Year :
1992
Title :
Mathematics (Core)
Exam :
WASSCE/WAEC MAY/JUNE
Paper 1 | Objectives
1 - 10 of 48 Questions
| # | Question | Ans |
|---|---|---|
| 1. |
Let U = {1, 2, 3, 4}, P = {2, 3} and Q = {2, 4}. What is (P∩Q)'? A. (1, 2, 3) B. (1, 3, 4) C. (2, 3) D. (1, 3) E. (1, 4) Detailed SolutionU = {1,2,3,4}; P = {2,3}; Q = {2,4}; P∩Q = {2}(P∩Q)' = {1,3,4} |
|
| 2. |
Simplify (3/4 + 1/3) x 41/3 + 31/4 A. 1/2 B. 13/12 C. 10/9 D. 17/12 E. 13/9 Detailed Solution(3/4 + 1/3) x 41/3 \(\div\) 314\(\begin{pmatrix} 9 + 4 \\ 12 \end{pmatrix}\) x \(\frac{13}{3}\) \(\frac{4}{13}\) = 149 |
|
| 3. |
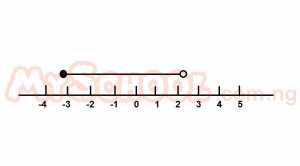 If x varies over the set of real numbers, which of the following is illustrated in the diagram above? A. -3 B. -3≤x<2 C. -3 D. -3≤x≤2 E. x≥2 |
B |
| 4. |
Convert 77 to a number in base two A. 1001 101 B. 111001 C. 100110 D. 10101 E. 10011 Detailed Solution\(\begin{array}{c|c} 2 & 77 \\ \hline 2 & 38 R1 \\ 2 & 19 R0 \\ 2 & 9 R1 \\ 2 & 4 R1 \\ 2 & 2 R0 \\ 2 & 1 R0 \\ & 0 R1\end{array}\)77ten = 1001101two |
|
| 5. |
A bricklayer measured the length of a wall and obtained 4.10m. If the actual length of the wall is 4.25m, find his percentage error. A. 3 9/17% B. 3 27/41% C. 15% D. 35 5/17% E. 36 24/41% Detailed SolutionError = 4.25 - 4.10 = 0.15% error = \(\frac{0.15}{4.25} \times 100%\) = \(\frac{15}{\frac{17}{4}} = \frac{15 \times 4}{17}\) = \(3\frac{9}{17} %\) |
|
| 6. |
The nth term of a sequence is given by 3.2\(^{n-2}\). Write down the first three terms of the sequence. A. 2/3, 0, 6 B. 3/2, 3, 6, C. 2/3, 3, 8/3 D. 2/3, 3/4, 6 E. 2/3, 3, 1/3 Detailed Solution\(T_n = 3. 2^{n - 2} \\T_{1} = 3. 2^{1 - 2} = 3. 2^{-1} \\ T_1 = \frac{3}{2} \) \(T_2 = 3. 2^{2 - 2} \\ T_2 = 3. 2^0 = 3\) \(T_3 = 3. 2^{3 - 2} = 3. 2^1 \\ T_3 = 6\) The first 3 terms of the sequence are \(\frac{3}{2}\), 3 and 6. |
|
| 7. |
Simplify: \((\frac{16}{81})^{\frac{1}{4}}\) A. 8/27 B. 1/3 C. 4/9 D. 2/3 E. -4/3 Detailed Solution\((\frac{16}{81})^{\frac{1}{4}}\)= \(((\frac{2}{3})^{4})^{\frac{1}{4}}\) = \(\frac{2}{3}\) |
|
| 8. |
Evaluate \(\log_{10} 25 + \log_{10} 32 - \log_{10} 8\) A. 0.2 B. 2 C. 100 D. 409 E. 490 Detailed Solution\(\log_{10} 25 + \log_{10} 32 - \log_{10} 8\)= \(\log_{10} (\frac{25 \times 32}{8})\) = \(\log_{10} 100 \) = 2 |
|
| 9. |
Factorize the expression 2y\(^2\) + xy - 3x\(^2\) A. 2y (y + x) - 3x2 B. (2y - x)(2y + x) C. (3x - 2y(x - y) D. (2y + 3x)(y - x) E. (x – y)(2y + 3x) Detailed Solution2y\(^2\) + xy - 3x\(^2\)2y\(^2\) + 3xy - 2xy - 3x\(^2\) y(2y + 3x) - x(2y + 3x) = (y - x)(2y + 3x) |
|
| 10. |
Construct a quadratic equation whose roots are \(-\frac{1}{2}\) and 2. A. 3x2-3x+2=0 B. 3x2+3x-2=0 C. 2x2+3x-2=0 D. 2x2-3x+2=0 E. 2x2-3x-2=0 Detailed SolutionIf x = \(-\frac{1}{2}\) and 2; then\(x + \frac{1}{2} = 0\) and \(x - 2 = 0\) \(\implies (x + \frac{1}{2})(x - 2) = 0\) \(x^2 - 2x + \frac{1}{2}x - 1 = 0\) \(x^2 - \frac{3}{2}x - 1 = 0\) \(2x^2 - 3x - 2 = 0\) |
| 1. |
Let U = {1, 2, 3, 4}, P = {2, 3} and Q = {2, 4}. What is (P∩Q)'? A. (1, 2, 3) B. (1, 3, 4) C. (2, 3) D. (1, 3) E. (1, 4) Detailed SolutionU = {1,2,3,4}; P = {2,3}; Q = {2,4}; P∩Q = {2}(P∩Q)' = {1,3,4} |
|
| 2. |
Simplify (3/4 + 1/3) x 41/3 + 31/4 A. 1/2 B. 13/12 C. 10/9 D. 17/12 E. 13/9 Detailed Solution(3/4 + 1/3) x 41/3 \(\div\) 314\(\begin{pmatrix} 9 + 4 \\ 12 \end{pmatrix}\) x \(\frac{13}{3}\) \(\frac{4}{13}\) = 149 |
|
| 3. |
 If x varies over the set of real numbers, which of the following is illustrated in the diagram above? A. -3 B. -3≤x<2 C. -3 D. -3≤x≤2 E. x≥2 |
B |
| 4. |
Convert 77 to a number in base two A. 1001 101 B. 111001 C. 100110 D. 10101 E. 10011 Detailed Solution\(\begin{array}{c|c} 2 & 77 \\ \hline 2 & 38 R1 \\ 2 & 19 R0 \\ 2 & 9 R1 \\ 2 & 4 R1 \\ 2 & 2 R0 \\ 2 & 1 R0 \\ & 0 R1\end{array}\)77ten = 1001101two |
|
| 5. |
A bricklayer measured the length of a wall and obtained 4.10m. If the actual length of the wall is 4.25m, find his percentage error. A. 3 9/17% B. 3 27/41% C. 15% D. 35 5/17% E. 36 24/41% Detailed SolutionError = 4.25 - 4.10 = 0.15% error = \(\frac{0.15}{4.25} \times 100%\) = \(\frac{15}{\frac{17}{4}} = \frac{15 \times 4}{17}\) = \(3\frac{9}{17} %\) |
| 6. |
The nth term of a sequence is given by 3.2\(^{n-2}\). Write down the first three terms of the sequence. A. 2/3, 0, 6 B. 3/2, 3, 6, C. 2/3, 3, 8/3 D. 2/3, 3/4, 6 E. 2/3, 3, 1/3 Detailed Solution\(T_n = 3. 2^{n - 2} \\T_{1} = 3. 2^{1 - 2} = 3. 2^{-1} \\ T_1 = \frac{3}{2} \) \(T_2 = 3. 2^{2 - 2} \\ T_2 = 3. 2^0 = 3\) \(T_3 = 3. 2^{3 - 2} = 3. 2^1 \\ T_3 = 6\) The first 3 terms of the sequence are \(\frac{3}{2}\), 3 and 6. |
|
| 7. |
Simplify: \((\frac{16}{81})^{\frac{1}{4}}\) A. 8/27 B. 1/3 C. 4/9 D. 2/3 E. -4/3 Detailed Solution\((\frac{16}{81})^{\frac{1}{4}}\)= \(((\frac{2}{3})^{4})^{\frac{1}{4}}\) = \(\frac{2}{3}\) |
|
| 8. |
Evaluate \(\log_{10} 25 + \log_{10} 32 - \log_{10} 8\) A. 0.2 B. 2 C. 100 D. 409 E. 490 Detailed Solution\(\log_{10} 25 + \log_{10} 32 - \log_{10} 8\)= \(\log_{10} (\frac{25 \times 32}{8})\) = \(\log_{10} 100 \) = 2 |
|
| 9. |
Factorize the expression 2y\(^2\) + xy - 3x\(^2\) A. 2y (y + x) - 3x2 B. (2y - x)(2y + x) C. (3x - 2y(x - y) D. (2y + 3x)(y - x) E. (x – y)(2y + 3x) Detailed Solution2y\(^2\) + xy - 3x\(^2\)2y\(^2\) + 3xy - 2xy - 3x\(^2\) y(2y + 3x) - x(2y + 3x) = (y - x)(2y + 3x) |
|
| 10. |
Construct a quadratic equation whose roots are \(-\frac{1}{2}\) and 2. A. 3x2-3x+2=0 B. 3x2+3x-2=0 C. 2x2+3x-2=0 D. 2x2-3x+2=0 E. 2x2-3x-2=0 Detailed SolutionIf x = \(-\frac{1}{2}\) and 2; then\(x + \frac{1}{2} = 0\) and \(x - 2 = 0\) \(\implies (x + \frac{1}{2})(x - 2) = 0\) \(x^2 - 2x + \frac{1}{2}x - 1 = 0\) \(x^2 - \frac{3}{2}x - 1 = 0\) \(2x^2 - 3x - 2 = 0\) |