Year :
2001
Title :
Mathematics (Core)
Exam :
WASSCE/WAEC MAY/JUNE
Paper 1 | Objectives
21 - 30 of 49 Questions
| # | Question | Ans |
|---|---|---|
| 21. |
The graph of the curve \(y = 2x^2 - 5x - 1\) and a straight line PQ were drawn to solve the equation \(2x^2 - 5x + 2 = 0\) A. y = -1 B. y = 1 C. y = 3 D. y = -3 Detailed SolutionLet the straight line PQ = y2x\(^2\) - 5x - 1 - y = 2x\(^2\) - 5x + 2 y = 2x\(^2\) - 5x - 1 - 2x\(^2\) + 5x - 2 y = -3 |
|
| 22. |
Subtract (-y + 3x + 5z) from (4y - x - 2z) A. 5y - 4x - 7z B. 3y + 2x + 3z C. -5y + 4x + 7z D. 2x - 5y + 3z Detailed Solution(4y - x - 2z) - (-y + 3x + 5z)= 4y + y - x - 3x - 2z - 5z = 5y - 4x - 7z |
|
| 23. |
If \(y \propto \frac{1}{\sqrt{x}}\) and x = 16 when y = 2, find x when y = 24 A. \(\frac{1}{9}\) B. \(\frac{1}{6}\) C. \(\frac{1}{3}\) D. \(\frac{2}{3}\) Detailed Solution\(y \propto \frac{1}{\sqrt{x}}\)\(y = \frac{k}{\sqrt{x}}\) When x = 16, y = 2. \(2 = \frac{k}{\sqrt{16}} \implies 2 = \frac{k}{4}\) \(k = 8\) \(y = \frac{8}{\sqrt{x}}\) When y = 24, \(24 = \frac{8}{\sqrt{x}}\) \(\sqrt{x} = \frac{8}{24} = \frac{1}{3}\) \(\therefore x = (\frac{1}{3})^2\) \(x = \frac{1}{9}\) |
|
| 24. |
If 2x : (x +1) = 3:2, what is the value of x? A. \(\frac{1}{2}\) B. 1 C. \(1\frac{1}{2}\) D. 3 Detailed Solution\(2x : (x + 1) = 3:2\\\frac{2x}{x+1}=\frac{3}{2}\\ ∴ 4x = 3x + 3 x =3\) |
|
| 25. |
The bearing S40°E is the same as A. 040o B. 050o C. 130o D. 140o Detailed Solution = 90° + 50° = 140° |
|
| 26. |
Given that sin \(P = \frac{5}{13}\), where p is acute, find the value of cos p - tan p A. \(\frac{79}{156}\) B. \(\frac{85}{156}\) C. \(\frac{7}{13}\) D. \(\frac{8}{1}\) Detailed Solution
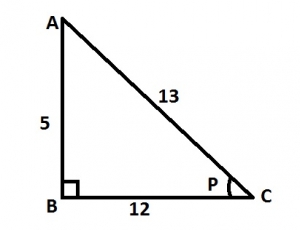 \(BC^2 = 13^2 - 5^2\\ =169-25\\ BC = \sqrt{144} = 12\\ ∴ cos P - tan P = \frac{12}{13} - \frac{5}{12}\\ =\frac{79}{156}\) |
|
| 27. |
Three observation posts P,Q and R are such that Q is due east of P and R is due north of Q. If |PQ| = 5km and |PR| = 10km, find |QR| A. 5.0km B. 7.5km C. 7.6km D. 8.7km Detailed Solution\((PR)^2 = (PQ)^2 + (QR)^2\)\(10^2 = 5^2 + (QR)^2\) \((QR)^2 = 100 - 25\) \(QR = \sqrt{75}\) = \(8.660\) \(\approxeq\) 8.7 km |
|
| 28. |
Express 25° 45' in decimal (Hint: 1° = 60') A. 25.75o B. 25.55o C. 25.45o D. 25.15o Detailed Solution25° 45' = 25° + \(\frac{45}{60}\)°= 25° + 0.75° = 25.75° |
|
| 29. |
A box contains 5 red, 3 green and 4 blue balls. A boy is allowed to take away two balls from the box. What is the probability that the two balls are red? A. \(\frac{5}{33}\) B. \(\frac{5}{36}\) C. \(\frac{103}{132}\) D. \(\frac{31}{36}\) Detailed SolutionTotal number of balls = 5 + 3 + 4= 12 balls P(first ball is red) = \(\frac{5}{12}\) P(second ball is red) = \(\frac{4}{11}\) \(\therefore\) P(both balls are red) = \(\frac{5}{12} \times \frac{4}{11}\) = \(\frac{5}{33}\) |
|
| 30. |
A box contains 5 red, 3 green and 4 blue balls. A boy is allowed to take away two balls from the box. What is the probability that one is green and the other is blue? A. \(\frac{2}{11}\) B. \(\frac{5}{12}\) C. \(\frac{8}{12}\) D. \(\frac{7}{11}\) Detailed SolutionTotal number of balls = 5 + 3 + 4 = 12 ballsP(one ball is green and the other is blue) = P(first ball is green and second blue) + P(first ball is blue and the second green) = \(\frac{3}{12} \times \frac{4}{11} + \frac{4}{12} \times \frac{3}{11}\) = \(\frac{2}{11}\) |
| 21. |
The graph of the curve \(y = 2x^2 - 5x - 1\) and a straight line PQ were drawn to solve the equation \(2x^2 - 5x + 2 = 0\) A. y = -1 B. y = 1 C. y = 3 D. y = -3 Detailed SolutionLet the straight line PQ = y2x\(^2\) - 5x - 1 - y = 2x\(^2\) - 5x + 2 y = 2x\(^2\) - 5x - 1 - 2x\(^2\) + 5x - 2 y = -3 |
|
| 22. |
Subtract (-y + 3x + 5z) from (4y - x - 2z) A. 5y - 4x - 7z B. 3y + 2x + 3z C. -5y + 4x + 7z D. 2x - 5y + 3z Detailed Solution(4y - x - 2z) - (-y + 3x + 5z)= 4y + y - x - 3x - 2z - 5z = 5y - 4x - 7z |
|
| 23. |
If \(y \propto \frac{1}{\sqrt{x}}\) and x = 16 when y = 2, find x when y = 24 A. \(\frac{1}{9}\) B. \(\frac{1}{6}\) C. \(\frac{1}{3}\) D. \(\frac{2}{3}\) Detailed Solution\(y \propto \frac{1}{\sqrt{x}}\)\(y = \frac{k}{\sqrt{x}}\) When x = 16, y = 2. \(2 = \frac{k}{\sqrt{16}} \implies 2 = \frac{k}{4}\) \(k = 8\) \(y = \frac{8}{\sqrt{x}}\) When y = 24, \(24 = \frac{8}{\sqrt{x}}\) \(\sqrt{x} = \frac{8}{24} = \frac{1}{3}\) \(\therefore x = (\frac{1}{3})^2\) \(x = \frac{1}{9}\) |
|
| 24. |
If 2x : (x +1) = 3:2, what is the value of x? A. \(\frac{1}{2}\) B. 1 C. \(1\frac{1}{2}\) D. 3 Detailed Solution\(2x : (x + 1) = 3:2\\\frac{2x}{x+1}=\frac{3}{2}\\ ∴ 4x = 3x + 3 x =3\) |
|
| 25. |
The bearing S40°E is the same as A. 040o B. 050o C. 130o D. 140o Detailed Solution = 90° + 50° = 140° |
| 26. |
Given that sin \(P = \frac{5}{13}\), where p is acute, find the value of cos p - tan p A. \(\frac{79}{156}\) B. \(\frac{85}{156}\) C. \(\frac{7}{13}\) D. \(\frac{8}{1}\) Detailed Solution
 \(BC^2 = 13^2 - 5^2\\ =169-25\\ BC = \sqrt{144} = 12\\ ∴ cos P - tan P = \frac{12}{13} - \frac{5}{12}\\ =\frac{79}{156}\) |
|
| 27. |
Three observation posts P,Q and R are such that Q is due east of P and R is due north of Q. If |PQ| = 5km and |PR| = 10km, find |QR| A. 5.0km B. 7.5km C. 7.6km D. 8.7km Detailed Solution\((PR)^2 = (PQ)^2 + (QR)^2\)\(10^2 = 5^2 + (QR)^2\) \((QR)^2 = 100 - 25\) \(QR = \sqrt{75}\) = \(8.660\) \(\approxeq\) 8.7 km |
|
| 28. |
Express 25° 45' in decimal (Hint: 1° = 60') A. 25.75o B. 25.55o C. 25.45o D. 25.15o Detailed Solution25° 45' = 25° + \(\frac{45}{60}\)°= 25° + 0.75° = 25.75° |
|
| 29. |
A box contains 5 red, 3 green and 4 blue balls. A boy is allowed to take away two balls from the box. What is the probability that the two balls are red? A. \(\frac{5}{33}\) B. \(\frac{5}{36}\) C. \(\frac{103}{132}\) D. \(\frac{31}{36}\) Detailed SolutionTotal number of balls = 5 + 3 + 4= 12 balls P(first ball is red) = \(\frac{5}{12}\) P(second ball is red) = \(\frac{4}{11}\) \(\therefore\) P(both balls are red) = \(\frac{5}{12} \times \frac{4}{11}\) = \(\frac{5}{33}\) |
|
| 30. |
A box contains 5 red, 3 green and 4 blue balls. A boy is allowed to take away two balls from the box. What is the probability that one is green and the other is blue? A. \(\frac{2}{11}\) B. \(\frac{5}{12}\) C. \(\frac{8}{12}\) D. \(\frac{7}{11}\) Detailed SolutionTotal number of balls = 5 + 3 + 4 = 12 ballsP(one ball is green and the other is blue) = P(first ball is green and second blue) + P(first ball is blue and the second green) = \(\frac{3}{12} \times \frac{4}{11} + \frac{4}{12} \times \frac{3}{11}\) = \(\frac{2}{11}\) |