Year :
2018
Title :
Mathematics (Core)
Exam :
WASSCE/WAEC MAY/JUNE
Paper 1 | Objectives
21 - 30 of 50 Questions
| # | Question | Ans |
|---|---|---|
| 21. |
The total surface area of a hemispher is 75\(\pi cm^2\). Find the radius. A. 5.0 cm B. 7.0 cm C. 8.5 cm D. 12.0 cm Detailed SolutionTotal surface area of hemisphere is3\(\pi r^2\) = 75\(\pi cm^2\) \(r^2\) = \(\frac{75 \pi}{3 \pi}\) \(r^2\) = 25 r = \(\sqrt{25}\) r = 5cm |
|
| 22. |
Find the value of x for which \(\frac{x - 5}{x(x - 1)}\) is defined A. 0 or 5 B. -5 or 5 C. -11 or 5 D. 0 or 1 Detailed SolutionThe expression \(\frac{x - 5}{x(x - 1)}\) is defined whtenx(x - 5) = 0.38 either x = 0 or x - 5 = 0 Hence, x = 0 or x = 5 |
|
| 23. |
Solved the equation \(2x^2 - x - 6\) = 0 A. x = \(\frac{-3}{2}\) or 2 B. x = -2 or \(\frac{3}{2}\) C. x = -3 or 2 D. x = 3 or -2 Detailed Solution\(2x^2 - x - 6\) = 0 \(2x^2 - 4x + 3x - 6\) = 0 2x(x - 2) + 3(x - 2) = 0 (2x + 3) (x - 2) = 0 Either; 2x + 3 = 0 or x - 2 = 0 x = \(\frac{-3}{2}\) or x = 2 |
|
| 24. |
Factorise completely the expression\((x + 2)^2\) - \((2x + 1)^2\) A. (3x + 2)(1 - x) B. (3x + 2)(2x + 1) C. 3\((x + 2)^2\) D. 3(x + 1)(1 - x) Detailed Solution\((x + 2)^2\) - \((2x + 1)^2\)= \((x^2 + 4x + 4) - (4x^2 + 4x + 1)\) = \(x^2 \) + 4x + 4 - 4 \(x^2 \) - 4x - 1 = -3 \(x^2 \) + 3 = 3 - 3 \(x^2 \) = 3(1 - \(x^2 \)) = 3(1 + x)(1 - x) |
|
| 25. |
Find the \(n^{th}\) term of the sequence 2 x 3, 4 x 6, 8 x 9, 16 x 12... A. 2\(^n\) x 3(n + 1) B. 2\(^n\) x 3n C. 2\(^n\) x 3\(^n\) D. 2\(^n\) x 3\(^n - 1\) Detailed Solution2 x 3, 4 x 6, 8 x 9, 16 x 12,...2\(^1\) x 3 x 1, 2\(^2\) x 3 x 2, 2\(^3\) x 3 x 3, 2\(^4\) x 3 x 4,.... 2\(^n\) x 3n |
|
| 26. |
If 3x\(^o\) 4(mod 5), find the least value of x A. 1 B. 2 C. 3 D. 4 Detailed Solution3x \(\equiv\) 4(mod 5)In modulo 5, multiples of 5 that give solution to the given equation are 5, 20, 35, 50,... but 5 will yield the leaast value of x. Thus; 3x = 4 + 5 = 9 x = \(\frac{9}{3}\) x = 3 |
|
| 27. |
Find the inter-quartile range of 1, 3, 4, 5, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 14, 16 A. 6 B. 7 C. 8 D. 9 Detailed Solution\(Q_1 = \frac{1}{4}\) (N + 1)th\(\frac{1}{4} \times 12^{th}\) no. = 3rd no (\(\cong\) 4) \(Q_3 = \frac{3}{4}\) (N + 1)th = \(\frac{3}{4}\) x 12th no. = 9th no. (\(\cong\) 12) Hence, interquartile range = \(Q_3 - Q_1\) = 12 - 4 = 8 |
|
| 28. |
If x : y = \(\frac{1}{4} : \frac{3}{8}\) and y : z = \(\frac{1}{3} : \frac{4}{9}\), find x : z A. 2:3 B. 3:4 C. 3:8 D. 1:2 Detailed Solution\(\frac{x}{y}\) = \(\frac{1}{4} \div \frac{3}{8}\) = \(\frac{1}{4} \times \frac{8}{3}\) = \(\frac{2}{3}\)\(\frac{y}{z}\) = \(\frac{1}{3} \div \frac{4}{9}\) = \(\frac{1}{3} \times \frac{9}{4}\) = \(\frac{3}{4}\) But, x = \(\frac{2}{5}T_1\), y = \(\frac{3}{5}T_1\) y = \(\frac{3}{7}T_2\), z = \(\frac{4}{7}T_2\) Using y = y \(\frac{3}{5}T_1\) = x = \(\frac{3}{7}T_2\) \(\frac{T_1}{T_2}\) = \(\frac{3}{7}\) x \(\frac{5}{3}\) = \(\frac{15}{21}\) \(T_1 = 15\) and \(T_2 = 21\) Thus , x = \(\frac{2}{5}\) x 15 = 6 y = \(\frac{3}{5}\) x 15 = 9 y = \(\frac{3}{7}\) x 21 = 9 z = \(\frac{4}{7}\) x 21 = 12 Hence; x : z = 6 : 12 = 1 |
|
| 29. |
Expression 0.612 in the form \(\frac{x}{y}\), where x and y are integers and y \(\neq\) 0 A. \(\frac{153}{250}\) B. \(\frac{68}{111}\) C. \(\frac{61}{100}\) D. \(\frac{21}{33}\) Detailed Solution0.612 = \(\frac{0.612}{1}\) x \(\frac{1000}{1000}\)= \(\frac{612}{1000}\) = \(\frac{153}{250}\) |
|
| 30. |
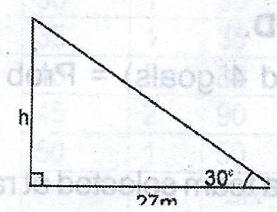
The angle of elevation of the top of a tree from a point 27m away and on the same horizontal ground as the foot of the tree is 30\(^o\). Find the height of the tree. A. 27m B. 13.5 \(\sqrt{3m}\) C. 13.5 \(\sqrt{2m}\) D. 9\(\sqrt{3m}\) Detailed Solution
tan 30\(^o\) = \(\frac{h}{27}\) h = 27 tan 30\(^o\) = 27 x \(\frac{1}{\sqrt{3}}\) = \(\frac{27}{\sqrt{3}}\) x \(\frac{\sqrt{3}}{\sqrt{3}}\) = \(\frac{27 \sqrt{3}}{3}\) = 9\(\sqrt{3m}\) |
| 21. |
The total surface area of a hemispher is 75\(\pi cm^2\). Find the radius. A. 5.0 cm B. 7.0 cm C. 8.5 cm D. 12.0 cm Detailed SolutionTotal surface area of hemisphere is3\(\pi r^2\) = 75\(\pi cm^2\) \(r^2\) = \(\frac{75 \pi}{3 \pi}\) \(r^2\) = 25 r = \(\sqrt{25}\) r = 5cm |
|
| 22. |
Find the value of x for which \(\frac{x - 5}{x(x - 1)}\) is defined A. 0 or 5 B. -5 or 5 C. -11 or 5 D. 0 or 1 Detailed SolutionThe expression \(\frac{x - 5}{x(x - 1)}\) is defined whtenx(x - 5) = 0.38 either x = 0 or x - 5 = 0 Hence, x = 0 or x = 5 |
|
| 23. |
Solved the equation \(2x^2 - x - 6\) = 0 A. x = \(\frac{-3}{2}\) or 2 B. x = -2 or \(\frac{3}{2}\) C. x = -3 or 2 D. x = 3 or -2 Detailed Solution\(2x^2 - x - 6\) = 0 \(2x^2 - 4x + 3x - 6\) = 0 2x(x - 2) + 3(x - 2) = 0 (2x + 3) (x - 2) = 0 Either; 2x + 3 = 0 or x - 2 = 0 x = \(\frac{-3}{2}\) or x = 2 |
|
| 24. |
Factorise completely the expression\((x + 2)^2\) - \((2x + 1)^2\) A. (3x + 2)(1 - x) B. (3x + 2)(2x + 1) C. 3\((x + 2)^2\) D. 3(x + 1)(1 - x) Detailed Solution\((x + 2)^2\) - \((2x + 1)^2\)= \((x^2 + 4x + 4) - (4x^2 + 4x + 1)\) = \(x^2 \) + 4x + 4 - 4 \(x^2 \) - 4x - 1 = -3 \(x^2 \) + 3 = 3 - 3 \(x^2 \) = 3(1 - \(x^2 \)) = 3(1 + x)(1 - x) |
|
| 25. |
Find the \(n^{th}\) term of the sequence 2 x 3, 4 x 6, 8 x 9, 16 x 12... A. 2\(^n\) x 3(n + 1) B. 2\(^n\) x 3n C. 2\(^n\) x 3\(^n\) D. 2\(^n\) x 3\(^n - 1\) Detailed Solution2 x 3, 4 x 6, 8 x 9, 16 x 12,...2\(^1\) x 3 x 1, 2\(^2\) x 3 x 2, 2\(^3\) x 3 x 3, 2\(^4\) x 3 x 4,.... 2\(^n\) x 3n |
| 26. |
If 3x\(^o\) 4(mod 5), find the least value of x A. 1 B. 2 C. 3 D. 4 Detailed Solution3x \(\equiv\) 4(mod 5)In modulo 5, multiples of 5 that give solution to the given equation are 5, 20, 35, 50,... but 5 will yield the leaast value of x. Thus; 3x = 4 + 5 = 9 x = \(\frac{9}{3}\) x = 3 |
|
| 27. |
Find the inter-quartile range of 1, 3, 4, 5, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 14, 16 A. 6 B. 7 C. 8 D. 9 Detailed Solution\(Q_1 = \frac{1}{4}\) (N + 1)th\(\frac{1}{4} \times 12^{th}\) no. = 3rd no (\(\cong\) 4) \(Q_3 = \frac{3}{4}\) (N + 1)th = \(\frac{3}{4}\) x 12th no. = 9th no. (\(\cong\) 12) Hence, interquartile range = \(Q_3 - Q_1\) = 12 - 4 = 8 |
|
| 28. |
If x : y = \(\frac{1}{4} : \frac{3}{8}\) and y : z = \(\frac{1}{3} : \frac{4}{9}\), find x : z A. 2:3 B. 3:4 C. 3:8 D. 1:2 Detailed Solution\(\frac{x}{y}\) = \(\frac{1}{4} \div \frac{3}{8}\) = \(\frac{1}{4} \times \frac{8}{3}\) = \(\frac{2}{3}\)\(\frac{y}{z}\) = \(\frac{1}{3} \div \frac{4}{9}\) = \(\frac{1}{3} \times \frac{9}{4}\) = \(\frac{3}{4}\) But, x = \(\frac{2}{5}T_1\), y = \(\frac{3}{5}T_1\) y = \(\frac{3}{7}T_2\), z = \(\frac{4}{7}T_2\) Using y = y \(\frac{3}{5}T_1\) = x = \(\frac{3}{7}T_2\) \(\frac{T_1}{T_2}\) = \(\frac{3}{7}\) x \(\frac{5}{3}\) = \(\frac{15}{21}\) \(T_1 = 15\) and \(T_2 = 21\) Thus , x = \(\frac{2}{5}\) x 15 = 6 y = \(\frac{3}{5}\) x 15 = 9 y = \(\frac{3}{7}\) x 21 = 9 z = \(\frac{4}{7}\) x 21 = 12 Hence; x : z = 6 : 12 = 1 |
|
| 29. |
Expression 0.612 in the form \(\frac{x}{y}\), where x and y are integers and y \(\neq\) 0 A. \(\frac{153}{250}\) B. \(\frac{68}{111}\) C. \(\frac{61}{100}\) D. \(\frac{21}{33}\) Detailed Solution0.612 = \(\frac{0.612}{1}\) x \(\frac{1000}{1000}\)= \(\frac{612}{1000}\) = \(\frac{153}{250}\) |
|
| 30. |
The angle of elevation of the top of a tree from a point 27m away and on the same horizontal ground as the foot of the tree is 30\(^o\). Find the height of the tree. A. 27m B. 13.5 \(\sqrt{3m}\) C. 13.5 \(\sqrt{2m}\) D. 9\(\sqrt{3m}\) Detailed Solution
tan 30\(^o\) = \(\frac{h}{27}\) h = 27 tan 30\(^o\) = 27 x \(\frac{1}{\sqrt{3}}\) = \(\frac{27}{\sqrt{3}}\) x \(\frac{\sqrt{3}}{\sqrt{3}}\) = \(\frac{27 \sqrt{3}}{3}\) = 9\(\sqrt{3m}\) |