Year :
1993
Title :
Mathematics (Core)
Exam :
JAMB Exam
Paper 1 | Objectives
41 - 50 of 51 Questions
| # | Question | Ans |
|---|---|---|
| 41. |
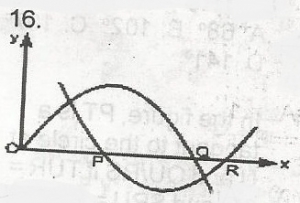 The figure represents the graphs of y = x(2 - x) and y = (x - 1)(x - 3). What are the x-coordinates of P, Q and F respectively? A. 1, 3, 2 B. 0, 0, 0 C. 0, 2, 3 D. 1, 2, 3 Detailed SolutionThe two equations are y = x(2 - x) and y = (x - 1)(x - 3)The root of these equations are points where the graph of the equations cuts the x axis; but at these points = 0 put y = 0; 0 = x(2 - x) 0 = (x - 1)(x - 3) x = 0 or x = 2; x = 1 or x = 3 The values of x at P, Q, R are increasing towards the positive direction of x-axis at P, x = 1 at Q, x = 2 at R, x = 3 P, Q, R are respectively (1, 2, 3) |
|
| 42. |
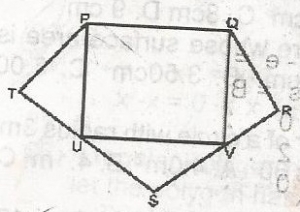 PQRST is a regular pentagon and PQVU is a rectangle with U and V lying on TS and SR respectively as shown in the diagram. Calculate TUP A. 18o B. 54o C. 90o D. 108o Detailed SolutionThe total angle in a regular pentagon = \((2(5) - 4) \times 90\)= \(6 \times 90 = 540°\) Each interior angle = \(\frac{540}{5} = 108°\) While the interior of a quadrilateral = \(\frac{360}{4} = 90°\) \(PTU + TPU + TUP = 180°\) \(108° + (180° - 90°) + TUP = 180°\) \(TUP = 180° - (108° + 18°) = 54°\) |
|
| 43. |
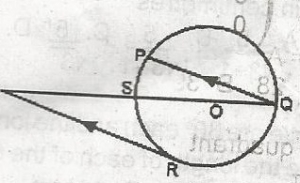 In the diagram, PQRS is a circle with O as centre and PQ/RT. If RTS = 32°. Find PSQ A. 32o B. 45o C. 58o D. 90o Detailed Solution< PSO = \(\frac{1}{2}\) < SOQ = \(\frac{1}{2}\)(180) = 90°< RTS = < PQS = 32° (Alternative angle) < PSQ = 90 - < PSQ = 90° - 32° = 58° |
|
| 44. |
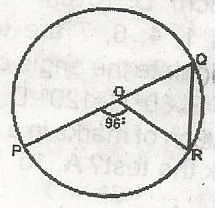 In the diagram, O is the centre of the circle and POQ a diameter. If POR = 96o, find the value of ORQ. A. 84o B. 48o C. 45o D. 42o Detailed SolutionOQ = OR = radii< ROQ = 180 - 86 = 84o \(\bigtriangleup\)OQR = Isosceles R = Q R + Q + 84 = 180(angle in a \(\bigtriangleup\)) 2R = 96 since R = Q R = 48o ORQ = 48o |
|
| 45. |
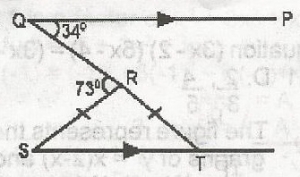 In the diagram, QP//ST:PQR = 34o qrs = 73o and Rs = RT. Find SRT A. 68o B. 102o C. 107o D. 141o Detailed SolutionConstruction joins R to P such that SRP = straight lineR = 180o - 107o < p = 180o - (107o - 34o) 108 - 141o = 39o Angle < S = 39o (corr. Ang.) But in \(\bigtriangleup\)SRT < S = < T = 39o SRT = 180 - (39o + 39o) = 180o - 78o = 102o |
|
| 46. |
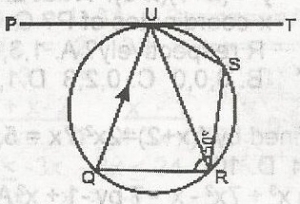 In the figure, PT is a tangent to the circle at U and QU/RS if TUR = 35o and SRU = 50o find x A. 95o B. 85o C. 50o D. 35o Detailed SolutionSince QRU= XoRSU = Xo, But RSU = 180o - (50o + 35o) = 180o - 85o = 95o x = 95o |
|
| 47. |
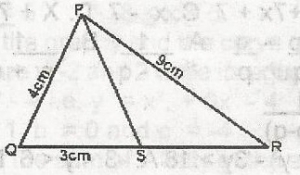 In the diagram, QPS = SPR, PR = 9cm. PQ = 4cm and QS = 3cm, find SR. A. 6\(\frac{3}{4}\)cm B. 3\(\frac{3}{8}\)cm C. 4\(\frac{3}{8}\)cm D. 2\(\frac{3}{8}\)cm Detailed SolutionUsing angle bisector theorem: line PS bisects angle QPRQS/QP = SR/PR 3/4 = SR/9 4SR = 27 SR = \(\frac{27}{4}\) = 6\(\frac{3}{4}\)cm |
|
| 48. |
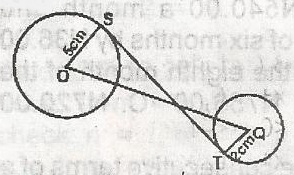 In the figure, the line segment ST is tangent to two circles at S and T. O and Q are the centres of the circles wih OS = 5cm. QT = 2cm and OR = 14cm. Find ST A. 7 \(\sqrt{3}\)cm B. 12.9cm C. \(\sqrt{87}\)cm D. 7cm Detailed SolutionSQ2 + OS2 = OQ2 + 52 = 142SQ2 = 142 - 52 196 - 25 = 171 ST2 + TQ2 = SQ2 ST2 + 22 = 171 ST2 = 171 - 4 = 167 ST = \(\sqrt{167}\) = 12.92 = 12.9cm |
|
| 49. |
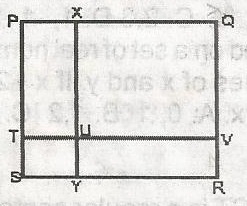 In the figure, the area of the square of the square PQRS is 100cm2. If the ratio of the area of the square TUYS to the area of the area of the square XQVU is 1 : 16, Find YR A. 6cm B. 7cm C. 8cm D. 9cm Detailed SolutionSince area of square PQRS = 100cm2each lenght = 10cm Also TUYS : XQVU = 1 : 16 lengths are in ratio 1 : 4, hence TU : UV = 1: 4 Let TU = x UV = 1: 4 hence TV = x + 4x = 5x = 10cm x = 2cm TU = 2cm UV = 8cm But TU = SY and UV = YR YR = 8cm |
|
| 50. |
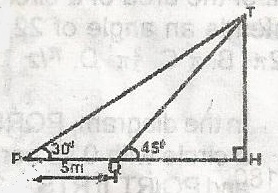 From the figure, calculate TH in centimeters A. \(\frac{5}{\sqrt{3} + 1}\) B. \(\frac{5}{\sqrt{3} - 1}\) C. \(\frac{5}{\sqrt{3}}\) D. \(\frac{\sqrt{3}}{5}\) Detailed SolutionTH = tan 45o, TH = QH\(\frac{TH}{5 + QH}\) = tan 30o TH = (b + QH) tan 30o QH = 56 (5 + QH) \(\frac{1}{\sqrt{3}}\) QH(1 - \(\frac{1}{\sqrt{3}}\)) = \(\frac{5}{\sqrt{3}}\) QH = \(\frac{5\sqrt{3}}{\sqrt{3}} - \frac{1}{\sqrt{3}}\) = \(\frac{5}{\sqrt{3} - 1}\) |
| 41. |
 The figure represents the graphs of y = x(2 - x) and y = (x - 1)(x - 3). What are the x-coordinates of P, Q and F respectively? A. 1, 3, 2 B. 0, 0, 0 C. 0, 2, 3 D. 1, 2, 3 Detailed SolutionThe two equations are y = x(2 - x) and y = (x - 1)(x - 3)The root of these equations are points where the graph of the equations cuts the x axis; but at these points = 0 put y = 0; 0 = x(2 - x) 0 = (x - 1)(x - 3) x = 0 or x = 2; x = 1 or x = 3 The values of x at P, Q, R are increasing towards the positive direction of x-axis at P, x = 1 at Q, x = 2 at R, x = 3 P, Q, R are respectively (1, 2, 3) |
|
| 42. |
 PQRST is a regular pentagon and PQVU is a rectangle with U and V lying on TS and SR respectively as shown in the diagram. Calculate TUP A. 18o B. 54o C. 90o D. 108o Detailed SolutionThe total angle in a regular pentagon = \((2(5) - 4) \times 90\)= \(6 \times 90 = 540°\) Each interior angle = \(\frac{540}{5} = 108°\) While the interior of a quadrilateral = \(\frac{360}{4} = 90°\) \(PTU + TPU + TUP = 180°\) \(108° + (180° - 90°) + TUP = 180°\) \(TUP = 180° - (108° + 18°) = 54°\) |
|
| 43. |
 In the diagram, PQRS is a circle with O as centre and PQ/RT. If RTS = 32°. Find PSQ A. 32o B. 45o C. 58o D. 90o Detailed Solution< PSO = \(\frac{1}{2}\) < SOQ = \(\frac{1}{2}\)(180) = 90°< RTS = < PQS = 32° (Alternative angle) < PSQ = 90 - < PSQ = 90° - 32° = 58° |
|
| 44. |
 In the diagram, O is the centre of the circle and POQ a diameter. If POR = 96o, find the value of ORQ. A. 84o B. 48o C. 45o D. 42o Detailed SolutionOQ = OR = radii< ROQ = 180 - 86 = 84o \(\bigtriangleup\)OQR = Isosceles R = Q R + Q + 84 = 180(angle in a \(\bigtriangleup\)) 2R = 96 since R = Q R = 48o ORQ = 48o |
|
| 45. |
 In the diagram, QP//ST:PQR = 34o qrs = 73o and Rs = RT. Find SRT A. 68o B. 102o C. 107o D. 141o Detailed SolutionConstruction joins R to P such that SRP = straight lineR = 180o - 107o < p = 180o - (107o - 34o) 108 - 141o = 39o Angle < S = 39o (corr. Ang.) But in \(\bigtriangleup\)SRT < S = < T = 39o SRT = 180 - (39o + 39o) = 180o - 78o = 102o |
| 46. |
 In the figure, PT is a tangent to the circle at U and QU/RS if TUR = 35o and SRU = 50o find x A. 95o B. 85o C. 50o D. 35o Detailed SolutionSince QRU= XoRSU = Xo, But RSU = 180o - (50o + 35o) = 180o - 85o = 95o x = 95o |
|
| 47. |
 In the diagram, QPS = SPR, PR = 9cm. PQ = 4cm and QS = 3cm, find SR. A. 6\(\frac{3}{4}\)cm B. 3\(\frac{3}{8}\)cm C. 4\(\frac{3}{8}\)cm D. 2\(\frac{3}{8}\)cm Detailed SolutionUsing angle bisector theorem: line PS bisects angle QPRQS/QP = SR/PR 3/4 = SR/9 4SR = 27 SR = \(\frac{27}{4}\) = 6\(\frac{3}{4}\)cm |
|
| 48. |
 In the figure, the line segment ST is tangent to two circles at S and T. O and Q are the centres of the circles wih OS = 5cm. QT = 2cm and OR = 14cm. Find ST A. 7 \(\sqrt{3}\)cm B. 12.9cm C. \(\sqrt{87}\)cm D. 7cm Detailed SolutionSQ2 + OS2 = OQ2 + 52 = 142SQ2 = 142 - 52 196 - 25 = 171 ST2 + TQ2 = SQ2 ST2 + 22 = 171 ST2 = 171 - 4 = 167 ST = \(\sqrt{167}\) = 12.92 = 12.9cm |
|
| 49. |
 In the figure, the area of the square of the square PQRS is 100cm2. If the ratio of the area of the square TUYS to the area of the area of the square XQVU is 1 : 16, Find YR A. 6cm B. 7cm C. 8cm D. 9cm Detailed SolutionSince area of square PQRS = 100cm2each lenght = 10cm Also TUYS : XQVU = 1 : 16 lengths are in ratio 1 : 4, hence TU : UV = 1: 4 Let TU = x UV = 1: 4 hence TV = x + 4x = 5x = 10cm x = 2cm TU = 2cm UV = 8cm But TU = SY and UV = YR YR = 8cm |
|
| 50. |
 From the figure, calculate TH in centimeters A. \(\frac{5}{\sqrt{3} + 1}\) B. \(\frac{5}{\sqrt{3} - 1}\) C. \(\frac{5}{\sqrt{3}}\) D. \(\frac{\sqrt{3}}{5}\) Detailed SolutionTH = tan 45o, TH = QH\(\frac{TH}{5 + QH}\) = tan 30o TH = (b + QH) tan 30o QH = 56 (5 + QH) \(\frac{1}{\sqrt{3}}\) QH(1 - \(\frac{1}{\sqrt{3}}\)) = \(\frac{5}{\sqrt{3}}\) QH = \(\frac{5\sqrt{3}}{\sqrt{3}} - \frac{1}{\sqrt{3}}\) = \(\frac{5}{\sqrt{3} - 1}\) |