Year :
2018
Title :
Chemistry
Exam :
WASSCE/WAEC MAY/JUNE
Paper 1 | Objectives
41 - 50 of 50 Questions
| # | Question | Ans |
|---|---|---|
| 41. |
What is the relative molecular mass of a compound which has empirical formula \(CH_{2}O\)? [C= 12, H= 1, O= 16] A. 42 B. 45 C. 126 D. 180 Detailed SolutionMolecular formula = (empirical formula x n)where n= (1,2,3,...) \(CH_{2}O = 12 + (2\times 1) + 16 = 30\) Relative molecular mass = (30 x n) From the options, only 180 is a multiple of 30, when n=6. |
|
| 42. |
Atoms are electrically neutral because they A. do not conduct electricity B. contain equal number of protons and electrons C. are composed of neutrons and electrons D. cannot be attracted by electromagnetic field. Detailed SolutionAtoms are electrically neutral because they contain equal amount of positive and negative charge. This is because they have equal number of protons and electrons. |
|
| 43. |
Common Salt (NaCl) is used to preserve foods. Which of the following properties can be used to determine its purity before use? A. Solubility in water B. Melting point C. Relative density D. Crystalline nature |
B |
| 44. |
Which of the following electron configurations represents the transition element Chromium \(_{24}Cr\)? A. \(1s^{2} 2s^{2} 2p^{6} 3s^{2} 3p^{6} 4s^{2} 3d^{4}\) B. \(1s^{2}2s^{2}2p^{6}3s^{2}3p^{6}3d^{6}\) C. \(1s^{2}2s^{2}2p^{6}3s^{2}3d^{4} 4s^{1}\) D. \(1s^{2}2s^{2}2p^{6}3s^{2}3p^{6}4s^{1}3d^{5}\) |
A |
| 45. |
The atomic number of an isotope of hydrogen is equal to its mass number because it A. has a totally filled valence shell B. has a high charge to mass ratio C. does not contain neutrons D. exhibits isotopy |
C |
| 46. |
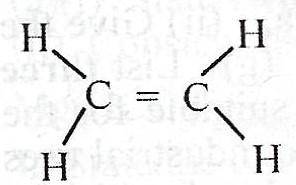 What is the total number of shared pair of electrons in the compound above? A. 5 B. 8 C. 10 D. 12 Detailed SolutionEach double bond has two pairs of valence electrons shared to form a covalent bonding. Also, every C-H bond, has 2 valence elctrons involved. Drawing the Lewis structure, you see that the above compound has 12 valence electrons shared. |
|
| 47. |
The bonding pair of electrons in a Hydrogen Chloride molecule is pulled towards the chlorine atom because A. chlorine has a larger atomic size B. chlorine has a larger atomic mass C. chlorine is more electronegative D. there is no bonding orbitals within the hydrogen atom Detailed SolutionThe chlorine atom is much more electronegative than the hydrogen atom, which makes this bond polar. |
|
| 48. |
The solubility of \(CO_{2}\) in water can be accounted for by A. Van der Waal's forces B. Ionic attraction C. dipole attraction D. covalent bonding Detailed SolutionIn CO2, due to electronegativity difference oxygens have slight negative charge, hence surrounded by polar water molecule forming a cage structure.This leads to its solubility. |
|
| 49. |
Which of the following properties would not influence electrovalent bond formation? A. Electronegativity B. Electron Affinity C. Ionization potential D. Catalytic ability Detailed SolutionEvery other factor influences the formation of elecrovalent or Ionic bonds except Catalytic ability. |
|
| 50. |
Particles in a solid exibit A. vibrational motion B. vibrational and translational motion C. vibrational and random motion D. random and translational motion Detailed SolutionSolids vibrate but generally do not move from place to place. |
| 41. |
What is the relative molecular mass of a compound which has empirical formula \(CH_{2}O\)? [C= 12, H= 1, O= 16] A. 42 B. 45 C. 126 D. 180 Detailed SolutionMolecular formula = (empirical formula x n)where n= (1,2,3,...) \(CH_{2}O = 12 + (2\times 1) + 16 = 30\) Relative molecular mass = (30 x n) From the options, only 180 is a multiple of 30, when n=6. |
|
| 42. |
Atoms are electrically neutral because they A. do not conduct electricity B. contain equal number of protons and electrons C. are composed of neutrons and electrons D. cannot be attracted by electromagnetic field. Detailed SolutionAtoms are electrically neutral because they contain equal amount of positive and negative charge. This is because they have equal number of protons and electrons. |
|
| 43. |
Common Salt (NaCl) is used to preserve foods. Which of the following properties can be used to determine its purity before use? A. Solubility in water B. Melting point C. Relative density D. Crystalline nature |
B |
| 44. |
Which of the following electron configurations represents the transition element Chromium \(_{24}Cr\)? A. \(1s^{2} 2s^{2} 2p^{6} 3s^{2} 3p^{6} 4s^{2} 3d^{4}\) B. \(1s^{2}2s^{2}2p^{6}3s^{2}3p^{6}3d^{6}\) C. \(1s^{2}2s^{2}2p^{6}3s^{2}3d^{4} 4s^{1}\) D. \(1s^{2}2s^{2}2p^{6}3s^{2}3p^{6}4s^{1}3d^{5}\) |
A |
| 45. |
The atomic number of an isotope of hydrogen is equal to its mass number because it A. has a totally filled valence shell B. has a high charge to mass ratio C. does not contain neutrons D. exhibits isotopy |
C |
| 46. |
 What is the total number of shared pair of electrons in the compound above? A. 5 B. 8 C. 10 D. 12 Detailed SolutionEach double bond has two pairs of valence electrons shared to form a covalent bonding. Also, every C-H bond, has 2 valence elctrons involved. Drawing the Lewis structure, you see that the above compound has 12 valence electrons shared. |
|
| 47. |
The bonding pair of electrons in a Hydrogen Chloride molecule is pulled towards the chlorine atom because A. chlorine has a larger atomic size B. chlorine has a larger atomic mass C. chlorine is more electronegative D. there is no bonding orbitals within the hydrogen atom Detailed SolutionThe chlorine atom is much more electronegative than the hydrogen atom, which makes this bond polar. |
|
| 48. |
The solubility of \(CO_{2}\) in water can be accounted for by A. Van der Waal's forces B. Ionic attraction C. dipole attraction D. covalent bonding Detailed SolutionIn CO2, due to electronegativity difference oxygens have slight negative charge, hence surrounded by polar water molecule forming a cage structure.This leads to its solubility. |
|
| 49. |
Which of the following properties would not influence electrovalent bond formation? A. Electronegativity B. Electron Affinity C. Ionization potential D. Catalytic ability Detailed SolutionEvery other factor influences the formation of elecrovalent or Ionic bonds except Catalytic ability. |
|
| 50. |
Particles in a solid exibit A. vibrational motion B. vibrational and translational motion C. vibrational and random motion D. random and translational motion Detailed SolutionSolids vibrate but generally do not move from place to place. |