Year :
2018
Title :
Chemistry
Exam :
JAMB Exam
Paper 1 | Objectives
51 - 60 of 87 Questions
| # | Question | Ans |
|---|---|---|
| 51. |
What mass of Cu would be produced by the cathodic reduction of Cu\(^{2+}\) when 1.60A of current passes through a solution of CuSO\(_4\) for 1 hour. (F=96500Cmol\(^{-1}\) , Cu=64) A. 7.64g B. 3.82g C. 1.91g D. 0.96g Detailed SolutionM = \(\frac{MmIT}{96500n}\)Where M=mass Mm = Molar mass = 64g/mol I = current = 1.6A T= Time =1h r=3600s N= No of Charge = +2 M = \(\frac{64x \times 1.6 \times 3600}{96500 \times 2}\) M=1.91g There is an explanation video available below. |
|
| 52. |
Calculate the pH of 0.05 moldm\(^{-3}\) H\(_2\)SO\(_4\) A. 1.30 B. 1.12 C. 1.00 D. 0.30 Detailed SolutionRecall from pH formula pH = -Log [H+]H2SO4 → 2H+ + SO42- 2H+ → 2 X0.05 = 0.1 pH= -Log [0.1] = 1 There is an explanation video available below. |
|
| 53. |
The choice of method for extracting a metal from its ores depends on the A. strength of the core B. position of the metal in the electrochemical series C. source of the core D. position of the metal in the periodic table Detailed SolutionThe method used to extract a metal from its ore depends upon the stability of its compound in the ore, which in turn depends upon the reactivity of the metal:• The oxides of very reactive metals, such as aluminum, form stable oxides and other compounds. A lot of energy is needed to reduce them to extract the metal. • The oxides of lesser reactive metals, such as iron, form less stable oxides and other compounds. Relatively little energy is needed to reduce them to extract the metal. So, the method of extraction of a metal from its ore depends on the metal's position in the reactivity series. There is an explanation video available |
|
| 54. |
Which of the following produces relatively few ions in solution? A. NaOH B. Ca(OH)\(_2\) C. KOH D. AI(OH)\(_3\) Detailed SolutionAluminium hydroxide is not soluble in water because it is polymeric and it also has high lattice energy and therefore it is hard to break bonds in this compound. So, water cannot dissolve such types of compounds.Al(OH)\(_3\) is not soluble in water There is an explanation video available below. |
|
| 55. |
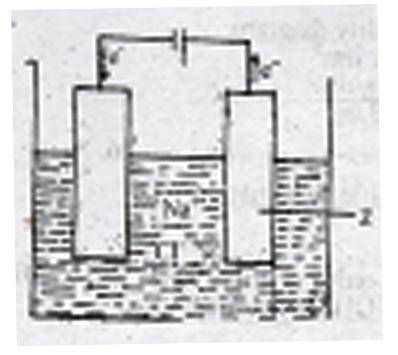 The figure above shows the electrolysis of molten sodium chloride. Z is the A. anode where the Cl\(^-\) ions are oxidized B. cathode where the Cl\(^-\) ions are reduced C. anode where the Na\(^+\) ions are reduced D. cathode where the Na\(^+\) ions are oxidized Detailed SolutionDuring the electrolysis of brine, the chlorine ions are discharged at the anode and are oxidized. While at the cathode Hydrogen ion is discharged.There is an explanation video available below. |
|
| 56. |
The knowledge of half-life can be used to A. Create an element B. Detect an element C. to combine elements D. Irradiate an element Detailed SolutionHalf-life, in radioactivity, the interval of time required for one-half of the atomic nuclei of a radioactive sample to decay (change spontaneously into other nuclear species by emitting particles and energy), or, equivalently, the time interval required for the number of disintegrations per second of a radioactive material to decrease by one-halfThere is an explanation video available below. |
|
| 57. |
An element X forms the following compounds with chlorine; XCl\(_4\), XCl\(_3\), XCl\(_2\). This illustrates the A. law of multiple proportions B. law of chemical proportions C. law of simple proportions D. law of conservation of mass Detailed SolutionThe law of multiple proportion states that when element A and B combine to form more than one chemical compound then the various masses of sample A react with a fixed mass of sample B are in a simple multiple ratio.There is an explanation video available below. |
|
| 58. |
The hydrogen ion concentration of a sample of orange juice is 2.0 X 10\(^{-11}\)moldm\(^{-3}\). What is its p\(^{OH}\)? [log102 = 0.3010] A. 3.30 B. 13.00 C. 10.70 D. 11.30 Detailed Solutionp\(^{OH}\) = -Log [OH\(^-\)][OH\(^-\) ] = 2.0 X 10\(^{-11}\)moldm\(^{-3}\) p\(^{OH}\) = -Log [2.0 X 10\(^{-11}\)] p\(^{OH}\) = 10.70 There is an explanation video available below. |
|
| 59. |
2SO\(_2\) \(_{(g) }\)+ O\(_2\) \(_{(g) }\) ↔ 2SO\(_3\)\(_{(g) }\) ΔH = -395.7kJmol\(^{-1}\) A. left and equilibrium constant decreases B. left and equilibrium constant increases C. right and equilibrium constant increases D. right and equilibrium constant decreases Detailed SolutionThis is typical of what happens with any equilibrium where the forward reaction is exothermic. Increasing the temperature decreases the value of the equilibrium constant. Where the forward reaction is endothermic, increasing the temperature increases the value of the equilibrium constant. Endothermic reaction has a Positive Enthalpy change. Exothermic reaction has a negative enthalpy change.There is an explanation video available below. |
|
| 60. |
The end products of burning a candle in the atmosphere are water and A. carbon (II) oxide B. sulphur (IV) oxide C. carbon (IV) oxide D. sulphur (VI) oxide Detailed SolutionWhen we ignite a candle, the hydrocarbon reacts with oxygen (in excess) to produce carbon dioxide and water. The burning sets an air current which gives dome shape to candle flame and it helps to get complete combustion at the bottom and the outer surface of the flame.CO\(_2\) is produced There is an explanation video available below. |
| 51. |
What mass of Cu would be produced by the cathodic reduction of Cu\(^{2+}\) when 1.60A of current passes through a solution of CuSO\(_4\) for 1 hour. (F=96500Cmol\(^{-1}\) , Cu=64) A. 7.64g B. 3.82g C. 1.91g D. 0.96g Detailed SolutionM = \(\frac{MmIT}{96500n}\)Where M=mass Mm = Molar mass = 64g/mol I = current = 1.6A T= Time =1h r=3600s N= No of Charge = +2 M = \(\frac{64x \times 1.6 \times 3600}{96500 \times 2}\) M=1.91g There is an explanation video available below. |
|
| 52. |
Calculate the pH of 0.05 moldm\(^{-3}\) H\(_2\)SO\(_4\) A. 1.30 B. 1.12 C. 1.00 D. 0.30 Detailed SolutionRecall from pH formula pH = -Log [H+]H2SO4 → 2H+ + SO42- 2H+ → 2 X0.05 = 0.1 pH= -Log [0.1] = 1 There is an explanation video available below. |
|
| 53. |
The choice of method for extracting a metal from its ores depends on the A. strength of the core B. position of the metal in the electrochemical series C. source of the core D. position of the metal in the periodic table Detailed SolutionThe method used to extract a metal from its ore depends upon the stability of its compound in the ore, which in turn depends upon the reactivity of the metal:• The oxides of very reactive metals, such as aluminum, form stable oxides and other compounds. A lot of energy is needed to reduce them to extract the metal. • The oxides of lesser reactive metals, such as iron, form less stable oxides and other compounds. Relatively little energy is needed to reduce them to extract the metal. So, the method of extraction of a metal from its ore depends on the metal's position in the reactivity series. There is an explanation video available |
|
| 54. |
Which of the following produces relatively few ions in solution? A. NaOH B. Ca(OH)\(_2\) C. KOH D. AI(OH)\(_3\) Detailed SolutionAluminium hydroxide is not soluble in water because it is polymeric and it also has high lattice energy and therefore it is hard to break bonds in this compound. So, water cannot dissolve such types of compounds.Al(OH)\(_3\) is not soluble in water There is an explanation video available below. |
|
| 55. |
 The figure above shows the electrolysis of molten sodium chloride. Z is the A. anode where the Cl\(^-\) ions are oxidized B. cathode where the Cl\(^-\) ions are reduced C. anode where the Na\(^+\) ions are reduced D. cathode where the Na\(^+\) ions are oxidized Detailed SolutionDuring the electrolysis of brine, the chlorine ions are discharged at the anode and are oxidized. While at the cathode Hydrogen ion is discharged.There is an explanation video available below. |
| 56. |
The knowledge of half-life can be used to A. Create an element B. Detect an element C. to combine elements D. Irradiate an element Detailed SolutionHalf-life, in radioactivity, the interval of time required for one-half of the atomic nuclei of a radioactive sample to decay (change spontaneously into other nuclear species by emitting particles and energy), or, equivalently, the time interval required for the number of disintegrations per second of a radioactive material to decrease by one-halfThere is an explanation video available below. |
|
| 57. |
An element X forms the following compounds with chlorine; XCl\(_4\), XCl\(_3\), XCl\(_2\). This illustrates the A. law of multiple proportions B. law of chemical proportions C. law of simple proportions D. law of conservation of mass Detailed SolutionThe law of multiple proportion states that when element A and B combine to form more than one chemical compound then the various masses of sample A react with a fixed mass of sample B are in a simple multiple ratio.There is an explanation video available below. |
|
| 58. |
The hydrogen ion concentration of a sample of orange juice is 2.0 X 10\(^{-11}\)moldm\(^{-3}\). What is its p\(^{OH}\)? [log102 = 0.3010] A. 3.30 B. 13.00 C. 10.70 D. 11.30 Detailed Solutionp\(^{OH}\) = -Log [OH\(^-\)][OH\(^-\) ] = 2.0 X 10\(^{-11}\)moldm\(^{-3}\) p\(^{OH}\) = -Log [2.0 X 10\(^{-11}\)] p\(^{OH}\) = 10.70 There is an explanation video available below. |
|
| 59. |
2SO\(_2\) \(_{(g) }\)+ O\(_2\) \(_{(g) }\) ↔ 2SO\(_3\)\(_{(g) }\) ΔH = -395.7kJmol\(^{-1}\) A. left and equilibrium constant decreases B. left and equilibrium constant increases C. right and equilibrium constant increases D. right and equilibrium constant decreases Detailed SolutionThis is typical of what happens with any equilibrium where the forward reaction is exothermic. Increasing the temperature decreases the value of the equilibrium constant. Where the forward reaction is endothermic, increasing the temperature increases the value of the equilibrium constant. Endothermic reaction has a Positive Enthalpy change. Exothermic reaction has a negative enthalpy change.There is an explanation video available below. |
|
| 60. |
The end products of burning a candle in the atmosphere are water and A. carbon (II) oxide B. sulphur (IV) oxide C. carbon (IV) oxide D. sulphur (VI) oxide Detailed SolutionWhen we ignite a candle, the hydrocarbon reacts with oxygen (in excess) to produce carbon dioxide and water. The burning sets an air current which gives dome shape to candle flame and it helps to get complete combustion at the bottom and the outer surface of the flame.CO\(_2\) is produced There is an explanation video available below. |