Year :
1981
Title :
Chemistry
Exam :
JAMB Exam
Paper 1 | Objectives
41 - 49 of 49 Questions
| # | Question | Ans |
|---|---|---|
| 41. |
Which one of the following metals is not normally extracted by chemical reduction because of its position in the electrochemical series? A. Copper B. Iron C. Lead D. Potassium E. Zinc |
D |
| 42. |
If one mole of aluminium contains 6 x 1023 atoms of aluminium, how many atoms are contained in 0.9g of aluminium? A. 1.0 x 1021 B. 6.6 x 1021 C. 2.0 x 1022 D. 1.0 x 1022 E. 5.4 x 1023 Detailed Solution1 Mole or 27 gms of Al contains 6 x 1021 atoms0.9 gms of Al will contain (6 x 1023 x 0 g)/(27 1) = 0.2 x 1023 or 1022 |
|
| 43. |
4g each of aluminium foil and aluminium powder were introduced respectively into flasks P and Q. A. There were more aluminium atoms in Q than P B. The heat given off in retarded the reaction C. Q generated more pressure than P during the reaction D. P generated more pressure than Q E. Q has a greater surface area for the reaction than P |
E |
| 44. |
What happens when the nitrates of potassium, calcium, zinc and copper are separately heated? A. All the nitrate will decompose to their respective metals B. The nitrates of calcium and potassium will decomposes to their nitrites C. Only copper nitrate decomposes to the metal D. Only the nitrates of zinc and copper will decompose to their oxides E. The nitrates of calcium, zinc and copper decompose to their oxides Detailed SolutionThe nitrates of calcium, zinc and copper decompose to their metal oxides |
|
| 45. |
The scale formation in a kinetic used for boiling water is caused by the presence in water of? A. calcium sulphate B. calcium carbonate C. calcium hydrogen carbonate D. calcium hydroxide E. magnesium sulphate Detailed SolutionThe scale is produced when soluble Ca(HCO3)2 breaks down on heating to form insoluble CaCO3eqn Ca (HCO3)2(aq) -----> CaCO3 (s) + CO2 (g) + H2O (l) |
|
| 46. |
An efflorescent compound is a substance that? A. absorbs water froom the air without dissolving in it B. is capable of giving off coloured luminosity C. gives out water to the atmosphere D. absorbs water from the air and dissolves in it E. gives out its water of crystallization on heating Detailed SolutionEfflorescence is a phenomenon where a crystalline salt loses all or part of its water of crystallization when exposed to the atmosphere to form a lower dehydrate or an anhydrous salt. |
|
| 47. |
The general formula of an alkyl halide (which represent the halide) is? A. CnH2n - 2X B. CnH2n + 1X C. CnH2n + 2X D. CnH2nX E. CnH2n - 1 |
B |
| 48. |
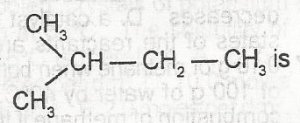 The IUPAC name for A. 1-methlpentane B. 3-methylbutane C. 2-methylbutane D. 1-dimethylpropane E. 2-methylpentane |
C |
| 49. |
Which of the following represents a precipitation reaction? A. H2SO4 + NaCl \(\to\) NaHSO4 + HCl B. Fe +H2SO4 \(\to\) FeSO4 + H2 C. 4HCl + MnO2 \(\to\) MnCl2 + 2H2O + Cl2 D. Na2SO4 + pb(NO3) \(\to\) PbSO4 + 2NaNO E. CuO +2HCl \(\to\) Cl2 + H2O |
D |
| 41. |
Which one of the following metals is not normally extracted by chemical reduction because of its position in the electrochemical series? A. Copper B. Iron C. Lead D. Potassium E. Zinc |
D |
| 42. |
If one mole of aluminium contains 6 x 1023 atoms of aluminium, how many atoms are contained in 0.9g of aluminium? A. 1.0 x 1021 B. 6.6 x 1021 C. 2.0 x 1022 D. 1.0 x 1022 E. 5.4 x 1023 Detailed Solution1 Mole or 27 gms of Al contains 6 x 1021 atoms0.9 gms of Al will contain (6 x 1023 x 0 g)/(27 1) = 0.2 x 1023 or 1022 |
|
| 43. |
4g each of aluminium foil and aluminium powder were introduced respectively into flasks P and Q. A. There were more aluminium atoms in Q than P B. The heat given off in retarded the reaction C. Q generated more pressure than P during the reaction D. P generated more pressure than Q E. Q has a greater surface area for the reaction than P |
E |
| 44. |
What happens when the nitrates of potassium, calcium, zinc and copper are separately heated? A. All the nitrate will decompose to their respective metals B. The nitrates of calcium and potassium will decomposes to their nitrites C. Only copper nitrate decomposes to the metal D. Only the nitrates of zinc and copper will decompose to their oxides E. The nitrates of calcium, zinc and copper decompose to their oxides Detailed SolutionThe nitrates of calcium, zinc and copper decompose to their metal oxides |
|
| 45. |
The scale formation in a kinetic used for boiling water is caused by the presence in water of? A. calcium sulphate B. calcium carbonate C. calcium hydrogen carbonate D. calcium hydroxide E. magnesium sulphate Detailed SolutionThe scale is produced when soluble Ca(HCO3)2 breaks down on heating to form insoluble CaCO3eqn Ca (HCO3)2(aq) -----> CaCO3 (s) + CO2 (g) + H2O (l) |
| 46. |
An efflorescent compound is a substance that? A. absorbs water froom the air without dissolving in it B. is capable of giving off coloured luminosity C. gives out water to the atmosphere D. absorbs water from the air and dissolves in it E. gives out its water of crystallization on heating Detailed SolutionEfflorescence is a phenomenon where a crystalline salt loses all or part of its water of crystallization when exposed to the atmosphere to form a lower dehydrate or an anhydrous salt. |
|
| 47. |
The general formula of an alkyl halide (which represent the halide) is? A. CnH2n - 2X B. CnH2n + 1X C. CnH2n + 2X D. CnH2nX E. CnH2n - 1 |
B |
| 48. |
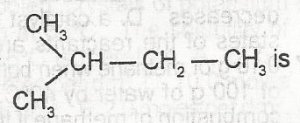 The IUPAC name for A. 1-methlpentane B. 3-methylbutane C. 2-methylbutane D. 1-dimethylpropane E. 2-methylpentane |
C |
| 49. |
Which of the following represents a precipitation reaction? A. H2SO4 + NaCl \(\to\) NaHSO4 + HCl B. Fe +H2SO4 \(\to\) FeSO4 + H2 C. 4HCl + MnO2 \(\to\) MnCl2 + 2H2O + Cl2 D. Na2SO4 + pb(NO3) \(\to\) PbSO4 + 2NaNO E. CuO +2HCl \(\to\) Cl2 + H2O |
D |