Year :
2003
Title :
Biology
Exam :
JAMB Exam
Paper 1 | Objectives
1 - 10 of 50 Questions
| # | Question | Ans |
|---|---|---|
| 1. |
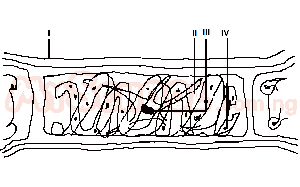 The structure that are common to both plant and animal cells are labelled A. IV and I B. II and IV C. II and III D. I and II |
C |
| 2. |
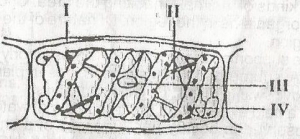 Food is stored in the structure labelled A. III B. I C. IV D. II |
C |
| 3. |
One distinctive feature in the life history of liverworts is that they exhibit A. Alternation of generation B. Vegetative reproduction C. Asexual reproduction D. Sexual reproduction |
A |
| 4. |
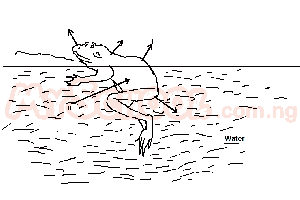 A noticeable adaptation of the animal to its aquatic habitat is the possession of A. a wide mouth B. large eyes C. webbed digits D. fore limbs |
C |
| 5. |
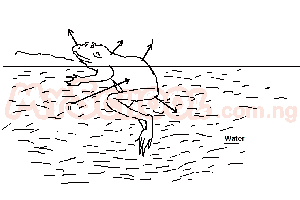 The process of water loss and intake indicated by the arrow labelled I and II are respectively A. exhalation and osmosis B. urination and diffusion C. osmosis and diffusion D. evaporation and osmosis Detailed Solution- Most frog species show little resistance to evaporative water loss (EWL) through their skin.- The movement of water across membranes from areas of high concentration (lots of water) to areas of low concentration (less water) is called osmosis. The reason frogs do not have to actively drink water and instead can sit in a bowl of water and absorb water passively is due, in large part, to osmosis. - That is, frogs do not drink like we do; they absorb water directly through their skin in an area known as the 'drinking patch' located on their belly and the underside of their thighs. |
|
| 6. |
The umbrella shaped fruiting body of a fully developed mushroom is the A. Pileus B. Mycelium C. Basidium D. Stipe |
A |
| 7. |
The similarity among organisms belonging to the same group will be least within each A. family B. order C. kingdom D. species |
C |
| 8. |
Hermophroditic reproduction can be found among the A. Arthropods and nematodes B. Pisces and amphibians C. Annelids and molluscs D. coelenterates and platyhelminthes Detailed SolutionMany platyhelminths ( flatworms) reproduce asexuallyCoelenterates reproduce asexually by budding. |
|
| 9. |
An insect whose economic importance is both harmful and beneficial is the A. Tsetsefly B. Blackfly C. Mosquito D. Butterfly |
D |
| 10. |
The cell component that is present in a prokaryotic cell is the A. Chloroplast B. Ribosome C. Mitochondrion D. Nuclear envelope |
B |
| 1. |
 The structure that are common to both plant and animal cells are labelled A. IV and I B. II and IV C. II and III D. I and II |
C |
| 2. |
 Food is stored in the structure labelled A. III B. I C. IV D. II |
C |
| 3. |
One distinctive feature in the life history of liverworts is that they exhibit A. Alternation of generation B. Vegetative reproduction C. Asexual reproduction D. Sexual reproduction |
A |
| 4. |
 A noticeable adaptation of the animal to its aquatic habitat is the possession of A. a wide mouth B. large eyes C. webbed digits D. fore limbs |
C |
| 5. |
 The process of water loss and intake indicated by the arrow labelled I and II are respectively A. exhalation and osmosis B. urination and diffusion C. osmosis and diffusion D. evaporation and osmosis Detailed Solution- Most frog species show little resistance to evaporative water loss (EWL) through their skin.- The movement of water across membranes from areas of high concentration (lots of water) to areas of low concentration (less water) is called osmosis. The reason frogs do not have to actively drink water and instead can sit in a bowl of water and absorb water passively is due, in large part, to osmosis. - That is, frogs do not drink like we do; they absorb water directly through their skin in an area known as the 'drinking patch' located on their belly and the underside of their thighs. |
| 6. |
The umbrella shaped fruiting body of a fully developed mushroom is the A. Pileus B. Mycelium C. Basidium D. Stipe |
A |
| 7. |
The similarity among organisms belonging to the same group will be least within each A. family B. order C. kingdom D. species |
C |
| 8. |
Hermophroditic reproduction can be found among the A. Arthropods and nematodes B. Pisces and amphibians C. Annelids and molluscs D. coelenterates and platyhelminthes Detailed SolutionMany platyhelminths ( flatworms) reproduce asexuallyCoelenterates reproduce asexually by budding. |
|
| 9. |
An insect whose economic importance is both harmful and beneficial is the A. Tsetsefly B. Blackfly C. Mosquito D. Butterfly |
D |
| 10. |
The cell component that is present in a prokaryotic cell is the A. Chloroplast B. Ribosome C. Mitochondrion D. Nuclear envelope |
B |