Year :
1980
Title :
Mathematics (Core)
Exam :
JAMB Exam
Paper 1 | Objectives
41 - 49 of 49 Questions
| # | Question | Ans |
|---|---|---|
| 41. |
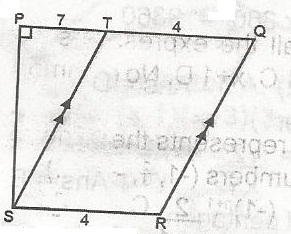
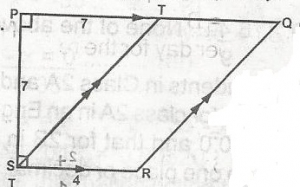 In the figure, PQ\\SR, ST\\, ST\\RQ, PS = 7cm, PT = 7cm, SR = 4cm. Find the ratio of the area QRST to the area of PQRS. A. 56.77 B. 56.105 C. 28:105 D. 28:49 E. 56:49 Detailed Solution
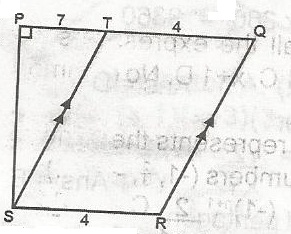 Area of PQRS = \(\frac{1}{2}\)(4 + 11) x 7 = \(\frac{7}{2}\) x \(\frac{15}{1}\) = 28:52.5 = 56:105 |
|
| 42. |
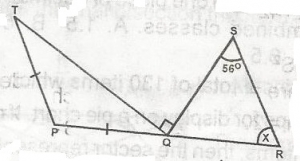 In the figure, If PT is parallel to RS, PQ = PT, and angle SQT = 90o, Find x A. 35o B. 50o C. 55o D. 70o E. 80o |
D |
| 43. |
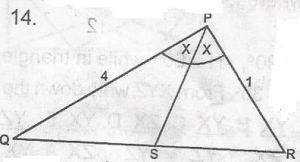 In the figure, PS bisects angle QPR. Find the ratio SR:QR. A. 1:2 B. 1:3 C. 1:4 D. 1:5 E. 1:6 Detailed SolutionFrom Internal bisection theorem, \(\frac{QP}{PR}\) = \(\frac{QS}{SR}\)= \(\frac{4}{1}\) = 1:4 |
|
| 44. |
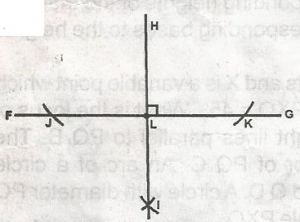 FG is a given straight line and H is a fixed point. The construction marks shown in the diagram indicate the A. perpendicular bisector of the line B. perpendicular bisector of th eline JK C. perpendicular bisector of the line HI D. perpendicular from H to the line FG |
D |
| 45. |
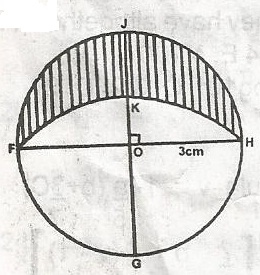 In the figure, FGHJ is a circle of radius 3cm centre O. FOH, GOJ are perpendicular diameters. With G as centre of an arc of a circle is drawn to pass through F and H. Find the length of the perimeter of the lunar portion shaded. A. 3\(\pi\)\(\sqrt{2 - 1}\)cm B. \(\frac{9}{2}\)\(\pi\)cm C. 3 \(\pi\)(1 + \(\frac{2}{2}\)) D. 3(1 + \(\frac{2}{2}\)) Detailed SolutionPerimeter of lunar portion = 3\(\pi\) + \(\frac{3\pi \sqrt{2}}{2}\)= 3 \(\pi\)(1 + \(\frac{2}{2}\)) |
|
| 46. |
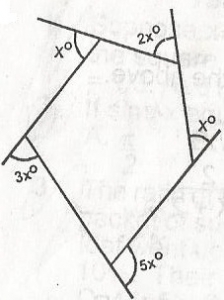 The angles marked in the figure are measured in degrees. Find x. A. 45o B. 90o C. 60o D. 15o E. 30o Detailed SolutionSum of external angles = 360o3x + 5x + x + 2x + x = 360o 12x = 360o x = 30o |
|
| 47. |
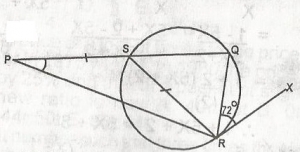 In the figure, PS = SR and Rx is a tangent to the circle at R, < QRX is equal to 72o. Find P A. 20o B. 36o C. 72o D. 30o E. 15o Detailed SolutionXRQ = RSQ (Alternate segment)s = 72o (80o - 72o = 180o) a + b + c = 190o = 2b + c = 180o 2b + 108 = 180o 2b = 72o b = 36o |
|
| 48. |
If \(\theta\) = \(\frac{3}{2}\) and \(\theta\) is less than 90o, calculate tan \(\frac{(90 - \theta)}{cos^2\theta}\) A. \(\frac{1}{2}\) B. \(\frac{4}{\sqrt{3}}\) C. \(\sqrt{3}\) D. 4\(\sqrt{3}\) |
B |
| 49. |
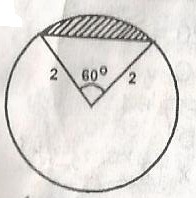 Find the area of the shades segments in the figure A. \(\sqrt{3} B. 4 \(\pi - \sqrt{3}\) C. -\(\frac{2}{3} \pi\) D. \(\frac{2\pi}{3}\) -3 Detailed SolutionArea of section = \(\frac{60^o}{360^o}\) x 11r2= \(\frac{60}{360} \times \pi \times 2^2\) = \(\frac{1}{6}\) x 4 = \(\frac{4\pi}{6}\) = \(\frac{2\pi}{3}\) Area of triangle = \(\frac{1}{2x}\) = 2 x 28.......60 Segment Area = Area of section - Area of triangle = \(\frac{2\pi}{3}\) -3 |
| 41. |
 In the figure, PQ\\SR, ST\\, ST\\RQ, PS = 7cm, PT = 7cm, SR = 4cm. Find the ratio of the area QRST to the area of PQRS. A. 56.77 B. 56.105 C. 28:105 D. 28:49 E. 56:49 Detailed Solution
 Area of PQRS = \(\frac{1}{2}\)(4 + 11) x 7 = \(\frac{7}{2}\) x \(\frac{15}{1}\) = 28:52.5 = 56:105 |
|
| 42. |
 In the figure, If PT is parallel to RS, PQ = PT, and angle SQT = 90o, Find x A. 35o B. 50o C. 55o D. 70o E. 80o |
D |
| 43. |
 In the figure, PS bisects angle QPR. Find the ratio SR:QR. A. 1:2 B. 1:3 C. 1:4 D. 1:5 E. 1:6 Detailed SolutionFrom Internal bisection theorem, \(\frac{QP}{PR}\) = \(\frac{QS}{SR}\)= \(\frac{4}{1}\) = 1:4 |
|
| 44. |
 FG is a given straight line and H is a fixed point. The construction marks shown in the diagram indicate the A. perpendicular bisector of the line B. perpendicular bisector of th eline JK C. perpendicular bisector of the line HI D. perpendicular from H to the line FG |
D |
| 45. |
 In the figure, FGHJ is a circle of radius 3cm centre O. FOH, GOJ are perpendicular diameters. With G as centre of an arc of a circle is drawn to pass through F and H. Find the length of the perimeter of the lunar portion shaded. A. 3\(\pi\)\(\sqrt{2 - 1}\)cm B. \(\frac{9}{2}\)\(\pi\)cm C. 3 \(\pi\)(1 + \(\frac{2}{2}\)) D. 3(1 + \(\frac{2}{2}\)) Detailed SolutionPerimeter of lunar portion = 3\(\pi\) + \(\frac{3\pi \sqrt{2}}{2}\)= 3 \(\pi\)(1 + \(\frac{2}{2}\)) |
| 46. |
 The angles marked in the figure are measured in degrees. Find x. A. 45o B. 90o C. 60o D. 15o E. 30o Detailed SolutionSum of external angles = 360o3x + 5x + x + 2x + x = 360o 12x = 360o x = 30o |
|
| 47. |
 In the figure, PS = SR and Rx is a tangent to the circle at R, < QRX is equal to 72o. Find P A. 20o B. 36o C. 72o D. 30o E. 15o Detailed SolutionXRQ = RSQ (Alternate segment)s = 72o (80o - 72o = 180o) a + b + c = 190o = 2b + c = 180o 2b + 108 = 180o 2b = 72o b = 36o |
|
| 48. |
If \(\theta\) = \(\frac{3}{2}\) and \(\theta\) is less than 90o, calculate tan \(\frac{(90 - \theta)}{cos^2\theta}\) A. \(\frac{1}{2}\) B. \(\frac{4}{\sqrt{3}}\) C. \(\sqrt{3}\) D. 4\(\sqrt{3}\) |
B |
| 49. |
 Find the area of the shades segments in the figure A. \(\sqrt{3} B. 4 \(\pi - \sqrt{3}\) C. -\(\frac{2}{3} \pi\) D. \(\frac{2\pi}{3}\) -3 Detailed SolutionArea of section = \(\frac{60^o}{360^o}\) x 11r2= \(\frac{60}{360} \times \pi \times 2^2\) = \(\frac{1}{6}\) x 4 = \(\frac{4\pi}{6}\) = \(\frac{2\pi}{3}\) Area of triangle = \(\frac{1}{2x}\) = 2 x 28.......60 Segment Area = Area of section - Area of triangle = \(\frac{2\pi}{3}\) -3 |