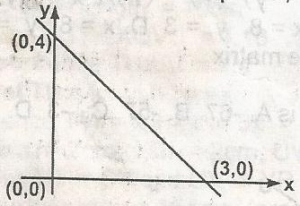Year :
1994
Title :
Mathematics (Core)
Exam :
JAMB Exam
Paper 1 | Objectives
41 - 48 of 48 Questions
| # | Question | Ans |
|---|---|---|
| 41. |
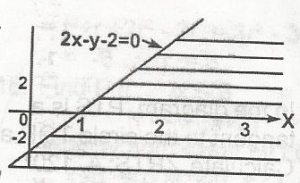 Find the inequality which represents the shaded portion in the diagram A. 2x - y - 2 \(\geq\) 0 B. 2x - y - 2 \(\leq\) 0 C. 2x - y - 2 < 0 D. 2x - y - 2 > 0 Detailed Solution2x - y - 2 \(\geq\) 0 = y \(\leq\) 2x - 2when x = 0, y = -2, when y = 0, x = 1 |
|
| 42. |
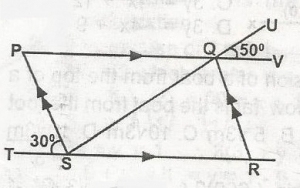 In the diagram, PQRS is a parallelogram. Find the value of < SQR A. 30o B. 50o C. 80o D. 100o Detailed SolutionSQR + RQV + VQU = 18o angle on a straight line SP is parallel to QR and PV is parallel to TR< STP = < RQV = 30o But SQR + 30o + 50o = 180o SQR = 180 - 80 = 100o |
|
| 43. |
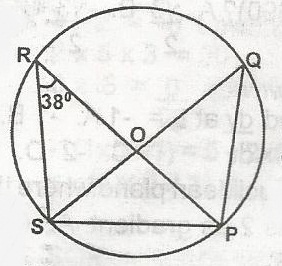 In the diagram, O is the centre of the circle. If SOQ is a diameter and < PRS is 38o, what is the value of < PSQ A. 148o B. 104o C. 80o D. 52o Detailed Solution< SRP = < SQP = 38o (angle in the same segment of a circle are equal)But < SPQ = 90o (angle in a semicircle) also < PSQ + < SQP + < SPQ = 180o (angles in a triangle = 180o) < PSQ + 38o + 90o = 190o < PSQ = 128o = 180o PSQ = 180o - 128o PSQ = 52o |
|
| 44. |
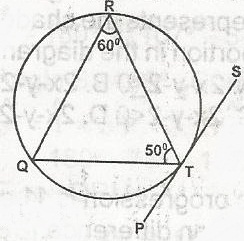
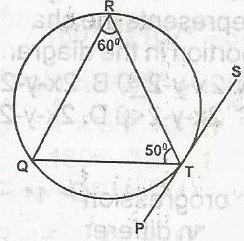 In the diagram, PTS is a tangent to the circle TQR at T. Calculate < RTS A. 120o B. 70o C. 60o D. 40o Detailed Solution
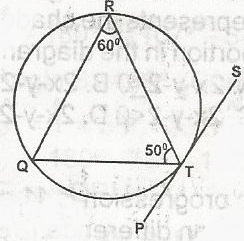 RQT = 180o - (50 + 60) = 180o - 110o = 70o Since RQT = RTS = 70o |
|
| 45. |
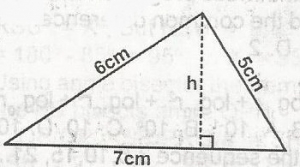 In the diagram. Find h A. \(\frac{12}{7}\)cm B. \(\frac{12}{7} \sqrt{6}\)cm C. \(\frac{7}{12}\)cm D. \(\frac{1}{2}\)cm Detailed SolutionA\(\bigtriangleup\) = \(\sqrt{S(S - a) (S - b)(S - c)}\) (Hero's Formula)S = \(\frac{a + b + c}{2}\) = \(\frac{5 + 6 + 7}{2}\) \(\frac{18}{2} = 9\) A\(\bigtriangleup\) \(\sqrt{9} \times 4 \times 3 \times 2\) \(\sqrt{216} = 6 \sqrt{6}cm^3\) A\(\bigtriangleup\) = \(\frac{1}{2} \times 6 \times h\) 6\(\sqrt{6} = \frac{1}{2} \times 7 \times h\) h = \(\frac{12}{h} \sqrt{6}\) |
|
| 46. |
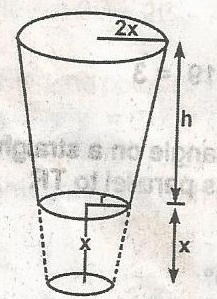
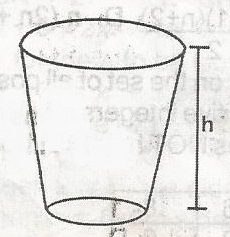 In the frustum of the cone, the top diagram is twice the bottom diameter. If the height of the frustum is h centimeters, find he height of the cone A. 2h B. 2\(\pi\)h C. \(\pi\)h D. \(\frac{\pi h}{2}\) Detailed Solution
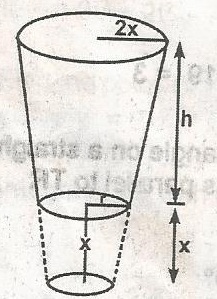 2 x r = r (x + h) Total height of cone = x + h but x = h total height = 2h |
|
| 47. |
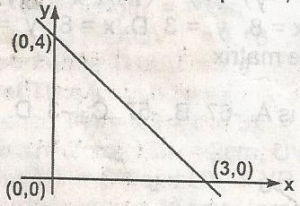 The equation of the line in the graph is A. 3y = 4x + 12 B. 3y = 3x + 12 C. 3y = -4x + 12 D. 3y = -4x + 9 Detailed Solution
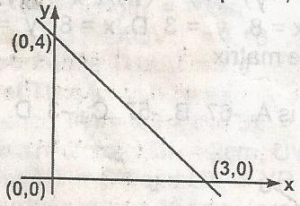 y2 = 0, y1 = 4 x2 = 3 and x1 = 0 \(\frac{y_2 - y_1}{x_2 - x_1} = \frac{0 - 4}{3 - 0} = \frac{-4}{3}\) Equation of straight line = y = mx + c where m = gradient and c = y intercept = 4 y = 4x + \(\frac{4}{3}\), multiple through by 3 & |
|
| 48. |
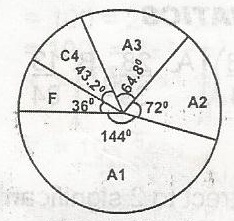 The grades A1, A2, A3, C4 and F earned by students in a particular course are shown in the pie chart. What percentage of the students obtained a C4 grade? A. 52.0 B. 43.2 C. 40.0 D. 12.0 |
D |
| 41. |
 Find the inequality which represents the shaded portion in the diagram A. 2x - y - 2 \(\geq\) 0 B. 2x - y - 2 \(\leq\) 0 C. 2x - y - 2 < 0 D. 2x - y - 2 > 0 Detailed Solution2x - y - 2 \(\geq\) 0 = y \(\leq\) 2x - 2when x = 0, y = -2, when y = 0, x = 1 |
|
| 42. |
 In the diagram, PQRS is a parallelogram. Find the value of < SQR A. 30o B. 50o C. 80o D. 100o Detailed SolutionSQR + RQV + VQU = 18o angle on a straight line SP is parallel to QR and PV is parallel to TR< STP = < RQV = 30o But SQR + 30o + 50o = 180o SQR = 180 - 80 = 100o |
|
| 43. |
 In the diagram, O is the centre of the circle. If SOQ is a diameter and < PRS is 38o, what is the value of < PSQ A. 148o B. 104o C. 80o D. 52o Detailed Solution< SRP = < SQP = 38o (angle in the same segment of a circle are equal)But < SPQ = 90o (angle in a semicircle) also < PSQ + < SQP + < SPQ = 180o (angles in a triangle = 180o) < PSQ + 38o + 90o = 190o < PSQ = 128o = 180o PSQ = 180o - 128o PSQ = 52o |
|
| 44. |
 In the diagram, PTS is a tangent to the circle TQR at T. Calculate < RTS A. 120o B. 70o C. 60o D. 40o Detailed Solution
 RQT = 180o - (50 + 60) = 180o - 110o = 70o Since RQT = RTS = 70o |
| 45. |
 In the diagram. Find h A. \(\frac{12}{7}\)cm B. \(\frac{12}{7} \sqrt{6}\)cm C. \(\frac{7}{12}\)cm D. \(\frac{1}{2}\)cm Detailed SolutionA\(\bigtriangleup\) = \(\sqrt{S(S - a) (S - b)(S - c)}\) (Hero's Formula)S = \(\frac{a + b + c}{2}\) = \(\frac{5 + 6 + 7}{2}\) \(\frac{18}{2} = 9\) A\(\bigtriangleup\) \(\sqrt{9} \times 4 \times 3 \times 2\) \(\sqrt{216} = 6 \sqrt{6}cm^3\) A\(\bigtriangleup\) = \(\frac{1}{2} \times 6 \times h\) 6\(\sqrt{6} = \frac{1}{2} \times 7 \times h\) h = \(\frac{12}{h} \sqrt{6}\) |
|
| 46. |
 In the frustum of the cone, the top diagram is twice the bottom diameter. If the height of the frustum is h centimeters, find he height of the cone A. 2h B. 2\(\pi\)h C. \(\pi\)h D. \(\frac{\pi h}{2}\) Detailed Solution
 2 x r = r (x + h) Total height of cone = x + h but x = h total height = 2h |
|
| 47. |
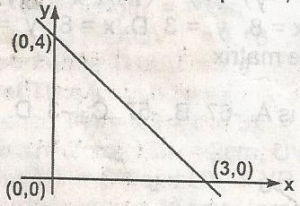 The equation of the line in the graph is A. 3y = 4x + 12 B. 3y = 3x + 12 C. 3y = -4x + 12 D. 3y = -4x + 9 Detailed Solution
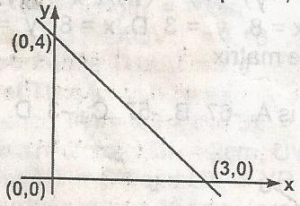 y2 = 0, y1 = 4 x2 = 3 and x1 = 0 \(\frac{y_2 - y_1}{x_2 - x_1} = \frac{0 - 4}{3 - 0} = \frac{-4}{3}\) Equation of straight line = y = mx + c where m = gradient and c = y intercept = 4 y = 4x + \(\frac{4}{3}\), multiple through by 3 & |
|
| 48. |
 The grades A1, A2, A3, C4 and F earned by students in a particular course are shown in the pie chart. What percentage of the students obtained a C4 grade? A. 52.0 B. 43.2 C. 40.0 D. 12.0 |
D |