
Biology
Paper 1 | Objectives | 59 Questions
WASSCE/WAEC MAY/JUNE
Year: 2011
Level: SHS
Time:
Type: Question Paper
Answers provided
FREE
No description provided
Feedbacks
This paper is yet to be rated

Paper 1 | Objectives | 59 Questions
WASSCE/WAEC MAY/JUNE
Year: 2011
Level: SHS
Time:
Type: Question Paper
Answers provided
No description provided
This paper is yet to be rated
Get full scholarship paid tuition from 5 countries with free education in 2022 for international students
Eat well during in test days for good grades. How can you plan your exam diet with good grades in mind?
Try studying past questions since it's a sure way to better grades in any subject at school and beyond.
| # | Question | Ans |
|---|---|---|
| 1. |
The branch of Biology that deals with the principles of classification of organisms is known as A. biological index B. nomenclature C. taxonomy D. ecology |
C |
| 2. |
Which of the following structures is a tissue A. Vessel element B. Blood C. Sieve tube element D. Erythrocyte |
B |
| 3. |
Which of the following cells are not regarded as specialized? A. Sperm cells B. Root up cells C. Muscle cells D. somatic cells |
D |
| 4. |
Which of the following pairs of cells carry out the same function? A. Check cell and red blood cell B. Spermatozoan and ovum C. Palisade cell and epidermal cell D. Root tip cell and guard cell |
B |
| 5. |
If Amoeba is placed in a salt solution. the contractile vacuoles would A. be bursting more frequently B. be more numerous C. be formed less frequently D. grow bigger before they burst |
C |
| 6. |
In which of the following habitats is Paramecium no found A. Pond B. Aquarium C. Lake D. Puddle |
B |
| 7. |
The following processes are involved in water movement in the endodermis except A. osmosis B. vacuolar pathway C. diffusion D. active transport |
C |
| 8. |
Cells that utilise a lot of energy are characterized by the presence of a large number of A. vacuoles B. mitochondria C. endoplasmic reticulum D. ribosomes |
B |
| 9. |
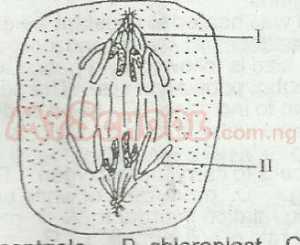 The part labelled II in the diagram is A. centriole B. chloroplast C. chromatid D. tonoplast |
C |
| 10. |
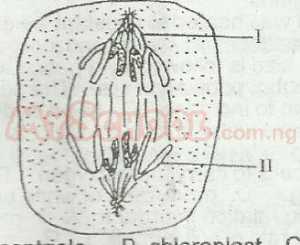 The part labelled I is called the A. nucleolus B. centromere C. centriole D. spindle |
D |
| 11. |
Secondary growth is brought about by the activities of the A. phellogen and phelloderm B. phellogen and procambium. C. vascular cambium and phelloderm D. vascular cambium and phellogen |
D |
| 12. |
A monocot root IS different from a dicot root by having A. endodermis B. cambium C. wide pith D. root hair. |
C |
Preview displays only 12 out of the 59 Questions