Year :
2017
Title :
Chemistry
Exam :
JAMB Exam
Paper 1 | Objectives
21 - 30 of 49 Questions
| # | Question | Ans |
|---|---|---|
| 21. |
\(^{226}_{88}Ra\) → \(^x_{86}Rn\) + alpha particle A. 226 B. 220 C. 227 D. 222 Detailed Solution\(^{226}_{88}Ra\) → \(^x_{86}Rn\) + \(^4_{2}He\)\(^4_{2}He\) = alpha particle considering the summation of the mass number 226 = x + 4 x = 226 - 4 x = 222 There is an explanation video available below. |
|
| 22. |
The shape of ammonia molecules is A. trigonal planar B. octahedral C. square planar D. tetrahedral |
|
| 23. |
The mass of silver deposited when a current of 10A is passed through a solution of silver salt for 4830s is – (Ag = 108 F = 96500(mol-1) A. 54.0g B. 27.0g C. 13.5g D. 108.0g Detailed SolutionRecall thatmass deposited = \(\frac{MmIt}{96500n}\) Mm =108, t = 4830s I = 10A, n = 1 m = 108 × 10 × (\(\frac{4830}{96500}\)) × 1 m = 54.0g There is an explanation video available below. |
|
| 24. |
Tin is unaffected by air at ordinary temperature due to its A. Low melting point B. Weak electropositive character C. High boiling point D. White lustrous appearance |
|
| 25. |
Calculate the amount in moles of silver deposited when 9650C of electricty is passed through a solution of silver salt [= 96500 Cmol-1] A. 0.05 B. 10.80 C. 10.00 D. 0.10 |
|
| 26. |
The reaction of halogens with alkanes in the presence of sunlight is an example of A. oxidation reaction B. addition reaction C. hydrogenation reaction D. substitution reaction Detailed SolutionAlkanes undergoes substitution reaction and it is an example of halogenation substitution reaction.Reaction of halogen with alkane in the presence of sunlight (ultraviolet) is termed halogenation. Halogenation is an example of substitution reaction. In addition, alkanes only undergo substitution reaction but not addition reaction. There is an explanation video available below. |
|
| 27. |
The enzyme used in the hydrolysis of starch to dextrin and maltose is? A. lipase B. amylase C. invertase D. zymase Detailed SolutionStarch is hydrolyzed by dilute acids to yield a mixture of dextrin (a shorter chain intermediate product), disaccharides (mainly maltose) and glucose. Further hydrolysis will eventually give glucose. Hydrolysis of starch to dextrin and maltose can also be brought about by the enzyme amylase present in saliva and in malt.There is an explanation video available below. |
|
| 28. |
The alkyl group is represented by the general formula A. CnH2n B. CnH2n − 2 C. CnH2n + 1 D. CnH2n + 2 |
|
| 29. |
Cu2S(g) + O2(g) → 2Cu + SO2(g) A. 0 to + 2 B. 0 to + 1 C. + 1 to 0 D. + 2 to + 1 Detailed SolutionIn the reactant;Cu2S 2 Cu - 2(1) = 0 2 Cu = 2 Cu = \(\frac{2}{2}\) Cu = +1 In the product, Cu Cu = O The oxidation number of Cu in Cu2S and Cu respectively is +1 and 0 respectively There is an explanation video available below. |
|
| 30. |
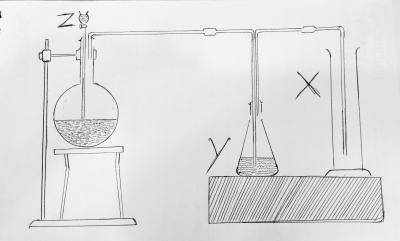 In the diagram above. X is A. SO3 B. SO2 C. S D. H2S Detailed SolutionThe setup represents the production of sulfur dioxide. And the cylinder marked X is SO2There is an explanation video available below. |
| 21. |
\(^{226}_{88}Ra\) → \(^x_{86}Rn\) + alpha particle A. 226 B. 220 C. 227 D. 222 Detailed Solution\(^{226}_{88}Ra\) → \(^x_{86}Rn\) + \(^4_{2}He\)\(^4_{2}He\) = alpha particle considering the summation of the mass number 226 = x + 4 x = 226 - 4 x = 222 There is an explanation video available below. |
|
| 22. |
The shape of ammonia molecules is A. trigonal planar B. octahedral C. square planar D. tetrahedral |
|
| 23. |
The mass of silver deposited when a current of 10A is passed through a solution of silver salt for 4830s is – (Ag = 108 F = 96500(mol-1) A. 54.0g B. 27.0g C. 13.5g D. 108.0g Detailed SolutionRecall thatmass deposited = \(\frac{MmIt}{96500n}\) Mm =108, t = 4830s I = 10A, n = 1 m = 108 × 10 × (\(\frac{4830}{96500}\)) × 1 m = 54.0g There is an explanation video available below. |
|
| 24. |
Tin is unaffected by air at ordinary temperature due to its A. Low melting point B. Weak electropositive character C. High boiling point D. White lustrous appearance |
|
| 25. |
Calculate the amount in moles of silver deposited when 9650C of electricty is passed through a solution of silver salt [= 96500 Cmol-1] A. 0.05 B. 10.80 C. 10.00 D. 0.10 |
| 26. |
The reaction of halogens with alkanes in the presence of sunlight is an example of A. oxidation reaction B. addition reaction C. hydrogenation reaction D. substitution reaction Detailed SolutionAlkanes undergoes substitution reaction and it is an example of halogenation substitution reaction.Reaction of halogen with alkane in the presence of sunlight (ultraviolet) is termed halogenation. Halogenation is an example of substitution reaction. In addition, alkanes only undergo substitution reaction but not addition reaction. There is an explanation video available below. |
|
| 27. |
The enzyme used in the hydrolysis of starch to dextrin and maltose is? A. lipase B. amylase C. invertase D. zymase Detailed SolutionStarch is hydrolyzed by dilute acids to yield a mixture of dextrin (a shorter chain intermediate product), disaccharides (mainly maltose) and glucose. Further hydrolysis will eventually give glucose. Hydrolysis of starch to dextrin and maltose can also be brought about by the enzyme amylase present in saliva and in malt.There is an explanation video available below. |
|
| 28. |
The alkyl group is represented by the general formula A. CnH2n B. CnH2n − 2 C. CnH2n + 1 D. CnH2n + 2 |
|
| 29. |
Cu2S(g) + O2(g) → 2Cu + SO2(g) A. 0 to + 2 B. 0 to + 1 C. + 1 to 0 D. + 2 to + 1 Detailed SolutionIn the reactant;Cu2S 2 Cu - 2(1) = 0 2 Cu = 2 Cu = \(\frac{2}{2}\) Cu = +1 In the product, Cu Cu = O The oxidation number of Cu in Cu2S and Cu respectively is +1 and 0 respectively There is an explanation video available below. |
|
| 30. |
 In the diagram above. X is A. SO3 B. SO2 C. S D. H2S Detailed SolutionThe setup represents the production of sulfur dioxide. And the cylinder marked X is SO2There is an explanation video available below. |