Year :
2017
Title :
Biology
Exam :
JAMB Exam
Paper 1 | Objectives
11 - 20 of 49 Questions
| # | Question | Ans |
|---|---|---|
| 11. |
Size, colour and fingerprints are examples of ______ A. physiological variation B. discontinuous variation C. morphological variation D. adaptive variation Detailed SolutionMorphological variation includes aspects of the outward appearance i.e shape, structure, color, pattern, size which is in contrast to physiology variation which deals primarily with function.Morphological variation arises from a number of factors which can be bluntly classified as either genetic or environmental implanted into the process of evolution. There is an explanation video available below. |
|
| 12. |
The level of organization in spirogyra and volvox is A. organ B. system C. cell D. Tissue Detailed SolutionThe spirogyra and volvox are cells. The spirogyra is a cell acting as a FILAMENT while in the Volvox, it's a cell as a COLONY.There is an explanation video available below. |
|
| 13. |
Which of the following scenarios is an example of cohesion? A. Water molecules stick to the surface of a mirror. B. Water sticks to the walls of blood vessels. C. Water molecules stay on the tip of a pine needle because the water is attracted to the surface of the needle. D. Water molecules stick to one another and form a bead |
|
| 14. |
The common thing in plant and animal cell is A. chloroplast B. cell wall C. nucleus D. centrioles |
|
| 15. |
The modification in structure, physiology and behaviour of plant and animal is called ______ A. adaptation B. evolution C. variation D. succession Detailed SolutionAdaptation is process by which an animal or plant species becomes fitted to its environment; it is the result of natural selection’s acting upon heritable variation. Even the simpler organisms must be adapted in a great variety of ways: in their structure, physiology, and genetics, in their locomotion or dispersal, in their means of defense and attack, in their reproduction and development, and in other respects.Evolution explains how living things change over a long time, and how they have come to be the way they are Variation is any difference between cells, individual organisms, or groups of organisms of any species caused either by genetic differences (genotypic variation) or |
|
| 16. |
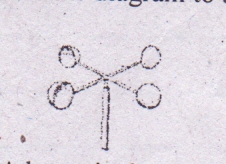 Use the diagram to answer the question that follows A. atmospheric pressure B. relative humidity C. direction of wind D. speed of wind Detailed SolutionAn Anemometer is a device used for measuring wind speed and direction.There is an explanation video available below. |
|
| 17. |
A bacteria that is spherically shaped is called? A. diplobacillus B. coccus C. bacillus D. vibrio |
|
| 18. |
The flame cells are used for excretion in A. Fluke B. Nematode C. Bacteria D. Volvox |
|
| 19. |
Food chain refers to the feeding relationships between animals in a ______? A. Family B. phylum C. community D. group |
|
| 20. |
The host of Taenia Solium is _________ A. cow B. pig C. sheep D. dog |
| 11. |
Size, colour and fingerprints are examples of ______ A. physiological variation B. discontinuous variation C. morphological variation D. adaptive variation Detailed SolutionMorphological variation includes aspects of the outward appearance i.e shape, structure, color, pattern, size which is in contrast to physiology variation which deals primarily with function.Morphological variation arises from a number of factors which can be bluntly classified as either genetic or environmental implanted into the process of evolution. There is an explanation video available below. |
|
| 12. |
The level of organization in spirogyra and volvox is A. organ B. system C. cell D. Tissue Detailed SolutionThe spirogyra and volvox are cells. The spirogyra is a cell acting as a FILAMENT while in the Volvox, it's a cell as a COLONY.There is an explanation video available below. |
|
| 13. |
Which of the following scenarios is an example of cohesion? A. Water molecules stick to the surface of a mirror. B. Water sticks to the walls of blood vessels. C. Water molecules stay on the tip of a pine needle because the water is attracted to the surface of the needle. D. Water molecules stick to one another and form a bead |
|
| 14. |
The common thing in plant and animal cell is A. chloroplast B. cell wall C. nucleus D. centrioles |
|
| 15. |
The modification in structure, physiology and behaviour of plant and animal is called ______ A. adaptation B. evolution C. variation D. succession Detailed SolutionAdaptation is process by which an animal or plant species becomes fitted to its environment; it is the result of natural selection’s acting upon heritable variation. Even the simpler organisms must be adapted in a great variety of ways: in their structure, physiology, and genetics, in their locomotion or dispersal, in their means of defense and attack, in their reproduction and development, and in other respects.Evolution explains how living things change over a long time, and how they have come to be the way they are Variation is any difference between cells, individual organisms, or groups of organisms of any species caused either by genetic differences (genotypic variation) or |
| 16. |
 Use the diagram to answer the question that follows A. atmospheric pressure B. relative humidity C. direction of wind D. speed of wind Detailed SolutionAn Anemometer is a device used for measuring wind speed and direction.There is an explanation video available below. |
|
| 17. |
A bacteria that is spherically shaped is called? A. diplobacillus B. coccus C. bacillus D. vibrio |
|
| 18. |
The flame cells are used for excretion in A. Fluke B. Nematode C. Bacteria D. Volvox |
|
| 19. |
Food chain refers to the feeding relationships between animals in a ______? A. Family B. phylum C. community D. group |
|
| 20. |
The host of Taenia Solium is _________ A. cow B. pig C. sheep D. dog |