Year :
1994
Title :
Mathematics (Core)
Exam :
JAMB Exam
Paper 1 | Objectives
31 - 40 of 48 Questions
| # | Question | Ans |
|---|---|---|
| 31. |
What is the value of sin(-690)? A. \(\frac{\sqrt{3}}{2}\) B. -\(\frac{\sqrt{3}}{2}\) C. \(\frac{-1}{2}\) D. \(\frac{1}{2}\) Detailed SolutionSin(-690o) = Sin(-360 -3300sin - 360 = sin 0 ∴ sin(-690o) = sin(330o) Negative angles are measured in clockwise direction The acute angle equivalent of sin(-330o) = sin(30o) sin(-330o) = sin(30o) = \(\frac{1}{2}\) = 0.5 |
|
| 32. |
If y = 3t3 + 2t2 - 7t + 3, find \(\frac{dy}{dt}\) at t = -1 A. -1 B. 1 C. -2 D. 2 Detailed Solutiony = 3t3 + 2t2 - 7t + 3\(\frac{dy}{dt}\) = 9t2 + 4t - 7 When t = -1 \(\frac{dy}{dt}\) = 9(-1)2 + 4(-1) - 7 = 9 - 4 -7 = 9 - 11 = -2 |
|
| 33. |
Find the point (x, y) on the Euclidean plane where the curve y = 2x2 - 2x + 3 has 2 as gradient A. (1, 3) B. (2, 7) C. (0, 3) D. (3, 15) Detailed SolutionEquation of curve;y = 2x2 - 2x + 3 gradient of curve; \(\frac{dy}{dx}\) = differential coefficient \(\frac{dy}{dx}\) = 4x - 2, for gradient to be 2 ∴ \(\frac{dy}{dx}\) = 2 4x - 2 = 2 4x = 4 ∴ x = 1 When x = 1, y = 2(1)2 - 2(1) + 3 = 2 - 2 + 3 = 5 - 2 = 3 coordinate of the point where the curve; y = 2x2 - 2x + 3 has gradient equal to 2 is (1, 3) |
|
| 34. |
Evaluate \(\int^{1}_{-1}(2x + 1)^2 \mathrm d x\) A. 3\(\frac{2}{3}\) B. 4 C. 4\(\frac{1}{3}\) D. 4\(\frac{2}{3}\) Detailed Solution\(\int^{1}_{-1}(2x + 1)^2 \mathrm d x\)= \(\int^{1}_{-1}(4x^2 + 4x + 1) \mathrm d x\) = \(\int^{1}_{-1}\)[\(\frac{4x^3}{3} + 2x^2 + c]\) = [\(\frac{4}{3}\) + 3 + c] - [4 + \(\frac{1}{3}\) + c] = \(\frac{8}{3}\) + 3 + -1 - C = \(\frac{8}{3}\) + 2 = \(\frac{14}{3}\) = \(4 \frac{2}{3}\) |
|
| 35. |
\(\begin{array}{c|c} x & 1 & 2 & 3 & 4 & 5 \\ \hline f & y + 2 & y - 2 & 2y - 3 & y + 4 & 3y - 4\end{array}\) A. 1 B. 2 C. 3 D. 4 Detailed SolutionMean = \(\frac{\sum fx}{\sum f}\)\(\therefore \frac{28y - 13}{8y - 2} = \frac{43}{14}\) \(\implies 14(28y - 13) = 43(8y - 2)\) \(392y - 182 = 344y - 86\) \(392y - 344y = -86 + 182 \implies 48y = 96\) \(y = 2\) |
|
| 36. |
Find the mean deviation of the set of numbers 4, 5, 9 A. zero B. 2 C. 5 D. 6 Detailed Solutionx = \(\frac{\sum x}{N}\)= \(\frac{18}{3}\) = 6 \(\begin{array}{c|c} x & x - x & x - x \\ \hline 4 & -2 & 2\\ 5 & 1 & 1\\ 9 & 3 & 3\\ \hline & & 6\end{array}\) M.D = \(\frac{|x - x|}{N}\) = \(\frac{6}{3}\) = 2 |
|
| 37. |
\(\begin{array}{c|c} \text{Class Interval} & 1 - 5 & 6 - 10 & 11 - 15 & 16 - 20 & 21 - 25 \\ \hline Frequency & 6 & 15 & 20 & 7 & 2\end{array}\) A. 10\(\frac{1}{2}\) B. 11\(\frac{1}{2}\) C. 12 D. 13 Detailed SolutionMedian = L + [\(\frac{\frac{N}{2} - f}{fm}\)]hN = Sum of frequencies L = lower class boundary of median class f = sum of all frequencies below L fm = frequency of modal class and h = class width of median class Median = 11 + [\(\frac{\frac{50}{2} - 21}{20}\)]5 = 11 + (\(\frac{25 - 21}{20}\))5 = 11 + (\(\frac{(4)}{20}\)) 11 + 1 = 12 |
|
| 38. |
\(\begin{array}{c|c} x & 1 & 2 & 3 & 4 & 5 \\ \hline f & 2 & 1 & 2 & 1 & 2\end{array}\) A. \(\frac{3}{2}\) B. \(\frac{9}{4}\) C. \(\frac{5}{2}\) D. 3 Detailed Solution\(\begin{array}{c|c} x & f & fx & \bar{x} - x & (\bar{x} - x)^2 & f(\bar{x} - x)^2 \\ \hline 1 & 2 & 2 & -2 & 4 & 8\\ 2 & 1 & 2 & -1 & 1 & 1\\ 3 & 2 & 6 & 0 & 0 & 0\\ 4 & 1 & 4 & 1 & 1 & 1\\ 2 & 2 & 10 & 2 & 4 & 8\\ \hline & 8 & 24 & & & 18 \end{array}\)x = \(\frac{\sum fx}{\sum f}\) = \(\frac{24}{8}\) = 3 Variance (62) = \(\frac{\sum f(\bar{x} - x)^2}{\sum f}\) = \(\frac{18}{8}\) = \(\frac{9}{4}\) |
|
| 39. |
In a survey, it was observed that 20 students read newspapers and 35 read novels. If 40 of the students read either newspapers or novels, what is the probability of the students who read both newspapers and novels? A. \(\frac{1}{2}\) B. \(\frac{2}{3}\) C. \(\frac{3}{8}\) D. \(\frac{3}{11}\) Detailed Solution40 = 20 - x + x + 35 - x40 = 55 - x x = 55 - 40 = 15 ∴ P(both) \(\frac{15}{40}\) = \(\frac{3}{8}\) |
|
| 40. |
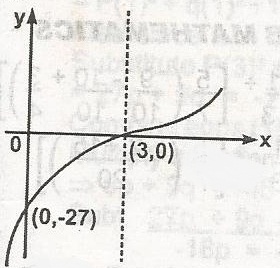 The equation of the graph is A. y = (x - 3)3 B. y = (x + 3)3 C. y = x3 - 27 D. y = -x3 + 27 Detailed Solutiony = x3 - 27, y = -27 \(\to\) (0, -27)when y = 0, x = 3 (3, 0) |
| 31. |
What is the value of sin(-690)? A. \(\frac{\sqrt{3}}{2}\) B. -\(\frac{\sqrt{3}}{2}\) C. \(\frac{-1}{2}\) D. \(\frac{1}{2}\) Detailed SolutionSin(-690o) = Sin(-360 -3300sin - 360 = sin 0 ∴ sin(-690o) = sin(330o) Negative angles are measured in clockwise direction The acute angle equivalent of sin(-330o) = sin(30o) sin(-330o) = sin(30o) = \(\frac{1}{2}\) = 0.5 |
|
| 32. |
If y = 3t3 + 2t2 - 7t + 3, find \(\frac{dy}{dt}\) at t = -1 A. -1 B. 1 C. -2 D. 2 Detailed Solutiony = 3t3 + 2t2 - 7t + 3\(\frac{dy}{dt}\) = 9t2 + 4t - 7 When t = -1 \(\frac{dy}{dt}\) = 9(-1)2 + 4(-1) - 7 = 9 - 4 -7 = 9 - 11 = -2 |
|
| 33. |
Find the point (x, y) on the Euclidean plane where the curve y = 2x2 - 2x + 3 has 2 as gradient A. (1, 3) B. (2, 7) C. (0, 3) D. (3, 15) Detailed SolutionEquation of curve;y = 2x2 - 2x + 3 gradient of curve; \(\frac{dy}{dx}\) = differential coefficient \(\frac{dy}{dx}\) = 4x - 2, for gradient to be 2 ∴ \(\frac{dy}{dx}\) = 2 4x - 2 = 2 4x = 4 ∴ x = 1 When x = 1, y = 2(1)2 - 2(1) + 3 = 2 - 2 + 3 = 5 - 2 = 3 coordinate of the point where the curve; y = 2x2 - 2x + 3 has gradient equal to 2 is (1, 3) |
|
| 34. |
Evaluate \(\int^{1}_{-1}(2x + 1)^2 \mathrm d x\) A. 3\(\frac{2}{3}\) B. 4 C. 4\(\frac{1}{3}\) D. 4\(\frac{2}{3}\) Detailed Solution\(\int^{1}_{-1}(2x + 1)^2 \mathrm d x\)= \(\int^{1}_{-1}(4x^2 + 4x + 1) \mathrm d x\) = \(\int^{1}_{-1}\)[\(\frac{4x^3}{3} + 2x^2 + c]\) = [\(\frac{4}{3}\) + 3 + c] - [4 + \(\frac{1}{3}\) + c] = \(\frac{8}{3}\) + 3 + -1 - C = \(\frac{8}{3}\) + 2 = \(\frac{14}{3}\) = \(4 \frac{2}{3}\) |
|
| 35. |
\(\begin{array}{c|c} x & 1 & 2 & 3 & 4 & 5 \\ \hline f & y + 2 & y - 2 & 2y - 3 & y + 4 & 3y - 4\end{array}\) A. 1 B. 2 C. 3 D. 4 Detailed SolutionMean = \(\frac{\sum fx}{\sum f}\)\(\therefore \frac{28y - 13}{8y - 2} = \frac{43}{14}\) \(\implies 14(28y - 13) = 43(8y - 2)\) \(392y - 182 = 344y - 86\) \(392y - 344y = -86 + 182 \implies 48y = 96\) \(y = 2\) |
| 36. |
Find the mean deviation of the set of numbers 4, 5, 9 A. zero B. 2 C. 5 D. 6 Detailed Solutionx = \(\frac{\sum x}{N}\)= \(\frac{18}{3}\) = 6 \(\begin{array}{c|c} x & x - x & x - x \\ \hline 4 & -2 & 2\\ 5 & 1 & 1\\ 9 & 3 & 3\\ \hline & & 6\end{array}\) M.D = \(\frac{|x - x|}{N}\) = \(\frac{6}{3}\) = 2 |
|
| 37. |
\(\begin{array}{c|c} \text{Class Interval} & 1 - 5 & 6 - 10 & 11 - 15 & 16 - 20 & 21 - 25 \\ \hline Frequency & 6 & 15 & 20 & 7 & 2\end{array}\) A. 10\(\frac{1}{2}\) B. 11\(\frac{1}{2}\) C. 12 D. 13 Detailed SolutionMedian = L + [\(\frac{\frac{N}{2} - f}{fm}\)]hN = Sum of frequencies L = lower class boundary of median class f = sum of all frequencies below L fm = frequency of modal class and h = class width of median class Median = 11 + [\(\frac{\frac{50}{2} - 21}{20}\)]5 = 11 + (\(\frac{25 - 21}{20}\))5 = 11 + (\(\frac{(4)}{20}\)) 11 + 1 = 12 |
|
| 38. |
\(\begin{array}{c|c} x & 1 & 2 & 3 & 4 & 5 \\ \hline f & 2 & 1 & 2 & 1 & 2\end{array}\) A. \(\frac{3}{2}\) B. \(\frac{9}{4}\) C. \(\frac{5}{2}\) D. 3 Detailed Solution\(\begin{array}{c|c} x & f & fx & \bar{x} - x & (\bar{x} - x)^2 & f(\bar{x} - x)^2 \\ \hline 1 & 2 & 2 & -2 & 4 & 8\\ 2 & 1 & 2 & -1 & 1 & 1\\ 3 & 2 & 6 & 0 & 0 & 0\\ 4 & 1 & 4 & 1 & 1 & 1\\ 2 & 2 & 10 & 2 & 4 & 8\\ \hline & 8 & 24 & & & 18 \end{array}\)x = \(\frac{\sum fx}{\sum f}\) = \(\frac{24}{8}\) = 3 Variance (62) = \(\frac{\sum f(\bar{x} - x)^2}{\sum f}\) = \(\frac{18}{8}\) = \(\frac{9}{4}\) |
|
| 39. |
In a survey, it was observed that 20 students read newspapers and 35 read novels. If 40 of the students read either newspapers or novels, what is the probability of the students who read both newspapers and novels? A. \(\frac{1}{2}\) B. \(\frac{2}{3}\) C. \(\frac{3}{8}\) D. \(\frac{3}{11}\) Detailed Solution40 = 20 - x + x + 35 - x40 = 55 - x x = 55 - 40 = 15 ∴ P(both) \(\frac{15}{40}\) = \(\frac{3}{8}\) |
|
| 40. |
 The equation of the graph is A. y = (x - 3)3 B. y = (x + 3)3 C. y = x3 - 27 D. y = -x3 + 27 Detailed Solutiony = x3 - 27, y = -27 \(\to\) (0, -27)when y = 0, x = 3 (3, 0) |