Year :
1992
Title :
Mathematics (Core)
Exam :
JAMB Exam
Paper 1 | Objectives
21 - 30 of 49 Questions
| # | Question | Ans |
|---|---|---|
| 21. |
P = \(\begin{vmatrix} x & 3 & 0 \\ 2 & y & 3\\ 4 & 2 & 4 \end{vmatrix}\) A. 48 B. 24 C. -24 D. -48 Detailed Solutionp = \(\begin{vmatrix} 0 & 3 & 0 \\ 2 & 1 & 3\\ 4 & 2 & 2 \end{vmatrix}\)PT = \(\begin{vmatrix}0 & 2 & 4 \\ 2 & 1 & 3\\ 0 & 3 & 2 \end{vmatrix}\) /pT/ = \(\begin{vmatrix}0 & 2 & 4 \\ 3 & 1 & 3\\ 0 & 3 & 2 \end{vmatrix}\) = 0[2 - 6] - 2[6 - 0] + 4[9 - 0] = 0 - 12 + 36 = 24 |
|
| 22. |
P = \(\begin{vmatrix} x & 3 & 0 \\ 2 & y & 3\\ 4 & 2 & 4 \end{vmatrix}\) A. PPT B. pp-1 C. qp D. pp Detailed Solutionp = \(\begin{vmatrix} 0 & 3 & 0 \\ 2 & 1 & 3\\ 4 & 2 & 2 \end{vmatrix}\)Q = \(\begin{vmatrix} 0 & 2 & 4 \\ 3 & 1 & 2\\ 0 & 3 & 2 \end{vmatrix}\) = pT pq = ppT |
|
| 23. |
If the angles of quadrilateral are (p + 10)°, (2p - 30)°, (3p + 20)° and 4p°, find p. A. 63 B. 40 C. 36 D. 28 Detailed SolutionThe sum of angles in a quadrilateral = 360°\(\therefore (p + 10) + (2p - 30) + (3p + 20) + 4p = 360\) \(10p = 360° \implies p = \frac{360}{10} = 36°\) |
|
| 24. |
Determine the distance on the earth's surface between two town P (lat 60°N, Long 20°E) and Q(Lat 60°N, Long 25°W) (Radius of the earth = 6400km) A. \(\frac{800\pi}{9}\)km B. \(\frac{800\sqrt{3\pi}}{9}\)km C. 800\(\pi\) km D. 800\(\sqrt{3\pi}\) km Detailed SolutionAngular difference (\(\theta\))= 25° + 20° = 45°\(\alpha\) = common latitude = 60° \(S = \frac{\theta}{360°} \times 2\pi R \cos \alpha\) \(S = \frac{45°}{360°} \times 2 \pi \times 6400 \times \cos 60°\) = \(\frac{6400\pi}{8} = 800\pi km\) |
|
| 25. |
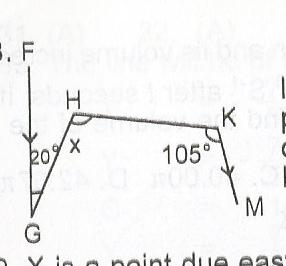 If in the diagram, FG is parallel to KM, find the value of x A. 75o B. 95o C. 105o D. 125o |
B |
| 26. |
X is a point due east of point Y on a coast: Z is another point on the coast but 6√3km due south of y.If the distance XZ is 12Km. Calculate the bearing of Z from X A. 240o B. 210o C. 150o D. 60o Detailed SolutionUsing sinØ = \(\frac{6√3}{12}\) → \(\frac{√3}{2}\)sinØ = \(\frac{√3}{2}\) or 60° The bearing of Z from X = [270 - 60]° → 210° |
|
| 27. |
The locus of a point which is equidistant from two given fixed points is the A. perpendicular bisector of the straight line joining them B. parallel line to the straight line joining them C. transverse to the straight line joining them D. angle bisector of 90o which the straight line joining them makes with the horizontal |
A |
| 28. |
What is the perpendicular distance of a point (2, 3) from the line 2x - 4y + 3 = 0? A. \(\frac{\sqrt{5}}{2}\) B. \(\frac{\sqrt{5}}{20}\) C. \(\frac{5}{\sqrt{13}}\) D. 6 Detailed Solution2x - 4y + 3 = 0Required distance = \(\frac{(2 \times 2) + 3(-4) + 3}{\sqrt{2^2} + (-4)^2}\) = \(\frac{4 - 12 + 3}{\sqrt{20}}\) = \(\frac{-5}{-2\sqrt{5}}\) = \(\frac{\sqrt{5}}{2}\) |
|
| 29. |
Find then equation line through (5, 7) parallel to the line 7x + 5y = 12 A. 5x + 7y = 120 B. 7x + 5y = 70 C. x + y = 7 D. 15x + 17y = 90 Detailed SolutionEquation (5, 7) parallel to the line 7x + 5y = 125Y = -7x + 12 y = \(\frac{-7x}{5}\) + \(\frac{12}{5}\) Gradient = \(\frac{-7}{5}\) ∴ Required equation = \(\frac{y - 7}{x - 5}\) = \(\frac{-7}{5}\) i.e. 5y - 35 = -7x + 35 5y + 7x = 70 |
|
| 30. |
Given that \(\theta\) is an acute angle and sin \(\theta\) = \(\frac{m}{n}\), find cos \(\theta\) A. \(\frac{\sqrt{n^2 - m^2}}{m}\) B. \(\frac{\sqrt{(n + m)(n - m)}}{n}\) C. \(\frac{m}{\sqrt{n^2 - m^2}}\) D. \(\sqrt{\frac{n}{n^2 - m^2}}\) Detailed Solutionsin \(\theta\) = \(\frac{m}{n}\)Opp = m; Hyp = n Adj = \(\sqrt{n^{2} - m^{2}}\) \(\cos \theta = \frac{\sqrt{n^{2} - m^{2}}}{n}\) = \(\frac{\sqrt{(n + m)(n - m)}}{n}\) |
| 21. |
P = \(\begin{vmatrix} x & 3 & 0 \\ 2 & y & 3\\ 4 & 2 & 4 \end{vmatrix}\) A. 48 B. 24 C. -24 D. -48 Detailed Solutionp = \(\begin{vmatrix} 0 & 3 & 0 \\ 2 & 1 & 3\\ 4 & 2 & 2 \end{vmatrix}\)PT = \(\begin{vmatrix}0 & 2 & 4 \\ 2 & 1 & 3\\ 0 & 3 & 2 \end{vmatrix}\) /pT/ = \(\begin{vmatrix}0 & 2 & 4 \\ 3 & 1 & 3\\ 0 & 3 & 2 \end{vmatrix}\) = 0[2 - 6] - 2[6 - 0] + 4[9 - 0] = 0 - 12 + 36 = 24 |
|
| 22. |
P = \(\begin{vmatrix} x & 3 & 0 \\ 2 & y & 3\\ 4 & 2 & 4 \end{vmatrix}\) A. PPT B. pp-1 C. qp D. pp Detailed Solutionp = \(\begin{vmatrix} 0 & 3 & 0 \\ 2 & 1 & 3\\ 4 & 2 & 2 \end{vmatrix}\)Q = \(\begin{vmatrix} 0 & 2 & 4 \\ 3 & 1 & 2\\ 0 & 3 & 2 \end{vmatrix}\) = pT pq = ppT |
|
| 23. |
If the angles of quadrilateral are (p + 10)°, (2p - 30)°, (3p + 20)° and 4p°, find p. A. 63 B. 40 C. 36 D. 28 Detailed SolutionThe sum of angles in a quadrilateral = 360°\(\therefore (p + 10) + (2p - 30) + (3p + 20) + 4p = 360\) \(10p = 360° \implies p = \frac{360}{10} = 36°\) |
|
| 24. |
Determine the distance on the earth's surface between two town P (lat 60°N, Long 20°E) and Q(Lat 60°N, Long 25°W) (Radius of the earth = 6400km) A. \(\frac{800\pi}{9}\)km B. \(\frac{800\sqrt{3\pi}}{9}\)km C. 800\(\pi\) km D. 800\(\sqrt{3\pi}\) km Detailed SolutionAngular difference (\(\theta\))= 25° + 20° = 45°\(\alpha\) = common latitude = 60° \(S = \frac{\theta}{360°} \times 2\pi R \cos \alpha\) \(S = \frac{45°}{360°} \times 2 \pi \times 6400 \times \cos 60°\) = \(\frac{6400\pi}{8} = 800\pi km\) |
|
| 25. |
 If in the diagram, FG is parallel to KM, find the value of x A. 75o B. 95o C. 105o D. 125o |
B |
| 26. |
X is a point due east of point Y on a coast: Z is another point on the coast but 6√3km due south of y.If the distance XZ is 12Km. Calculate the bearing of Z from X A. 240o B. 210o C. 150o D. 60o Detailed SolutionUsing sinØ = \(\frac{6√3}{12}\) → \(\frac{√3}{2}\)sinØ = \(\frac{√3}{2}\) or 60° The bearing of Z from X = [270 - 60]° → 210° |
|
| 27. |
The locus of a point which is equidistant from two given fixed points is the A. perpendicular bisector of the straight line joining them B. parallel line to the straight line joining them C. transverse to the straight line joining them D. angle bisector of 90o which the straight line joining them makes with the horizontal |
A |
| 28. |
What is the perpendicular distance of a point (2, 3) from the line 2x - 4y + 3 = 0? A. \(\frac{\sqrt{5}}{2}\) B. \(\frac{\sqrt{5}}{20}\) C. \(\frac{5}{\sqrt{13}}\) D. 6 Detailed Solution2x - 4y + 3 = 0Required distance = \(\frac{(2 \times 2) + 3(-4) + 3}{\sqrt{2^2} + (-4)^2}\) = \(\frac{4 - 12 + 3}{\sqrt{20}}\) = \(\frac{-5}{-2\sqrt{5}}\) = \(\frac{\sqrt{5}}{2}\) |
|
| 29. |
Find then equation line through (5, 7) parallel to the line 7x + 5y = 12 A. 5x + 7y = 120 B. 7x + 5y = 70 C. x + y = 7 D. 15x + 17y = 90 Detailed SolutionEquation (5, 7) parallel to the line 7x + 5y = 125Y = -7x + 12 y = \(\frac{-7x}{5}\) + \(\frac{12}{5}\) Gradient = \(\frac{-7}{5}\) ∴ Required equation = \(\frac{y - 7}{x - 5}\) = \(\frac{-7}{5}\) i.e. 5y - 35 = -7x + 35 5y + 7x = 70 |
|
| 30. |
Given that \(\theta\) is an acute angle and sin \(\theta\) = \(\frac{m}{n}\), find cos \(\theta\) A. \(\frac{\sqrt{n^2 - m^2}}{m}\) B. \(\frac{\sqrt{(n + m)(n - m)}}{n}\) C. \(\frac{m}{\sqrt{n^2 - m^2}}\) D. \(\sqrt{\frac{n}{n^2 - m^2}}\) Detailed Solutionsin \(\theta\) = \(\frac{m}{n}\)Opp = m; Hyp = n Adj = \(\sqrt{n^{2} - m^{2}}\) \(\cos \theta = \frac{\sqrt{n^{2} - m^{2}}}{n}\) = \(\frac{\sqrt{(n + m)(n - m)}}{n}\) |