Year :
1979
Title :
Mathematics (Core)
Exam :
JAMB Exam
Paper 1 | Objectives
41 - 50 of 51 Questions
| # | Question | Ans |
|---|---|---|
| 41. |
A man is standing in the corridor of a 10-storey building and looking down at a tall tree in front of the building. He sees the top of the tree at angle of depression of 30o. If the tree is 200m tall and the man's eyes are 300m above the ground, calculate the angle of depression of the foot tree as seen by the man A. 30o B. 60o C. 45o D. 25o Detailed SolutionLet x rep. the angle of depression of the foot of the tree.tan 30o = \(\frac{y}{100}\) y = 100 tan 30o = 57.8 By Pythagoras, AC2 = 3002 + 582 = 900 + 3354 tan x = \(\frac{opp}{adj}\) = \(\frac{58}{300}\) = 0.19 tan x = 0.19 x = tan 0.19 = 60o |
|
| 42. |
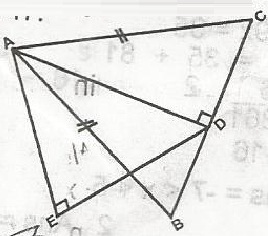 In the figure, \(\bigtriangleup\) ABC are in adjacent planes. AB = AC = 5cm, BC = 6cm and A. 3\(\sqrt{2}\) B. 2\(\sqrt{3}\) C. \(\frac{\sqrt{3}}{2}\) D. \(\frac{2}{\sqrt{3}}\) Detailed SolutionBC = 6 : DC = \(\frac{6}{2}\) = 3cmBy construction < EDE = 180o(90o + 60o) = 180o - 150o = 30o(angle on a strt. line) From rt < triangle ADC, AD2 = 52 - 32 = 25 - 9 = 6 AD = 4 From < AEC, let AS = x \(\frac{x}{sin 60^o}\) - \(\frac{4}{sin 90^o}\) sin 90o = 1 sin 60o = \(\frac{\sqrt{3}}{2}\)< |
|
| 43. |
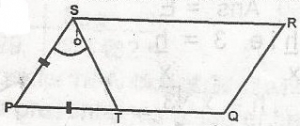 In this figure, PQRS is a parallelogram, PS = PT and < PST = 55\(^o\). The size of <PQR is A. 125o B. 120o C. 115o D. 110o E. 10o Detailed SolutionBoth pairs of opp. angles are equal< STP = 55\(^o\) - isosceles angle < TSR = 55\(^o\) - alternate angle to < STP Hence, < PSR = 55\(^o\) + 55\(^o\) = 110\(^o\) \(\therefore\) < PQR = 110\(^o\) |
|
| 44. |
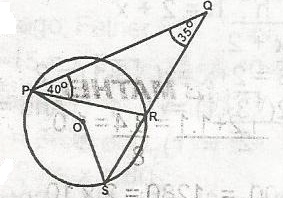 If O is the centre of the circle, < POS equls A. 70o B. 75o C. 105o D. 140o E. 150o Detailed SolutionSince O is the centre of the circle < POS = 150oi.e. < substended at the centre is twice that substended at any part of the circumference |
|
| 45. |
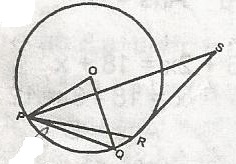 In the figure, PQ and QR are chords of the circle PQR. QRS is a straight line and PR is equal to RS, < PSR is 20o. What is the size of A. 70o B. 90o C. 80o D. 40o E. 60o Detailed SolutionThe site of POQ = 80o |
|
| 46. |
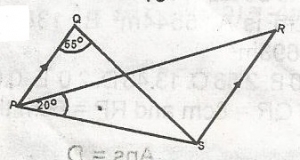 In the figure, PQ is parallel to SQ ; QS bisets < PSQ, < PQS is 65o and < RPS is 20o. What is the size of < PRS? A. 45o B. 35o C. 40o D. 30o E. 42o Detailed SolutionPSR = 65o x 2= 130o PRS = 180o - (130o + 20o) = 30o |
|
| 47. |
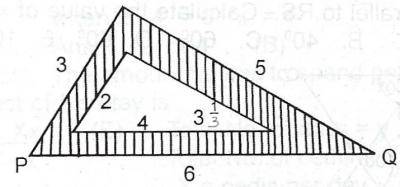 (Numbers indicate the lengths of the sides of the triangles) If the area of \(\bigtriangleup\) PQR is k2sq. units what is the area of the shades portion? A. units B. units C. units D. units E. u Detailed SolutionArea of shaded portion = Area of triangle PQR - Area of inner triangleArea of triangle given 3 sides a, b, c = \(\sqrt{s(s - a)(s - b)(s - c)}\) where \(s = \frac{a + b + c}{2} \) Area of PQR : \(s = \frac{3 + 5 + 6}{2} = \frac{14}{2} = 7\) Area = \(\sqrt{7(7 - 3)(7 - 5)(7 - 6)}\) = \(\sqrt{7(4)(2)(1)} = \sqrt{56}\) \(\implies K^{2} = \sqrt{56}\) Area of inner triangle : \(s = \frac{2 + 4 + \frac{10}{3}}{2} = \frac{14}{3}\) Area = \(\sqrt{\frac{14}{3} (\frac{14}{3} - 2)(\frac{14}{3} - 4)(\frac{14}{3} - \frac{10}{3})}\) = \(\sqrt{\frac{14}{3} (\frac{8}{3})(\frac{2}{3})(\frac{4}{3})}\) = \(\sqrt{\frac{896}{81}}\) = \(\sqrt{\fr |
|
| 48. |
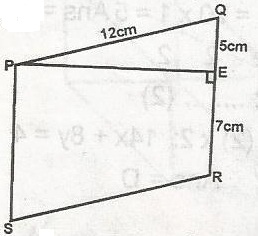 In the parallelogram PQRS, PE is perpendicular to QR. Find the area of the parallelogram. A. 60cm2 B. 65cm2 C. 72cm2 D. 132cm2 E. 156cm2 Detailed SolutionBy Pythagoras, PE\(^2\) = 12\(^2\) - 5\(^2\)= 144 - 25 = 119 h = PE\(^2\) = √119 = 10.9 ≈ 11cm, Area of 11gm = b x h QR = b =(5 + 7)cm = 12cm area = 12 x 11 = 132cm\(^2\) |
|
| 49. |
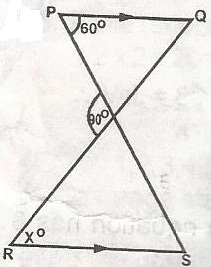 PQ is parallel to RS. Calculate the value of x. A. 20o B. 40o C. 60o D. 80o E. 100o Detailed Solution< D = 180o - 100v= 80o (< on a str. line) < s = 60o - alternate angle x = 180o - (80o + 60o) 180o - 140o = 40o |
|
| 50. |
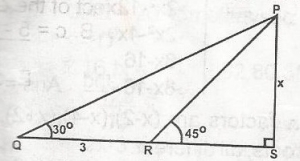 Find x in the diagram below. A. 3\(\sqrt{3}\) B. \(\frac{3(\sqrt{3} - 1)}{\sqrt{3} + 1}\) C. \(\frac{(\sqrt{3} - 1)}{\sqrt{3} + 1}\) D. \(\frac{3 - 1}{\sqrt{3} + 1}\) Detailed Solution\(\frac{x + 3}{sin 60^o}\) = \(\frac{x}{sin 306o}\)3sin 30o = x sin 60o - x sin 30o = x(sin 60o - sin 30o) but sin 30o = \(\frac{1}{2}\) sin 60o = \(\frac{3}{2}\) = \(\frac{3(\sqrt{3} - 1)}{\sqrt{3} + 1}\) |
| 41. |
A man is standing in the corridor of a 10-storey building and looking down at a tall tree in front of the building. He sees the top of the tree at angle of depression of 30o. If the tree is 200m tall and the man's eyes are 300m above the ground, calculate the angle of depression of the foot tree as seen by the man A. 30o B. 60o C. 45o D. 25o Detailed SolutionLet x rep. the angle of depression of the foot of the tree.tan 30o = \(\frac{y}{100}\) y = 100 tan 30o = 57.8 By Pythagoras, AC2 = 3002 + 582 = 900 + 3354 tan x = \(\frac{opp}{adj}\) = \(\frac{58}{300}\) = 0.19 tan x = 0.19 x = tan 0.19 = 60o |
|
| 42. |
 In the figure, \(\bigtriangleup\) ABC are in adjacent planes. AB = AC = 5cm, BC = 6cm and A. 3\(\sqrt{2}\) B. 2\(\sqrt{3}\) C. \(\frac{\sqrt{3}}{2}\) D. \(\frac{2}{\sqrt{3}}\) Detailed SolutionBC = 6 : DC = \(\frac{6}{2}\) = 3cmBy construction < EDE = 180o(90o + 60o) = 180o - 150o = 30o(angle on a strt. line) From rt < triangle ADC, AD2 = 52 - 32 = 25 - 9 = 6 AD = 4 From < AEC, let AS = x \(\frac{x}{sin 60^o}\) - \(\frac{4}{sin 90^o}\) sin 90o = 1 sin 60o = \(\frac{\sqrt{3}}{2}\)< |
|
| 43. |
 In this figure, PQRS is a parallelogram, PS = PT and < PST = 55\(^o\). The size of <PQR is A. 125o B. 120o C. 115o D. 110o E. 10o Detailed SolutionBoth pairs of opp. angles are equal< STP = 55\(^o\) - isosceles angle < TSR = 55\(^o\) - alternate angle to < STP Hence, < PSR = 55\(^o\) + 55\(^o\) = 110\(^o\) \(\therefore\) < PQR = 110\(^o\) |
|
| 44. |
 If O is the centre of the circle, < POS equls A. 70o B. 75o C. 105o D. 140o E. 150o Detailed SolutionSince O is the centre of the circle < POS = 150oi.e. < substended at the centre is twice that substended at any part of the circumference |
|
| 45. |
 In the figure, PQ and QR are chords of the circle PQR. QRS is a straight line and PR is equal to RS, < PSR is 20o. What is the size of A. 70o B. 90o C. 80o D. 40o E. 60o Detailed SolutionThe site of POQ = 80o |
| 46. |
 In the figure, PQ is parallel to SQ ; QS bisets < PSQ, < PQS is 65o and < RPS is 20o. What is the size of < PRS? A. 45o B. 35o C. 40o D. 30o E. 42o Detailed SolutionPSR = 65o x 2= 130o PRS = 180o - (130o + 20o) = 30o |
|
| 47. |
 (Numbers indicate the lengths of the sides of the triangles) If the area of \(\bigtriangleup\) PQR is k2sq. units what is the area of the shades portion? A. units B. units C. units D. units E. u Detailed SolutionArea of shaded portion = Area of triangle PQR - Area of inner triangleArea of triangle given 3 sides a, b, c = \(\sqrt{s(s - a)(s - b)(s - c)}\) where \(s = \frac{a + b + c}{2} \) Area of PQR : \(s = \frac{3 + 5 + 6}{2} = \frac{14}{2} = 7\) Area = \(\sqrt{7(7 - 3)(7 - 5)(7 - 6)}\) = \(\sqrt{7(4)(2)(1)} = \sqrt{56}\) \(\implies K^{2} = \sqrt{56}\) Area of inner triangle : \(s = \frac{2 + 4 + \frac{10}{3}}{2} = \frac{14}{3}\) Area = \(\sqrt{\frac{14}{3} (\frac{14}{3} - 2)(\frac{14}{3} - 4)(\frac{14}{3} - \frac{10}{3})}\) = \(\sqrt{\frac{14}{3} (\frac{8}{3})(\frac{2}{3})(\frac{4}{3})}\) = \(\sqrt{\frac{896}{81}}\) = \(\sqrt{\fr |
|
| 48. |
 In the parallelogram PQRS, PE is perpendicular to QR. Find the area of the parallelogram. A. 60cm2 B. 65cm2 C. 72cm2 D. 132cm2 E. 156cm2 Detailed SolutionBy Pythagoras, PE\(^2\) = 12\(^2\) - 5\(^2\)= 144 - 25 = 119 h = PE\(^2\) = √119 = 10.9 ≈ 11cm, Area of 11gm = b x h QR = b =(5 + 7)cm = 12cm area = 12 x 11 = 132cm\(^2\) |
|
| 49. |
 PQ is parallel to RS. Calculate the value of x. A. 20o B. 40o C. 60o D. 80o E. 100o Detailed Solution< D = 180o - 100v= 80o (< on a str. line) < s = 60o - alternate angle x = 180o - (80o + 60o) 180o - 140o = 40o |
|
| 50. |
 Find x in the diagram below. A. 3\(\sqrt{3}\) B. \(\frac{3(\sqrt{3} - 1)}{\sqrt{3} + 1}\) C. \(\frac{(\sqrt{3} - 1)}{\sqrt{3} + 1}\) D. \(\frac{3 - 1}{\sqrt{3} + 1}\) Detailed Solution\(\frac{x + 3}{sin 60^o}\) = \(\frac{x}{sin 306o}\)3sin 30o = x sin 60o - x sin 30o = x(sin 60o - sin 30o) but sin 30o = \(\frac{1}{2}\) sin 60o = \(\frac{3}{2}\) = \(\frac{3(\sqrt{3} - 1)}{\sqrt{3} + 1}\) |