Year :
2005
Title :
Mathematics (Core)
Exam :
WASSCE/WAEC MAY/JUNE
Paper 1 | Objectives
1 - 10 of 47 Questions
| # | Question | Ans |
|---|---|---|
| 1. |
Correct 0.04945 to two significant figures A. 0.040 B. 0.049 C. 0.050 D. 0.49 Detailed Solution0.04945 \(\approxeq\) 0.049. (to 2 sig. figs) |
|
| 2. |
Simplify \(\frac{5}{\sqrt{3}}-\frac{3}{\sqrt{2}}\) A. \(\frac{1}{6}(5\sqrt{3}-3\sqrt{2}\) B. \(\frac{1}{6}(15\sqrt{3}-6\sqrt{2}\) C. \(\frac{1}{6}(3\sqrt{2}-\sqrt{3}\) D. \(\frac{1}{6}(10\sqrt{3}-9\sqrt{2}\) Detailed Solution\(\frac{5}{\sqrt{3}}-\frac{3}{\sqrt{2}}=\frac{5\sqrt{2}-3\sqrt{3}}{\sqrt{6}}\\=\frac{5\sqrt{2}-3\sqrt{3}}{\sqrt{6}} \times \frac{\sqrt{6}}{\sqrt{6}}Rationalize\\ \frac{\sqrt{6}(5\sqrt{2}-3\sqrt{3})}{6}\\ \frac{5\sqrt{12}-3\sqrt{18}}{6}=\frac{10\sqrt{3}-9\sqrt{2}}{6}\\ \frac{1}{6}(10\sqrt{3}-9\sqrt{2})\) |
|
| 3. |
Evaluate, correct to the nearest whole number \(7\frac{1}{2}-\left(2\frac{1}{2}+3\right)\div\frac{33}{2}\) A. 33 B. 8 C. 7 D. o Detailed Solution\(7\frac{1}{2}-\left(2\frac{1}{2}+3\right)\div\frac{33}{2}\\=\frac{15}{2}-\left(\frac{5}{2}+\frac{3}{1}\right)\times\frac{2}{33}\\ =\frac{15}{2}-\left(\frac{5+6}{2}\right)\times \frac{2}{33}=\frac{15}{2}-\frac{11}{2}\times \frac{2}{33}=\frac{15}{2}-\frac{1}{3}\\ =\frac{45-2}{6}=\frac{43}{6}\) |
|
| 4. |
Simplify the expression \(log_{10}18 - log_{10}2.88+log_{10}16\) A. 31.12 B. 3.112 C. 2 D. 1 Detailed Solution\(log_{10}18 - log_{10}2.88+log_{10}16\\=log_{10}18 - log_{10}\left(\frac{288}{100}\right)+log_{10}16 = log_{10}\left(\frac{18\times 16}{1}\times \frac{100}{288}\right)\\ =log_{10}\left(\frac{288\times 100}{288}\right)=log_{10}100=log_{10}10^2=2log_{10}10=2\) |
|
| 5. |
Find the equation whose roots are 2 and \(-3\frac{1}{2}\) A. 2x2 + 3x + 14 = 0 B. 2x2 + 5x + 7 = 0 C. 2x2 + 5x - 7 = 0 D. 2x2 + 3x - 14 = 0 Detailed Solutionx2 (sum of roots)x + (product of roots) = 0Sum of roots \(2+-3\frac{1}{2} = -1\frac{1}{2}=-\frac{1}{2}\) Product of roots \(=2 \times -3\frac{1}{2}=-7\\ x^2-\left(\frac{-3}{2}\right)x+(-7)=0\Rightarrow 2x^2 + 3x - 14 = 0\) |
|
| 6. |
A man bought 220 mangoes at N5x. He sold each for 3x kobo and made a gain of N8. Find the value of x A. 2 B. 5 C. 6 D. 10 Detailed SolutionThe cost price of the whole mangoes = N5xThe sold amount of the mangoes = 3x * 220 = N6.60x The gain made on mangoes = N6.60x - N5x = N8.00 => N1.60x = N8 => \(x=\frac{8}{1.60}=\frac{1}{0.2}=\frac{10}{2}=5\) |
|
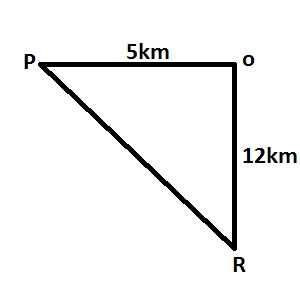
| 7. |
From a point P, R is 5km due west and 12km due south. Find the distance between P and R A. 5km B. 12km C. 13km D. 17km Detailed Solution
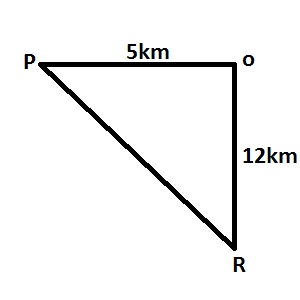 \(|PR|^2=|PO|^2+|OR|^2\\ |PR|^2=5^2+12^2\\ |PR|=\sqrt{25+144}=\sqrt{169}=13km\) |
|
| 8. |
A fair die is tossed once, what is the probability of obtaining neither 5 or 2 A. \(\frac{5}{6}\) B. \(\frac{2}{3}\) C. \(\frac{1}{2}\) D. \(\frac{1}{6}\) Detailed SolutionProbability of obtaining a 5 is P(5)=\(\frac{1}{6}\)Probability of obtaining a 2 is P(2)=\(\frac{1}{6}\) Probability of obatining either 2 or 5 = P(2∪5) = \(\frac{2}{6}\) Probability of obtaining neither 5 or 2 = \(1 - \frac{2}{6}=\frac{4}{6}=\frac{2}{3}\) |
|
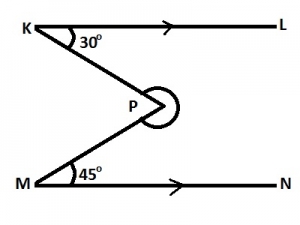
| 9. |
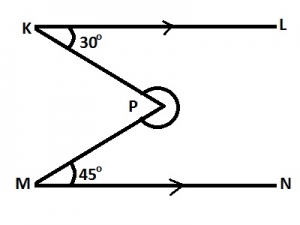 In the diagram, KL//MN, ∠LKP = 30o and ∠NMP = 45o. Find the size of the reflex ∠KPM. A. 285o B. 255o C. 225o D. 210o Detailed Solution
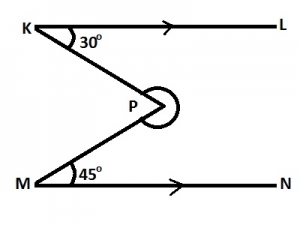 = 360o - 75o = 285o |
|
| 10. |
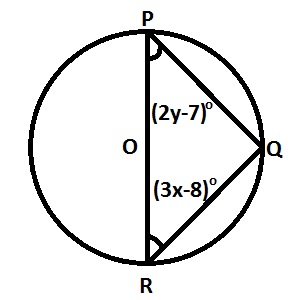 In the diagram, PR is a diameter, ∠PRQ = (3x-8)o and ∠RPQ = (2y-7)o. s x in terms of y A. \(x=\frac{75-2y}{3}\) B. \(x=\frac{105-3y}{2}\) C. \(x=\frac{105-2y}{3}\) D. \(x=\frac{75-3y}{2}\) Detailed Solution180 = ∠RPQ + ∠PRQ + ∠PQR Since PQR = 90 (theorem: angle in a semi circle)180 = ∠RPQ + ∠PRQ + 90 => 180o = (3x-8)o+(2y-7)o+90o; 90+8+7 = 3x+2y =>\(\frac{105-2y}{3}=x\) |
| 1. |
Correct 0.04945 to two significant figures A. 0.040 B. 0.049 C. 0.050 D. 0.49 Detailed Solution0.04945 \(\approxeq\) 0.049. (to 2 sig. figs) |
|
| 2. |
Simplify \(\frac{5}{\sqrt{3}}-\frac{3}{\sqrt{2}}\) A. \(\frac{1}{6}(5\sqrt{3}-3\sqrt{2}\) B. \(\frac{1}{6}(15\sqrt{3}-6\sqrt{2}\) C. \(\frac{1}{6}(3\sqrt{2}-\sqrt{3}\) D. \(\frac{1}{6}(10\sqrt{3}-9\sqrt{2}\) Detailed Solution\(\frac{5}{\sqrt{3}}-\frac{3}{\sqrt{2}}=\frac{5\sqrt{2}-3\sqrt{3}}{\sqrt{6}}\\=\frac{5\sqrt{2}-3\sqrt{3}}{\sqrt{6}} \times \frac{\sqrt{6}}{\sqrt{6}}Rationalize\\ \frac{\sqrt{6}(5\sqrt{2}-3\sqrt{3})}{6}\\ \frac{5\sqrt{12}-3\sqrt{18}}{6}=\frac{10\sqrt{3}-9\sqrt{2}}{6}\\ \frac{1}{6}(10\sqrt{3}-9\sqrt{2})\) |
|
| 3. |
Evaluate, correct to the nearest whole number \(7\frac{1}{2}-\left(2\frac{1}{2}+3\right)\div\frac{33}{2}\) A. 33 B. 8 C. 7 D. o Detailed Solution\(7\frac{1}{2}-\left(2\frac{1}{2}+3\right)\div\frac{33}{2}\\=\frac{15}{2}-\left(\frac{5}{2}+\frac{3}{1}\right)\times\frac{2}{33}\\ =\frac{15}{2}-\left(\frac{5+6}{2}\right)\times \frac{2}{33}=\frac{15}{2}-\frac{11}{2}\times \frac{2}{33}=\frac{15}{2}-\frac{1}{3}\\ =\frac{45-2}{6}=\frac{43}{6}\) |
|
| 4. |
Simplify the expression \(log_{10}18 - log_{10}2.88+log_{10}16\) A. 31.12 B. 3.112 C. 2 D. 1 Detailed Solution\(log_{10}18 - log_{10}2.88+log_{10}16\\=log_{10}18 - log_{10}\left(\frac{288}{100}\right)+log_{10}16 = log_{10}\left(\frac{18\times 16}{1}\times \frac{100}{288}\right)\\ =log_{10}\left(\frac{288\times 100}{288}\right)=log_{10}100=log_{10}10^2=2log_{10}10=2\) |
|
| 5. |
Find the equation whose roots are 2 and \(-3\frac{1}{2}\) A. 2x2 + 3x + 14 = 0 B. 2x2 + 5x + 7 = 0 C. 2x2 + 5x - 7 = 0 D. 2x2 + 3x - 14 = 0 Detailed Solutionx2 (sum of roots)x + (product of roots) = 0Sum of roots \(2+-3\frac{1}{2} = -1\frac{1}{2}=-\frac{1}{2}\) Product of roots \(=2 \times -3\frac{1}{2}=-7\\ x^2-\left(\frac{-3}{2}\right)x+(-7)=0\Rightarrow 2x^2 + 3x - 14 = 0\) |
| 6. |
A man bought 220 mangoes at N5x. He sold each for 3x kobo and made a gain of N8. Find the value of x A. 2 B. 5 C. 6 D. 10 Detailed SolutionThe cost price of the whole mangoes = N5xThe sold amount of the mangoes = 3x * 220 = N6.60x The gain made on mangoes = N6.60x - N5x = N8.00 => N1.60x = N8 => \(x=\frac{8}{1.60}=\frac{1}{0.2}=\frac{10}{2}=5\) |
|
| 7. |
From a point P, R is 5km due west and 12km due south. Find the distance between P and R A. 5km B. 12km C. 13km D. 17km Detailed Solution
 \(|PR|^2=|PO|^2+|OR|^2\\ |PR|^2=5^2+12^2\\ |PR|=\sqrt{25+144}=\sqrt{169}=13km\) |
|
| 8. |
A fair die is tossed once, what is the probability of obtaining neither 5 or 2 A. \(\frac{5}{6}\) B. \(\frac{2}{3}\) C. \(\frac{1}{2}\) D. \(\frac{1}{6}\) Detailed SolutionProbability of obtaining a 5 is P(5)=\(\frac{1}{6}\)Probability of obtaining a 2 is P(2)=\(\frac{1}{6}\) Probability of obatining either 2 or 5 = P(2∪5) = \(\frac{2}{6}\) Probability of obtaining neither 5 or 2 = \(1 - \frac{2}{6}=\frac{4}{6}=\frac{2}{3}\) |
|
| 9. |
 In the diagram, KL//MN, ∠LKP = 30o and ∠NMP = 45o. Find the size of the reflex ∠KPM. A. 285o B. 255o C. 225o D. 210o Detailed Solution
 = 360o - 75o = 285o |
|
| 10. |
 In the diagram, PR is a diameter, ∠PRQ = (3x-8)o and ∠RPQ = (2y-7)o. s x in terms of y A. \(x=\frac{75-2y}{3}\) B. \(x=\frac{105-3y}{2}\) C. \(x=\frac{105-2y}{3}\) D. \(x=\frac{75-3y}{2}\) Detailed Solution180 = ∠RPQ + ∠PRQ + ∠PQR Since PQR = 90 (theorem: angle in a semi circle)180 = ∠RPQ + ∠PRQ + 90 => 180o = (3x-8)o+(2y-7)o+90o; 90+8+7 = 3x+2y =>\(\frac{105-2y}{3}=x\) |