \times 5\) = \(\frac{1}{2}(24) \times 5\) 12 x 5 = 60cm2 |
|
| 35. |
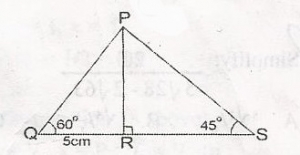 In the diagram, |QR| = 5cm, PQR = 60o and PSR = 45o. Find |PS|, leaving your answe in surd form. A. 4\(\sqrt{5}\)cm B. 3\(\sqrt{7}\)cm C. 4\(\sqrt{6}\)cm D. 5\(\sqrt{6}\)cm Detailed Solutiontan 6o = \(\frac{|PR|}{|QR|}\)\(\sqrt{3} = \frac{|PR|}{5}\) = |PR| = \(5 \sqrt{3}\)cm sin 45 = \(\frac{|PR|}{|PS|}\) \(\frac{1}{\sqrt{2}}\) = \(\frac{5 \sqrt{3}}{|PS|}\) |PS| = \(5 \sqrt{3}\) x \(\sqrt{2}\) = 5\(\sqrt{6}\)cm |
|
| 36. |
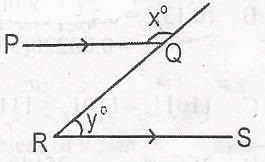 In the diagram, \(\frac{PQ}{RS}\), find xo + yo A. 360o B. 300o C. 270o D. 180o Detailed SolutionPQR = QRS = Y(alt. amgles)PQR + x = 180o(angles on a straight line) y + x = 180o |
|
| 37. |
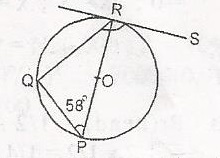 In the diagram, PR is a diameter of the circle centre O. RS is a tangent at R and QPR = 58o. Find < QRS A. 112o B. 116o C. 122o D. 148o Detailed SolutionPRQ = 90 - 58 = 32o(angle in a semi-circle)Since PRS = 90o(radius angular to tangent) QRS = 90 + 32 = 122o |
|
| 38. |
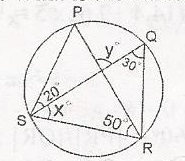 In the diagram P, Q, R, S are points on the circle RQS = 30o. PRS = 50o and PSQ = 20o. What is the value of xo + yo? A. 260o B. 130o C. 100o D. 80o Detailed SolutionDraw a line from P to Q< PQS = < PRS (angle in the sam segment) < PQS = 50o Also, < QSR = < QPR(angles in the segment) < QPR = xo x + y + 5= = 180(angles in a triangle) x + y = 180 - 50 x + y = 130o |
|
| 39. |
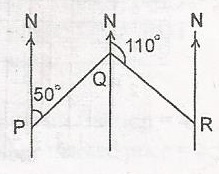 In the diagram, P, Q and R are three points in a plane such that the bearing of R from Q is 110o and the bearing of Q from P is 050o. Find angle PQR. A. 60o B. 70o C. 120o D. 160o Detailed SolutionQ1 = 50(alternate angle)Q2 = 180o - 110o (straight line angle) Q2 = 70 PQR = Q1 + Q2 = 50o + 70o = 120o |
|
| 40. |
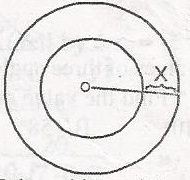 In the diagram, the two circles have a common centre O. If the area of the larger circle is 100\(\pi\) and that of the smaller circle is 49\(\pi\), find x A. 2 B. 3 C. 4 D. 6 Detailed Solutionarea of larger circle = 100\(\pi\)\(\pi r^2 = 100\pi\) R2 = 100 R = 10(Radius) Area of smaller circle = \(49 \pi\) \(\pi r^2 = 49\pi\) r2 = 49 r = 7(radius) Since R = x + r x = R - r x = 10 - 7 = 3 |
| 31. |
The temperature in a chemical plant was -5oC at 2.00 am. The temperature fell by 6oC and then rose again by 7oC. What was the final temperature? A. -6oC B. -4oC C. 4oC D. 8oC Detailed SolutionTemperature = -5oCIt fell by 6oC = -5oC - 6oC = -11oC Then rose by 7oC = -11 + 7 = -4oC (final temperature) |
|
| 32. |
Simplify \(\frac{20}{5\sqrt{28} - 2 \sqrt{63}}\) A. \(\frac{5\sqrt{7}}{7}\) B. \(\frac{5\sqrt{5}}{7}\) C. \(\frac{7\sqrt{5}}{7}\) D. \(\frac{7\sqrt{7}}{5}\) Detailed Solution\(\frac{20}{5 \sqrt{4 \times 7} - 2\sqrt{9 \times 7}}\)\(\frac{20}{10 \sqrt{7} - 6\sqrt{7}}\) = \(\frac{20 \sqrt{7}}{4 \sqrt{7}}\) = \(\frac{5\sqrt{7}}{7}\) |
|
| 33. |
A ladder 16m long leans against an electric pole. If the ladder makes an angle of 65o with the ground, how far up the electric pole does its top reach A. 6.8m B. 14.5m C. 17.7m D. 34.3m Detailed SolutionSin 65o = \(\frac{x}{16}\)x = 16x sin 65 = 16 x 0.9063 x = 14.5m |
|
| 34. |
 In the diagram, PQUV, PQTU, QRTU and QRST are parallelograms. |UV| = 4.8cm and the perpendicular distance between PR and VS is 5cm. Calculate the area of quadrilateral PRSV A. 96cm2 B. 72cm2 C. 60cm2 D. 24cm2 Detailed Solution|VU| = |UT| = |TS||VS| = (4.8) x 3 = 14.4cm |PQ| = |QR| = 4.8 |PR| = (4.8) x 2 = 9.6cm Since quad. PRSV is a trapezium of height 5cm Area of quad. PRSV = \(\frac{1}{2}(a + b)h\) = \(\frac{1}{2}(14.4 + 9.6) \times 5\) = \(\frac{1}{2}(24) \times 5\) 12 x 5 = 60cm2 |
|
| 35. |
 In the diagram, |QR| = 5cm, PQR = 60o and PSR = 45o. Find |PS|, leaving your answe in surd form. A. 4\(\sqrt{5}\)cm B. 3\(\sqrt{7}\)cm C. 4\(\sqrt{6}\)cm D. 5\(\sqrt{6}\)cm Detailed Solutiontan 6o = \(\frac{|PR|}{|QR|}\)\(\sqrt{3} = \frac{|PR|}{5}\) = |PR| = \(5 \sqrt{3}\)cm sin 45 = \(\frac{|PR|}{|PS|}\) \(\frac{1}{\sqrt{2}}\) = \(\frac{5 \sqrt{3}}{|PS|}\) |PS| = \(5 \sqrt{3}\) x \(\sqrt{2}\) = 5\(\sqrt{6}\)cm |
| 36. |
 In the diagram, \(\frac{PQ}{RS}\), find xo + yo A. 360o B. 300o C. 270o D. 180o Detailed SolutionPQR = QRS = Y(alt. amgles)PQR + x = 180o(angles on a straight line) y + x = 180o |
|
| 37. |
 In the diagram, PR is a diameter of the circle centre O. RS is a tangent at R and QPR = 58o. Find < QRS A. 112o B. 116o C. 122o D. 148o Detailed SolutionPRQ = 90 - 58 = 32o(angle in a semi-circle)Since PRS = 90o(radius angular to tangent) QRS = 90 + 32 = 122o |
|
| 38. |
 In the diagram P, Q, R, S are points on the circle RQS = 30o. PRS = 50o and PSQ = 20o. What is the value of xo + yo? A. 260o B. 130o C. 100o D. 80o Detailed SolutionDraw a line from P to Q< PQS = < PRS (angle in the sam segment) < PQS = 50o Also, < QSR = < QPR(angles in the segment) < QPR = xo x + y + 5= = 180(angles in a triangle) x + y = 180 - 50 x + y = 130o |
|
| 39. |
 In the diagram, P, Q and R are three points in a plane such that the bearing of R from Q is 110o and the bearing of Q from P is 050o. Find angle PQR. A. 60o B. 70o C. 120o D. 160o Detailed SolutionQ1 = 50(alternate angle)Q2 = 180o - 110o (straight line angle) Q2 = 70 PQR = Q1 + Q2 = 50o + 70o = 120o |
|
| 40. |
 In the diagram, the two circles have a common centre O. If the area of the larger circle is 100\(\pi\) and that of the smaller circle is 49\(\pi\), find x A. 2 B. 3 C. 4 D. 6 Detailed Solutionarea of larger circle = 100\(\pi\)\(\pi r^2 = 100\pi\) R2 = 100 R = 10(Radius) Area of smaller circle = \(49 \pi\) \(\pi r^2 = 49\pi\) r2 = 49 r = 7(radius) Since R = x + r x = R - r x = 10 - 7 = 3 |