Year :
2020
Title :
Economics
Exam :
WASSCE/WAEC MAY/JUNE
Paper 1 | Objectives
1 - 10 of 49 Questions
| # | Question | Ans |
|---|---|---|
| 1. |
Which of the following is central to the definition of Economics? A. resources B. wants C. scarcity D. capital Detailed SolutionScarcity is one of the most important components of the definition of economics. It signifies the gap between limited resources and limitless wants. |
|
| 2. |
When the production possibility curve shifts outwards, the economy experiences A. growth B. over-production C. inefficient use of resources D. under-production Detailed Solution
|
|
| 3. |
Land as a factor of production is made useful through the A. application of human effort B. acts of nature C. application of fertilizer D. use of machines |
A |
| 4. |
In a free market economy, resources are allocated through the A. government department B. price mechanisms C. trade union D. state planning committee. Detailed SolutionIn a free market economy, the allocation of resources and distribution of goods and services are made on the basis of the relative market price known as the price mechanism. |
|
| 5. |
Use the figure below to answer question that follows A. simple bar chart B. complex bar chart C. component bar chart Detailed SolutionA component bar chart is used to represent data in which the total magnitude is divided into different or components with each component, or part, of the bar is shaded differently. |
|
| 6. |
The figure below shows the change in demand for Commodity X which is a normal good. Use it to answer the question that follows. A. Fall in the income of consumers B. Rise in the price of a substitute C. Rise in the price of a complement D. Fall in the supply of commodity X |
B |
| 7. |
Use the figure below to answer the question that follows A. The supply curve will shift from S\(_{0}\)S\(_{2}\) to S\(_{2}\)S\(_{0}\) B. The supply curve will shift from S\(_{0}\)S\(_{0}\) to S\(_{1}\)S\(_{1}\) C. The demand curve will shift from D\(_{0}\)D\(_{0}\) to D\(_{1}\)D\(_{1}\) D. The supply curve will shift from S\(_{0}\)S\(_{0}\) to S\(_{0}\)S\(_{0}\) |
B |
| 8. |
A. excess demand B. excess supply C. equilibrium quantity D. equilibrium price Detailed SolutionDemand and supply were at equilibrium at points P\(_{2}\) and q\(_{2}\). At point YZ, supply is in excess |
|
| 9. |
Goods are described as inferior if their demand A. decreases as price falls B. increases as income rises C. decreases as income increases D. increases as price increases Detailed SolutionIn economics, an inferior good is a good whose demand drops when people's incomes rise. T |
|
| 10. |
A consumer is in equilibrium when A. his market Supply is equal to his market demand B. he maximizes his satisfaction from spending his income C. the market is also in equilibrium D. he has consumed all he wants Detailed SolutionA consumer is in equilibrium when he derives maximum satisfaction from the goods, given his income and the market prices. |
| 1. |
Which of the following is central to the definition of Economics? A. resources B. wants C. scarcity D. capital Detailed SolutionScarcity is one of the most important components of the definition of economics. It signifies the gap between limited resources and limitless wants. |
|
| 2. |
When the production possibility curve shifts outwards, the economy experiences A. growth B. over-production C. inefficient use of resources D. under-production Detailed Solution
|
|
| 3. |
Land as a factor of production is made useful through the A. application of human effort B. acts of nature C. application of fertilizer D. use of machines |
A |
| 4. |
In a free market economy, resources are allocated through the A. government department B. price mechanisms C. trade union D. state planning committee. Detailed SolutionIn a free market economy, the allocation of resources and distribution of goods and services are made on the basis of the relative market price known as the price mechanism. |
|
| 5. |
Use the figure below to answer question that follows A. simple bar chart B. complex bar chart C. component bar chart Detailed SolutionA component bar chart is used to represent data in which the total magnitude is divided into different or components with each component, or part, of the bar is shaded differently. |
| 6. |
The figure below shows the change in demand for Commodity X which is a normal good. Use it to answer the question that follows. A. Fall in the income of consumers B. Rise in the price of a substitute C. Rise in the price of a complement D. Fall in the supply of commodity X |
B |
| 7. |
Use the figure below to answer the question that follows A. The supply curve will shift from S\(_{0}\)S\(_{2}\) to S\(_{2}\)S\(_{0}\) B. The supply curve will shift from S\(_{0}\)S\(_{0}\) to S\(_{1}\)S\(_{1}\) C. The demand curve will shift from D\(_{0}\)D\(_{0}\) to D\(_{1}\)D\(_{1}\) D. The supply curve will shift from S\(_{0}\)S\(_{0}\) to S\(_{0}\)S\(_{0}\) |
B |
| 8. |
A. excess demand B. excess supply C. equilibrium quantity D. equilibrium price Detailed SolutionDemand and supply were at equilibrium at points P\(_{2}\) and q\(_{2}\). At point YZ, supply is in excess |
|
| 9. |
Goods are described as inferior if their demand A. decreases as price falls B. increases as income rises C. decreases as income increases D. increases as price increases Detailed SolutionIn economics, an inferior good is a good whose demand drops when people's incomes rise. T |
|
| 10. |
A consumer is in equilibrium when A. his market Supply is equal to his market demand B. he maximizes his satisfaction from spending his income C. the market is also in equilibrium D. he has consumed all he wants Detailed SolutionA consumer is in equilibrium when he derives maximum satisfaction from the goods, given his income and the market prices. |
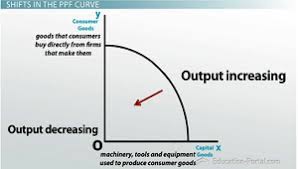



 In the figure above
In the figure above

