Year :
2019
Title :
Economics
Exam :
WASSCE/WAEC MAY/JUNE
Paper 1 | Objectives
11 - 20 of 50 Questions
| # | Question | Ans |
|---|---|---|
| 11. |
Which of the following factors is not a condition for a change in the supply of a commodity A. improved technoly B. cost of production C. the price of the commodity D. government tax policies Detailed SolutionSome of the factors that may cause a change in supply include; changes in the costs of production, improvements in technology, taxes, subsidies, weather conditions, health of livestock, and also by the price of other products.The price of the commodity itself does not affect the change in supply, but rather it affects the change in the quantity supplied. |
|
| 12. |
Supply of agricultural products is likely to be elastic in the A. intermediate period B. long-run C. market period D. short-run Detailed SolutionThe elasticity of supply measures how changes in prices would affect supply. The supply of agricultural products is most likely to be elastic in the long run, (a period of time where all factors of production and costs are variable). This means that in the long run, the cost of farm inputs and factors of production used in farming would be subject to change, and farmers cannot as a matter of fact place a fixed cost on their estimated expenses |
|
| 13. |
Two commodities X and Y are in joint supply when A. X is a by-product of Y B. X and Y are produced by the same firm C. increase in the quantity of X leads to a decrease in Y D. X and Y cannot be produced in the same process |
B |
| 14. |
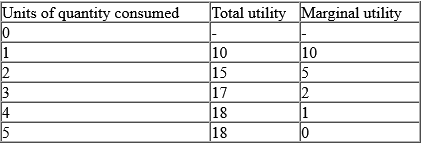 The table above illustrates the law of? A. diminishing returns B. diminishing marginal productivity C. diminishing marginal utility D. variable proportion Detailed SolutionThe law of diminishing marginal utility explains that all things being the same, as consumption increases, the marginal utility derived from each additional unit of a commodity declines.What this means is that, as you consume a particular commodity, the satisfaction derived from it increases, but it gets to a point where additional consumption of that particular product will no longer give you as much satisfaction as the first few ones you consumed. From the table above, the consumer started from 1 unit to five units, and at first, the total utility derived from consuming the product was rising from 10 -> 15 -> 17 -> 18 and remained at 18 However, the marginal utility kept declining after co |
|
| 15. |
When the price of a good is above the equilibrium, there will be A. a shortage B. a surplus. C. unemployment D. inflation Detailed SolutionIf the price of a good is above equilibrium, this means that the quantity of the good supplied exceeds the quantity of the good demanded. There is a surplus of the goods on the market. |
|
| 16. |
What happens when a minimum price is imposed in a market? A. Shortage occurs B. Surplus occurs C. market maintains its equilibrium D. Many firms will close down Detailed SolutionA minimum price is when the government doesn't allow prices to go below a certain level. At this point, suppliers will be willing to supply more in the market because they are certain to sell above a particular price. This will lead to a surplus in the market.The minimum price policy has been used in agriculture to increase farmers' income. |
|
| 17. |
When an increase in inputs leads to a more than proportionate increase in output, there is A. decreasing returns to scale B. Increase in marginal product C. increasing retums to scale D. constant retums to scale Detailed SolutionIncreasing returns to scale happens when the output increases in a greater proportion than the increase in input. |
|
| 18. |
The short-run in production is the time period when A. techniques of production can easily be changed B. all factors of production are vaiable C. at least a factor is fixed while others are variable D. variable factors cannot be changed Detailed SolutionThe short-run production phase refers to a production cycle in which at least one factor of production is fixed. |
|
| 19. |
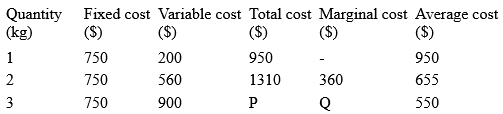 The table above shows the short-run cost of a firm. Use it to answer the question below. A. $350 B. $340 C. $360 D. $370 Detailed SolutionTo get Q, we first have to solve for P, hence we have;Total cost (P) = fixed cost + variable 750 + 900 = 1650 Marginal cost (Q) = 1650 - 1310 = 340 |
|
| 20. |
A cost of production that is positively related to output is the A. total fixed cost B. average fioxed cost C. variable cost D. social cost Detailed SolutionVariable cost has a positive relationship with output in such a way that if a firm produces more output, the variable cost will be greater, and if a firm produces no output, then the variable cost will be zero. The variable cost depends on the level of output. |
| 11. |
Which of the following factors is not a condition for a change in the supply of a commodity A. improved technoly B. cost of production C. the price of the commodity D. government tax policies Detailed SolutionSome of the factors that may cause a change in supply include; changes in the costs of production, improvements in technology, taxes, subsidies, weather conditions, health of livestock, and also by the price of other products.The price of the commodity itself does not affect the change in supply, but rather it affects the change in the quantity supplied. |
|
| 12. |
Supply of agricultural products is likely to be elastic in the A. intermediate period B. long-run C. market period D. short-run Detailed SolutionThe elasticity of supply measures how changes in prices would affect supply. The supply of agricultural products is most likely to be elastic in the long run, (a period of time where all factors of production and costs are variable). This means that in the long run, the cost of farm inputs and factors of production used in farming would be subject to change, and farmers cannot as a matter of fact place a fixed cost on their estimated expenses |
|
| 13. |
Two commodities X and Y are in joint supply when A. X is a by-product of Y B. X and Y are produced by the same firm C. increase in the quantity of X leads to a decrease in Y D. X and Y cannot be produced in the same process |
B |
| 14. |
 The table above illustrates the law of? A. diminishing returns B. diminishing marginal productivity C. diminishing marginal utility D. variable proportion Detailed SolutionThe law of diminishing marginal utility explains that all things being the same, as consumption increases, the marginal utility derived from each additional unit of a commodity declines.What this means is that, as you consume a particular commodity, the satisfaction derived from it increases, but it gets to a point where additional consumption of that particular product will no longer give you as much satisfaction as the first few ones you consumed. From the table above, the consumer started from 1 unit to five units, and at first, the total utility derived from consuming the product was rising from 10 -> 15 -> 17 -> 18 and remained at 18 However, the marginal utility kept declining after co |
|
| 15. |
When the price of a good is above the equilibrium, there will be A. a shortage B. a surplus. C. unemployment D. inflation Detailed SolutionIf the price of a good is above equilibrium, this means that the quantity of the good supplied exceeds the quantity of the good demanded. There is a surplus of the goods on the market. |
| 16. |
What happens when a minimum price is imposed in a market? A. Shortage occurs B. Surplus occurs C. market maintains its equilibrium D. Many firms will close down Detailed SolutionA minimum price is when the government doesn't allow prices to go below a certain level. At this point, suppliers will be willing to supply more in the market because they are certain to sell above a particular price. This will lead to a surplus in the market.The minimum price policy has been used in agriculture to increase farmers' income. |
|
| 17. |
When an increase in inputs leads to a more than proportionate increase in output, there is A. decreasing returns to scale B. Increase in marginal product C. increasing retums to scale D. constant retums to scale Detailed SolutionIncreasing returns to scale happens when the output increases in a greater proportion than the increase in input. |
|
| 18. |
The short-run in production is the time period when A. techniques of production can easily be changed B. all factors of production are vaiable C. at least a factor is fixed while others are variable D. variable factors cannot be changed Detailed SolutionThe short-run production phase refers to a production cycle in which at least one factor of production is fixed. |
|
| 19. |
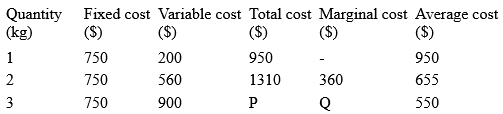 The table above shows the short-run cost of a firm. Use it to answer the question below. A. $350 B. $340 C. $360 D. $370 Detailed SolutionTo get Q, we first have to solve for P, hence we have;Total cost (P) = fixed cost + variable 750 + 900 = 1650 Marginal cost (Q) = 1650 - 1310 = 340 |
|
| 20. |
A cost of production that is positively related to output is the A. total fixed cost B. average fioxed cost C. variable cost D. social cost Detailed SolutionVariable cost has a positive relationship with output in such a way that if a firm produces more output, the variable cost will be greater, and if a firm produces no output, then the variable cost will be zero. The variable cost depends on the level of output. |