Year :
1995
Title :
Mathematics (Core)
Exam :
WASSCE/WAEC MAY/JUNE
Paper 1 | Objectives
31 - 40 of 48 Questions
| # | Question | Ans |
|---|---|---|
| 31. |
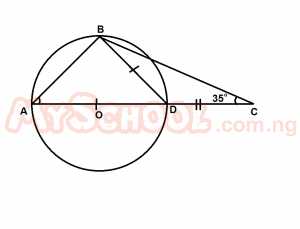 In the diagram above; O is the centre of the circle and |BD| = |DC|. If ∠DCB = 35°, find ∠BAO. A. 20o B. 25o C. 30o D. 35o E. 40o Detailed Solution< DBC = 35° (base angles of an isosceles triangle)< CDB = 180° - (35° + 35°) = 110° < ADB = 70°; < ADB = 90° \(\therefore\) < BAO = 180° - (70° + 90°) = 20° |
|
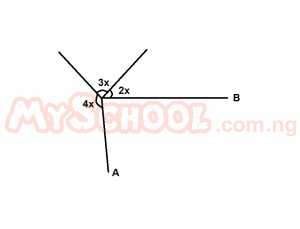
| 32. |
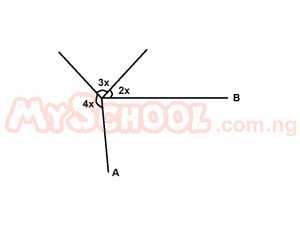 In the diagram above, AO is perpendicular to OB. Find x A. 7.5o B. 15o C. 22.5o D. 30o E. 38.6o Detailed Solution
9x + 90 = 360° 9x = 360° - 90° 9x = 270 x = 270/9 x = 30° |
|
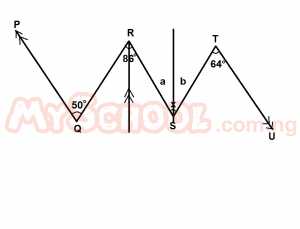
| 33. |
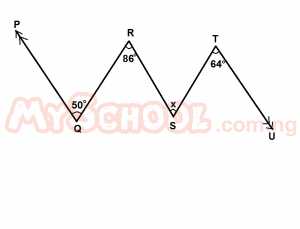 In the diagram above, PQ is parallel to TU, ∠PQR = 50°, ∠QRS = 86° and ∠STU = 64°. Calculate the value of x. A. 136o B. 120o C. 108o D. 100o E. 96o Detailed Solution
y = 86° - 50° = 36° a = y = 36° [Alternate ∠s]; b = 64° [Alternate ∠s;] x = a + b = (36° + 64°) =100° |
|
| 34. |
If log\(_{10}\) x = \(\bar{2}.3675\) and log\(_{10}\) y = \(\bar{2}.9738\), what is the value of x + y, correct lo three significant figures? A. O.117 B. 0.118 C. 0.903 D. O.944 E. 0.946 Detailed Solutionlog\(_{10}\) x = \(\bar{2}.3675\) => x = 0.023log\(_{10}\) y = \(\bar{2}.9738\) => y = 0.094 x + y = 0.117 |
|
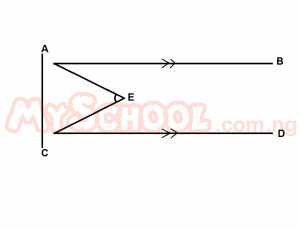
| 35. |
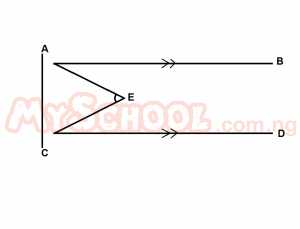 In the diagram above, AB//CD, the bisector of ∠BAC and ∠ACD meet at E. Find the value of ∠AEC A. 30o B. 45o C. 60o D. 75o E. 90o Detailed Solution
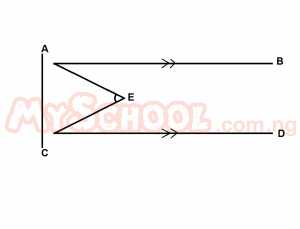 CE is the bisector of ACD => ACE = 45o AEC = 180o - [EAC + ACE] = 180o - (45o + 45o) = 180o - 90o = 90o |
|
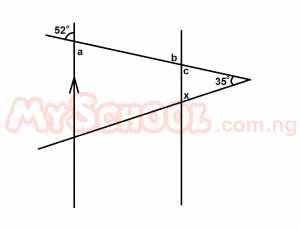
| 36. |
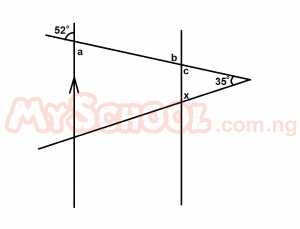 In the diagram above, AB//CD. What is the size of the angle marked x? A. 103o B. 93o C. 77o D. 62o E. 52o Detailed Solution
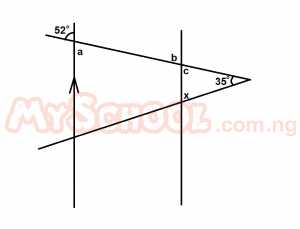 a = b = 52o [Alternate ∠s] b = c = 52o [vertical opp ∠s] c + x + 35o = 180o [sum of angles in a triangle] 52o + x + 35o = 180o x + 87o = 180o x = 180o - 87o = 93o < |
|
| 37. |
The locus of a point which is equidistant from two given fixed points is the A. perpendicular bisector of the straight line joining them B. angle bisector of the straight lines joining the points to the origin C. perpendiculars to the straight line joining them D. parallel-line to the straight line joining them E. a line making an acute angle with the line joining the two points |
A |
| 38. |
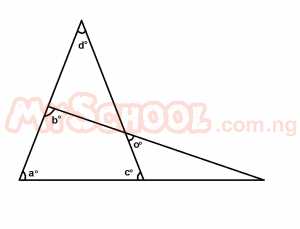
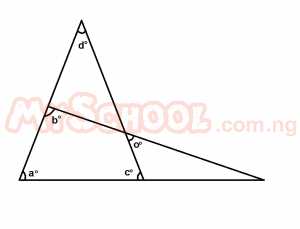 In the diagram above, the value of angles b + c is A. 180o B. 90o C. 45o D. ao E. do Detailed Solution
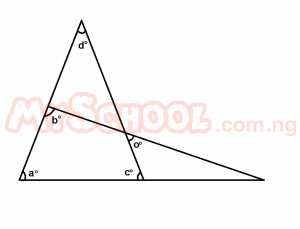 x = a[vertical opp. ∠s] y + x + d = 180o[sum of ∠s in a Δ] y + a + d = 180o y + a + d = a + c + d y = c but b + y = 180o [sum of ∠s on a straight line ] b + c = 180o; Ans = A = 180o |
|
| 39. |
Which of the following angles is an exterior angle of a regular polygon? A. 95o B. 85o C. 78o D. 75o E. 72o Detailed SolutionThe formula for the exterior angle of a regular polygon = \(\frac{360}{n}\).Among the options, only 72° is divisible by 360° to give an integer. |
|
| 40. |
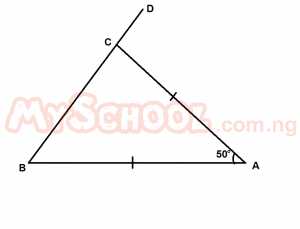 In ΔABC above, BC is produced to D, /AB/ = /AC/ and ∠BAC = 50o. Find ∠ACD A. 50o B. 60o C. 65o D. 100o E. 115o Detailed SolutionACB = ABC [Base angles of isoceles triangle]ACB + ABC + 50o = 180o[sum of angles in a triangle] ACB + ABC = 180o - 50o = 130o ACB 130o2 = 65oACD + ACB = 180o[sum of ∠s on a straight line] ACD + 65o = 180o ACD = |
| 31. |
 In the diagram above; O is the centre of the circle and |BD| = |DC|. If ∠DCB = 35°, find ∠BAO. A. 20o B. 25o C. 30o D. 35o E. 40o Detailed Solution< DBC = 35° (base angles of an isosceles triangle)< CDB = 180° - (35° + 35°) = 110° < ADB = 70°; < ADB = 90° \(\therefore\) < BAO = 180° - (70° + 90°) = 20° |
|
| 32. |
 In the diagram above, AO is perpendicular to OB. Find x A. 7.5o B. 15o C. 22.5o D. 30o E. 38.6o Detailed Solution
9x + 90 = 360° 9x = 360° - 90° 9x = 270 x = 270/9 x = 30° |
|
| 33. |
 In the diagram above, PQ is parallel to TU, ∠PQR = 50°, ∠QRS = 86° and ∠STU = 64°. Calculate the value of x. A. 136o B. 120o C. 108o D. 100o E. 96o Detailed Solution
y = 86° - 50° = 36° a = y = 36° [Alternate ∠s]; b = 64° [Alternate ∠s;] x = a + b = (36° + 64°) =100° |
|
| 34. |
If log\(_{10}\) x = \(\bar{2}.3675\) and log\(_{10}\) y = \(\bar{2}.9738\), what is the value of x + y, correct lo three significant figures? A. O.117 B. 0.118 C. 0.903 D. O.944 E. 0.946 Detailed Solutionlog\(_{10}\) x = \(\bar{2}.3675\) => x = 0.023log\(_{10}\) y = \(\bar{2}.9738\) => y = 0.094 x + y = 0.117 |
|
| 35. |
 In the diagram above, AB//CD, the bisector of ∠BAC and ∠ACD meet at E. Find the value of ∠AEC A. 30o B. 45o C. 60o D. 75o E. 90o Detailed Solution
 CE is the bisector of ACD => ACE = 45o AEC = 180o - [EAC + ACE] = 180o - (45o + 45o) = 180o - 90o = 90o |
| 36. |
 In the diagram above, AB//CD. What is the size of the angle marked x? A. 103o B. 93o C. 77o D. 62o E. 52o Detailed Solution
 a = b = 52o [Alternate ∠s] b = c = 52o [vertical opp ∠s] c + x + 35o = 180o [sum of angles in a triangle] 52o + x + 35o = 180o x + 87o = 180o x = 180o - 87o = 93o < |
|
| 37. |
The locus of a point which is equidistant from two given fixed points is the A. perpendicular bisector of the straight line joining them B. angle bisector of the straight lines joining the points to the origin C. perpendiculars to the straight line joining them D. parallel-line to the straight line joining them E. a line making an acute angle with the line joining the two points |
A |
| 38. |
 In the diagram above, the value of angles b + c is A. 180o B. 90o C. 45o D. ao E. do Detailed Solution
 x = a[vertical opp. ∠s] y + x + d = 180o[sum of ∠s in a Δ] y + a + d = 180o y + a + d = a + c + d y = c but b + y = 180o [sum of ∠s on a straight line ] b + c = 180o; Ans = A = 180o |
|
| 39. |
Which of the following angles is an exterior angle of a regular polygon? A. 95o B. 85o C. 78o D. 75o E. 72o Detailed SolutionThe formula for the exterior angle of a regular polygon = \(\frac{360}{n}\).Among the options, only 72° is divisible by 360° to give an integer. |
|
| 40. |
 In ΔABC above, BC is produced to D, /AB/ = /AC/ and ∠BAC = 50o. Find ∠ACD A. 50o B. 60o C. 65o D. 100o E. 115o Detailed SolutionACB = ABC [Base angles of isoceles triangle]ACB + ABC + 50o = 180o[sum of angles in a triangle] ACB + ABC = 180o - 50o = 130o ACB 130o2 = 65oACD + ACB = 180o[sum of ∠s on a straight line] ACD + 65o = 180o ACD = |