Year :
2005
Title :
Mathematics (Core)
Exam :
JAMB Exam
Paper 1 | Objectives
11 - 20 of 47 Questions
| # | Question | Ans |
|---|---|---|
| 11. |
A polynomial in x whose zeros are -2, -1 and 3 is A. x3 - 7x + 6 B. x3 + 7x - 6 C. x3 + 7x + 6 D. x3 - 7x - 6 Detailed Solutionx = -2, x = -1 and x = 3∴x+2 = 0, x+1 = 0 and x-3 = 0 Product of the factors (x+2)(x+1)(x-3) = 0 (x2 + 3x + 2)(x-3) x(x2 + 3x + 2) -3(x2 + 3x + 2) = 0 x3 + 3x2 + 2x - 3x2 - 9x - 6 = 0 x3 - 7x - 6 = 0 |
|
| 12. |
The time taken to do a piece of work is inversely proportional to the number of men employed. If it takes 30 men to do a piece of work in 6 days, how many men are required to do the work in 4 days? A. 20 B. 35 C. 45 D. 60 Detailed Solutiont = time taken and N = number of ment ∝ 1/N t = K/N K = Nt K = 30 * 6 K = 180 ∴t = 180/N 4 = 180/N 4N = 180 N = 180/4 45 men |
|
| 13. |
The weight W kg of a metal bar varies jointly as its length L meters and the square of its diameter d meters. If w = 140 when d = 42/3 and L = 54, find d in terms of W and L. A. \(\sqrt{\frac{42W}{5L}}\) B. \(\sqrt{\frac{6L}{42W}}\) C. \(\frac{42W}{5L}\) D. \(\frac{5L}{42W}\) Detailed Solution\(W\infty LD^2\\W=KLd^2\\K=\frac{W}{Ld^2}\\=\frac{140}{54}\times\left(4\frac{2}{3}\right)^2 \\=\frac{140}{54}\times\left(\frac{14}{3}\right)^2\\=\frac{140\times 9}{54\times 14\times 14}\\=\frac{5}{42}\\∴W=\frac{5}{42Ld^2}\\42W=5Ld^2\\\frac{42W}{5L}=d^2\\d=\sqrt{\frac{42W}{5L}}\) |
|
| 14. |
Find the range of values of x for which 7x - 3 > 25 + 3x A. x >7 B. x<7 C. x>-7 D. x<-7 Detailed Solution7x - 3 > 25 + 3x7x - 3x > 25 + 3 4x > 28 x > 28/4 x > 7 |
|
| 15. |
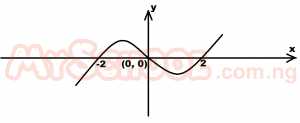 The diagram above is the graph of the function f(x). Determine the range of values of x for which f(x) \(\geq\) 0 A. x \(\leq\) 2 B. 0 \(\leq\) x \(\leq\) 2 C. -2 \(\leq\) x \(\leq\) 0, x \(\geq\) 2 D. x \(\leq\) -2, 0 \(\leq\) x \(\leq\) 2 |
C |
| 16. |
If the 7th term of an AP is twice the third term and the sum of the first four terms is 42, find the common difference. A. 6 B. 3 C. 2 D. 1 Detailed SolutionU7 = a + (7 - 1)d= a + 6d U3 = a + (3 - 1)d = a + 2d But U7 = 2(U3) ∴a + 6d = 2(a + 2d) a + 6d = 2a + 4d 2a - a + 4d - 6d = 0 a - 2d = 0 → eqn1 Sn = n/2 (2a + (n - 1)d) 42 = 4/2 (2a + (4 - 1)d) 42 = 2(2a + 3d) 21 = 2a + 3d → eqn2 eqn1 * eqn2 0 = 2a - 4d 21 = 7d ∴d = 21/7 d = 3 |
|
| 17. |
Find the sum of the first 20 terms of the series 8, 12, 16, ....., 96 A. 1400 B. 1040 C. 960 D. 920 Detailed Solution8, 12, 16, .....96a = 8, d = 4, l = 96, n = 20 \(S_{20} = \frac{n}{2}(2a + (n-1)d\) \(S_{20} = \frac{20}{2}((2\times 8) + (20-1)\times 4)\) \(S_{20} = 10(16 + (19\times 4)) = 10 \times 92\) =920 |
|
| 18. |
An operation * is defined on the set of real numbers by a * b = ab + 2(a + b + 1). find the identity element A. 2 B. 1 C. -1 D. -2 Detailed Solutiona * b = ab + 2(a + b + 1)let e be the identity element ∴ a * e = e * a = a ∴ a * e = a ae + 2(a + e + 1) = a ae + 2a + 2e + 2 = a ae + 2e = a - 2a = 2 (a + 2)e = -a - 2 e = -a-2 / (a+2) e = -(a+2) / (a+2) e = -1 |
|
| 19. |
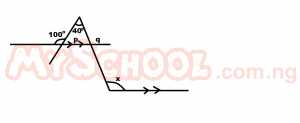 In the diagram above calculate the value of x A. 60o B. 100o C. 120o D. 140o Detailed Solutionp + 40o = 100o (exterior ∠ = sum of two interior opp ∠s)p = 100o - 40o P = 60o But q + p = 180o (∠s on a straight line) q + 60o q = 180o - 60o q = 120o x = q (corresponding ∠) ∴x = 120o |
|
| 20. |
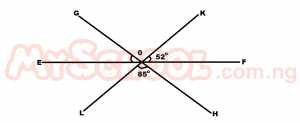 Three straight lines EF, GH and LK interest at O as shown above. If ∠KOF = 52o and ∠LOH = 85o, calculate the size of ∠EOG. A. 26o B. 43o C. 52o D. 85o Detailed Solution∠GOK = 85o (vertical opposite angle ∠s)∠EOG + ∠GOK + ∠KOF = 180 (∠s on a straight line) ∠EOg + 85o + 52o = 180o ∠EOG + 137o = 180o ∠EOG = 43o |
| 11. |
A polynomial in x whose zeros are -2, -1 and 3 is A. x3 - 7x + 6 B. x3 + 7x - 6 C. x3 + 7x + 6 D. x3 - 7x - 6 Detailed Solutionx = -2, x = -1 and x = 3∴x+2 = 0, x+1 = 0 and x-3 = 0 Product of the factors (x+2)(x+1)(x-3) = 0 (x2 + 3x + 2)(x-3) x(x2 + 3x + 2) -3(x2 + 3x + 2) = 0 x3 + 3x2 + 2x - 3x2 - 9x - 6 = 0 x3 - 7x - 6 = 0 |
|
| 12. |
The time taken to do a piece of work is inversely proportional to the number of men employed. If it takes 30 men to do a piece of work in 6 days, how many men are required to do the work in 4 days? A. 20 B. 35 C. 45 D. 60 Detailed Solutiont = time taken and N = number of ment ∝ 1/N t = K/N K = Nt K = 30 * 6 K = 180 ∴t = 180/N 4 = 180/N 4N = 180 N = 180/4 45 men |
|
| 13. |
The weight W kg of a metal bar varies jointly as its length L meters and the square of its diameter d meters. If w = 140 when d = 42/3 and L = 54, find d in terms of W and L. A. \(\sqrt{\frac{42W}{5L}}\) B. \(\sqrt{\frac{6L}{42W}}\) C. \(\frac{42W}{5L}\) D. \(\frac{5L}{42W}\) Detailed Solution\(W\infty LD^2\\W=KLd^2\\K=\frac{W}{Ld^2}\\=\frac{140}{54}\times\left(4\frac{2}{3}\right)^2 \\=\frac{140}{54}\times\left(\frac{14}{3}\right)^2\\=\frac{140\times 9}{54\times 14\times 14}\\=\frac{5}{42}\\∴W=\frac{5}{42Ld^2}\\42W=5Ld^2\\\frac{42W}{5L}=d^2\\d=\sqrt{\frac{42W}{5L}}\) |
|
| 14. |
Find the range of values of x for which 7x - 3 > 25 + 3x A. x >7 B. x<7 C. x>-7 D. x<-7 Detailed Solution7x - 3 > 25 + 3x7x - 3x > 25 + 3 4x > 28 x > 28/4 x > 7 |
|
| 15. |
 The diagram above is the graph of the function f(x). Determine the range of values of x for which f(x) \(\geq\) 0 A. x \(\leq\) 2 B. 0 \(\leq\) x \(\leq\) 2 C. -2 \(\leq\) x \(\leq\) 0, x \(\geq\) 2 D. x \(\leq\) -2, 0 \(\leq\) x \(\leq\) 2 |
C |
| 16. |
If the 7th term of an AP is twice the third term and the sum of the first four terms is 42, find the common difference. A. 6 B. 3 C. 2 D. 1 Detailed SolutionU7 = a + (7 - 1)d= a + 6d U3 = a + (3 - 1)d = a + 2d But U7 = 2(U3) ∴a + 6d = 2(a + 2d) a + 6d = 2a + 4d 2a - a + 4d - 6d = 0 a - 2d = 0 → eqn1 Sn = n/2 (2a + (n - 1)d) 42 = 4/2 (2a + (4 - 1)d) 42 = 2(2a + 3d) 21 = 2a + 3d → eqn2 eqn1 * eqn2 0 = 2a - 4d 21 = 7d ∴d = 21/7 d = 3 |
|
| 17. |
Find the sum of the first 20 terms of the series 8, 12, 16, ....., 96 A. 1400 B. 1040 C. 960 D. 920 Detailed Solution8, 12, 16, .....96a = 8, d = 4, l = 96, n = 20 \(S_{20} = \frac{n}{2}(2a + (n-1)d\) \(S_{20} = \frac{20}{2}((2\times 8) + (20-1)\times 4)\) \(S_{20} = 10(16 + (19\times 4)) = 10 \times 92\) =920 |
|
| 18. |
An operation * is defined on the set of real numbers by a * b = ab + 2(a + b + 1). find the identity element A. 2 B. 1 C. -1 D. -2 Detailed Solutiona * b = ab + 2(a + b + 1)let e be the identity element ∴ a * e = e * a = a ∴ a * e = a ae + 2(a + e + 1) = a ae + 2a + 2e + 2 = a ae + 2e = a - 2a = 2 (a + 2)e = -a - 2 e = -a-2 / (a+2) e = -(a+2) / (a+2) e = -1 |
|
| 19. |
 In the diagram above calculate the value of x A. 60o B. 100o C. 120o D. 140o Detailed Solutionp + 40o = 100o (exterior ∠ = sum of two interior opp ∠s)p = 100o - 40o P = 60o But q + p = 180o (∠s on a straight line) q + 60o q = 180o - 60o q = 120o x = q (corresponding ∠) ∴x = 120o |
|
| 20. |
 Three straight lines EF, GH and LK interest at O as shown above. If ∠KOF = 52o and ∠LOH = 85o, calculate the size of ∠EOG. A. 26o B. 43o C. 52o D. 85o Detailed Solution∠GOK = 85o (vertical opposite angle ∠s)∠EOG + ∠GOK + ∠KOF = 180 (∠s on a straight line) ∠EOg + 85o + 52o = 180o ∠EOG + 137o = 180o ∠EOG = 43o |