Year :
2011
Title :
Chemistry
Exam :
JAMB Exam
Paper 1 | Objectives
21 - 30 of 47 Questions
| # | Question | Ans |
|---|---|---|
| 21. |
A chemical reaction which the hydration energy is greater than the lattice energy is referred to as A. a spontaneous reaction B. an endothermic reaction C. an exothermic reaction D. a reversible reaction Detailed SolutionWhen the hydration energy is greater than the lattice energy, then it is exothermic.There is an explanation video available below. |
|
| 22. |
The function of zinc electrode in a galvanic cells is that it A. undergoes reduction B. serves as the positive electrode C. production of electons D. uses up electrons Detailed SolutionIf an external electrical conductor connects the copper and zinc electrodes, zinc from the zinc electrode dissolves into the solution as Zn2+ ions (oxidation), releasing electrons that enter the external conductor.There is an explanation video available below. |
|
| 23. |
CH4(g) + Cl2(g) → CH3 Cl(s) + HCl(g) A. catalyst B. temperature C. concentration D. light |
|
| 24. |
The condition required for corrosion to take place is the presence of A. water and carbon (IV) oxide B. water, carbon (IV) oxide and oxygen C. oxygen and carbon (IV) oxide D. water and oxygen |
|
| 25. |
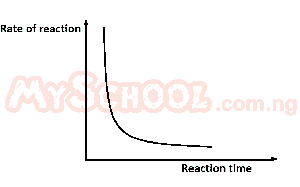 The diagram above best illustrates the effect of decrease in A. concentration B. temperature C. surface area D. pressure |
|
| 26. |
MnO-4(aq) + Y + 5Fe2+(aq) → Mn2+(aq) + 5Fe2+(aq) + 4H2O(l) A. 5H+(aq) B. 4H+(aq) C. 10H+(aq) D. 8H+(aq) |
|
| 27. |
Given that M is the mass of a substance deposited during electrolysis and Q is the quantity of electricity consumed, then Faraday's first law can be written as A. M = E/Q B. M = EQ C. M = Q/E D. M = E/2Q |
|
| 28. |
The impurities formed during the laboratory preparation of chlorine gas are removed by A. H2O B. NH3 C. H2SO4 D. HCl |
|
| 29. |
The effect of the presence of impurities such as carbon and sulphur on iron is that they A. give it high tensile strenght B. make it malleable and ductile C. increase its melting point D. lower its melting point |
|
| 30. |
A few drops of concentrated HNO\(_3\) is added to an unknown solution and boiled for a while. If this produces a brown solution, the cation present is likely to be A. Pb2+ B. Cu2+ C. Fe3+ D. Fe2+ Detailed SolutionThe brown color indicates the presence of iron (III) (Fe\(^{3+}\)).There is an explanation video available below. |
| 21. |
A chemical reaction which the hydration energy is greater than the lattice energy is referred to as A. a spontaneous reaction B. an endothermic reaction C. an exothermic reaction D. a reversible reaction Detailed SolutionWhen the hydration energy is greater than the lattice energy, then it is exothermic.There is an explanation video available below. |
|
| 22. |
The function of zinc electrode in a galvanic cells is that it A. undergoes reduction B. serves as the positive electrode C. production of electons D. uses up electrons Detailed SolutionIf an external electrical conductor connects the copper and zinc electrodes, zinc from the zinc electrode dissolves into the solution as Zn2+ ions (oxidation), releasing electrons that enter the external conductor.There is an explanation video available below. |
|
| 23. |
CH4(g) + Cl2(g) → CH3 Cl(s) + HCl(g) A. catalyst B. temperature C. concentration D. light |
|
| 24. |
The condition required for corrosion to take place is the presence of A. water and carbon (IV) oxide B. water, carbon (IV) oxide and oxygen C. oxygen and carbon (IV) oxide D. water and oxygen |
|
| 25. |
 The diagram above best illustrates the effect of decrease in A. concentration B. temperature C. surface area D. pressure |
| 26. |
MnO-4(aq) + Y + 5Fe2+(aq) → Mn2+(aq) + 5Fe2+(aq) + 4H2O(l) A. 5H+(aq) B. 4H+(aq) C. 10H+(aq) D. 8H+(aq) |
|
| 27. |
Given that M is the mass of a substance deposited during electrolysis and Q is the quantity of electricity consumed, then Faraday's first law can be written as A. M = E/Q B. M = EQ C. M = Q/E D. M = E/2Q |
|
| 28. |
The impurities formed during the laboratory preparation of chlorine gas are removed by A. H2O B. NH3 C. H2SO4 D. HCl |
|
| 29. |
The effect of the presence of impurities such as carbon and sulphur on iron is that they A. give it high tensile strenght B. make it malleable and ductile C. increase its melting point D. lower its melting point |
|
| 30. |
A few drops of concentrated HNO\(_3\) is added to an unknown solution and boiled for a while. If this produces a brown solution, the cation present is likely to be A. Pb2+ B. Cu2+ C. Fe3+ D. Fe2+ Detailed SolutionThe brown color indicates the presence of iron (III) (Fe\(^{3+}\)).There is an explanation video available below. |