Year :
2010
Title :
Mathematics (Core)
Exam :
WASSCE/WAEC MAY/JUNE
Paper 1 | Objectives
31 - 40 of 49 Questions
| # | Question | Ans |
|---|---|---|
| 31. |
If x2 + kx + \(\frac{16}{9}\) is a perfect square, find the value of k A. \(\frac{8}{3}\) B. \(\frac{7}{3}\) C. \(\frac{5}{3}\) D. \(\frac{2}{3}\) Detailed Solutionx2 + kx + \(\frac{16}{9}\); Perfect squareBut, b2 - 4ac = 0, for a perfect square where a - 1; b = k; c = \(\frac{16}{9}\) k2 - 4(1) x \(\frac{16}{9}\) = 0 k2 - \(\frac{64}{9}\) = 0 k2 = \(\frac{64}{9}\) k = \(\sqrt{\frac{64}{9}}\) k = \(\frac{8}{3}\) |
|
| 32. |
If x km/h = y m/s, then y = A. \(\frac{7}{18}\)x B. \(\frac{11}{20}\)x C. \(\frac{4}{15}\)x D. \(\frac{5}{18}\)x Detailed Solutionx kmh-1 = y ms-1\(\frac{x km}{1 hr}\) = y ms-1 \(x \times \frac{1km}{1hr}\) = y ms-1 \(x \times \frac{1000m}{60 \times 60s}\) = y ms-1 \(x \times \frac{1000}{3600} \frac{m}{s}\) = y ms-1 \(x \times \frac{5}{18} ms^{-1}\) \(x \times \frac{5}{18} ms^{-1}\) = y ms-1 y = \(\frac{5}{18}\)x |
|
| 33. |
The mean of the numbers 2, 5, 2x and 7 is less than or equal to 5. Find the range of the values of x A. x \(\leq\) 3 B. x \(\geq\) 3 C. x < 3 D. x > 3 Detailed Solutionmean \(\leq\) 5; \(\frac{2 + 5 + 2x + 7}{4}\) \(\leq\) 5= \(\frac{14 + 2x}{4} \leq 5\) = 14 + 2x \(\leq\) 5 x 4 14 + 2x \(\leq\) 20 ; 2x \(\leq\) 20 - 14 2x \(\leq\) 20 - 14 2x \(\leq\) 6 x \(\leq\) \(\frac{6}{2}\) x \(\leq\) 3 |
|
| 34. |
In an athletic composition, the probability that an athlete wins a 100m race is \(\frac{1}{8}\) and the probability that he wins in high jump is \(\frac{1}{4}\). What is the probability that he wins only one of the events? A. \(\frac{3}{32}\) B. \(\frac{7}{3}\) C. \(\frac{5}{3}\) D. \(\frac{5}{16}\) Detailed SolutionPr. (winning 100m race) = \(\frac{1}{8}\)Pr. (losing 100m race) = 1 - \(\frac{1}{8}\) = \(\frac{7}{8}\) Pr. (winning high jump) = \(\frac{1}{4}\) Pr. (losing high jump ) = 1 - \(\frac{1}{4}\) = \(\frac{3}{4}\) Pr. (winning only one) = Pr. (Winning 100m race and losing high jump) or Pr.(Losing 100m race and winning high jump) = (\(\frac{1}{8} \times \frac{3}{4}\)) + (\(\frac{7}{8} \times \frac{1}{4}\)) = \(\frac{3}{32} + \frac{7}{32}\) = \(\frac{10}{32}\) = \(\frac{5}{16}\) |
|
| 35. |
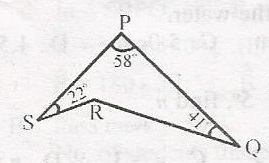 In the diagram, < PSR = 220o, < SPQ = 58o and < PQR = 41o. Calculate the obtuse angle QRS. A. 90o B. 100o C. 121o D. 60o Detailed SolutionJoining SQ. In \(\bigtriangleup\) SPQ,(22o + a) + 55o + (41o + b) = 180o 121o + a + b = 180o a + b = 180 - 121 a + b = 59o.....(1) In \(\bigtriangleup\) SRPQ; R + a + b = 180o R + 59o = 180o (in (1), a + b = 59o) R = 180 - 59 R = 121o |
|
| 36. |
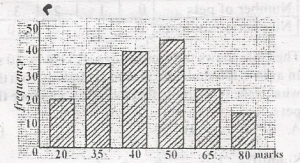 The bar chart shows the marks distribution in am English test. If 50% is the pass mark, how many students passed the test? A. 100 B. 85 C. 80 D. 70 Detailed SolutionPass mark = 50%No. of students that passed = f50 + f65 + f80 = 45 + 25 + 15 = 85 |
|
| 37. |
 The bar chart shows the marks distribution in am English test. What percentage of the students had marks ranging from 35 to 50? A. 55\(\frac{1}{3}\)% B. 60% C. 65% D. 66\(\frac{2}{3}\)% Detailed SolutionPercentage of students with marks ranging from 35 to 50 = \(\frac{f_{35} + f{40} + f{50}}{\sum f}\)= \(\frac{35 + 40 + 45}{20 + 35 + 40 + 45 + 25 + 15}\) x 100% = \(\frac{120}{180}\) x 100% = 66\(\frac{2}{3}\)% |
|
| 38. |
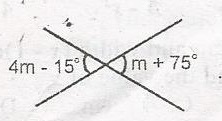 What is the value of m in the diagram? A. 20o B. 30o C. 40o D. 50o Detailed Solution4m - 15o = m + 75o(Vertically opposite angles are equal) 4m - m = 75 + 15 3m = 90 m = \(\frac{90}{3}\) m = 30o |
|
| 39. |
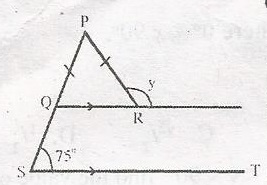 In the diagram, QR//ST, /PQ/ = /PR/ and < PST = 75o. Find the value of y A. 105o B. 110o C. 130o D. 150o Detailed SolutionIn \(\bigtriangleup\) PQR,Q = S = 75o (Corresponding angle) R = Q = 75o (Base angles of an isosceles \(\bigtriangleup\)) But, y + 75o = 180o (Sum of angles in a straight line) y = 180 - 75 y = 105o |
|
| 40. |
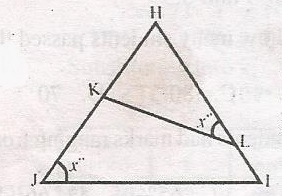 In the diagram, triangles HKL and HIJ are similar. Which of the following ratios is equal to \(\frac{LH}{JH}\) A. \(\frac{KL}{JI}\) B. \(\frac{HK}{JK}\) C. \(\frac{JI}{KL}\) D. \(\frac{HK}{LK}\) Detailed Solution\(\bigtriangleup\) is similar to \(\bigtriangleup\) HIJ< HKL = HJI = xo Hence, \(\frac{LH}{JH} = \frac{KH}{JH} \frac{KL}{IJ}\) \(\frac{LH}{JH} = \frac{KL}{JI}\) |
| 31. |
If x2 + kx + \(\frac{16}{9}\) is a perfect square, find the value of k A. \(\frac{8}{3}\) B. \(\frac{7}{3}\) C. \(\frac{5}{3}\) D. \(\frac{2}{3}\) Detailed Solutionx2 + kx + \(\frac{16}{9}\); Perfect squareBut, b2 - 4ac = 0, for a perfect square where a - 1; b = k; c = \(\frac{16}{9}\) k2 - 4(1) x \(\frac{16}{9}\) = 0 k2 - \(\frac{64}{9}\) = 0 k2 = \(\frac{64}{9}\) k = \(\sqrt{\frac{64}{9}}\) k = \(\frac{8}{3}\) |
|
| 32. |
If x km/h = y m/s, then y = A. \(\frac{7}{18}\)x B. \(\frac{11}{20}\)x C. \(\frac{4}{15}\)x D. \(\frac{5}{18}\)x Detailed Solutionx kmh-1 = y ms-1\(\frac{x km}{1 hr}\) = y ms-1 \(x \times \frac{1km}{1hr}\) = y ms-1 \(x \times \frac{1000m}{60 \times 60s}\) = y ms-1 \(x \times \frac{1000}{3600} \frac{m}{s}\) = y ms-1 \(x \times \frac{5}{18} ms^{-1}\) \(x \times \frac{5}{18} ms^{-1}\) = y ms-1 y = \(\frac{5}{18}\)x |
|
| 33. |
The mean of the numbers 2, 5, 2x and 7 is less than or equal to 5. Find the range of the values of x A. x \(\leq\) 3 B. x \(\geq\) 3 C. x < 3 D. x > 3 Detailed Solutionmean \(\leq\) 5; \(\frac{2 + 5 + 2x + 7}{4}\) \(\leq\) 5= \(\frac{14 + 2x}{4} \leq 5\) = 14 + 2x \(\leq\) 5 x 4 14 + 2x \(\leq\) 20 ; 2x \(\leq\) 20 - 14 2x \(\leq\) 20 - 14 2x \(\leq\) 6 x \(\leq\) \(\frac{6}{2}\) x \(\leq\) 3 |
|
| 34. |
In an athletic composition, the probability that an athlete wins a 100m race is \(\frac{1}{8}\) and the probability that he wins in high jump is \(\frac{1}{4}\). What is the probability that he wins only one of the events? A. \(\frac{3}{32}\) B. \(\frac{7}{3}\) C. \(\frac{5}{3}\) D. \(\frac{5}{16}\) Detailed SolutionPr. (winning 100m race) = \(\frac{1}{8}\)Pr. (losing 100m race) = 1 - \(\frac{1}{8}\) = \(\frac{7}{8}\) Pr. (winning high jump) = \(\frac{1}{4}\) Pr. (losing high jump ) = 1 - \(\frac{1}{4}\) = \(\frac{3}{4}\) Pr. (winning only one) = Pr. (Winning 100m race and losing high jump) or Pr.(Losing 100m race and winning high jump) = (\(\frac{1}{8} \times \frac{3}{4}\)) + (\(\frac{7}{8} \times \frac{1}{4}\)) = \(\frac{3}{32} + \frac{7}{32}\) = \(\frac{10}{32}\) = \(\frac{5}{16}\) |
|
| 35. |
 In the diagram, < PSR = 220o, < SPQ = 58o and < PQR = 41o. Calculate the obtuse angle QRS. A. 90o B. 100o C. 121o D. 60o Detailed SolutionJoining SQ. In \(\bigtriangleup\) SPQ,(22o + a) + 55o + (41o + b) = 180o 121o + a + b = 180o a + b = 180 - 121 a + b = 59o.....(1) In \(\bigtriangleup\) SRPQ; R + a + b = 180o R + 59o = 180o (in (1), a + b = 59o) R = 180 - 59 R = 121o |
| 36. |
 The bar chart shows the marks distribution in am English test. If 50% is the pass mark, how many students passed the test? A. 100 B. 85 C. 80 D. 70 Detailed SolutionPass mark = 50%No. of students that passed = f50 + f65 + f80 = 45 + 25 + 15 = 85 |
|
| 37. |
 The bar chart shows the marks distribution in am English test. What percentage of the students had marks ranging from 35 to 50? A. 55\(\frac{1}{3}\)% B. 60% C. 65% D. 66\(\frac{2}{3}\)% Detailed SolutionPercentage of students with marks ranging from 35 to 50 = \(\frac{f_{35} + f{40} + f{50}}{\sum f}\)= \(\frac{35 + 40 + 45}{20 + 35 + 40 + 45 + 25 + 15}\) x 100% = \(\frac{120}{180}\) x 100% = 66\(\frac{2}{3}\)% |
|
| 38. |
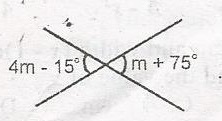 What is the value of m in the diagram? A. 20o B. 30o C. 40o D. 50o Detailed Solution4m - 15o = m + 75o(Vertically opposite angles are equal) 4m - m = 75 + 15 3m = 90 m = \(\frac{90}{3}\) m = 30o |
|
| 39. |
 In the diagram, QR//ST, /PQ/ = /PR/ and < PST = 75o. Find the value of y A. 105o B. 110o C. 130o D. 150o Detailed SolutionIn \(\bigtriangleup\) PQR,Q = S = 75o (Corresponding angle) R = Q = 75o (Base angles of an isosceles \(\bigtriangleup\)) But, y + 75o = 180o (Sum of angles in a straight line) y = 180 - 75 y = 105o |
|
| 40. |
 In the diagram, triangles HKL and HIJ are similar. Which of the following ratios is equal to \(\frac{LH}{JH}\) A. \(\frac{KL}{JI}\) B. \(\frac{HK}{JK}\) C. \(\frac{JI}{KL}\) D. \(\frac{HK}{LK}\) Detailed Solution\(\bigtriangleup\) is similar to \(\bigtriangleup\) HIJ< HKL = HJI = xo Hence, \(\frac{LH}{JH} = \frac{KH}{JH} \frac{KL}{IJ}\) \(\frac{LH}{JH} = \frac{KL}{JI}\) |